Abstract
In the title compound, C9H13NO2S, the dihedral angle between the thiophene ring and the carbamate group is 15.79 (14)°. In the crystal structure, intramolecular C—H⋯O interactions in tandem with the tert-butyl groups render the packing of adjacent molecules in the [001] direction nearly perpendicular [the angle between adjacent thiophene rings is 74.83 (7)°]. An intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond gives rise to a chain extending along [001]. The crystal studied was found to be a racemic twin.
Related literature
For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Binder et al. (1977 ▶); Kruse et al. (1989 ▶). For related structures, see: Arsenyan et al. (2008 ▶); Elshaarawy & Janiak (2011 ▶); Low et al. (2009 ▶); Hsu et al. (2013 ▶).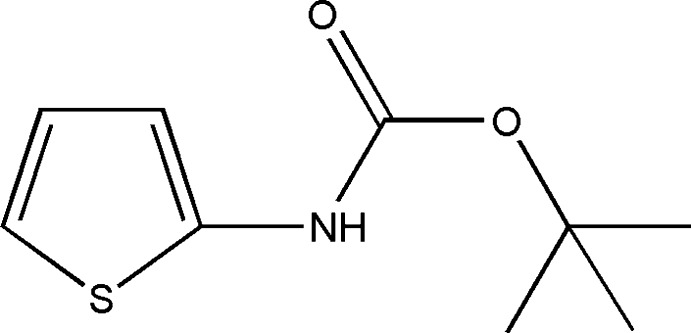
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H13NO2S
M r = 199.26
Orthorhombic,
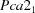
a = 11.732 (2) Å
b = 8.6513 (17) Å
c = 9.879 (2) Å
V = 1002.7 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.29 mm−1
T = 153 K
0.20 × 0.10 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (DENZO and SCALEPACK; Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.944, T max = 0.977
2112 measured reflections
2112 independent reflections
1816 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.078
S = 1.04
2112 reflections
125 parameters
2 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 703 quotients [(I+)−(I−)]/[(I+)+(I−)] (Parsons & Flack, 2004 ▶)
Absolute structure parameter: 0.53 (4)
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: COLLECT; data reduction: DENZO and SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, enCIFer (Allen et al., 2004 ▶) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302196X/zs2273sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302196X/zs2273Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302196X/zs2273Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯O1i | 0.90 (2) | 2.04 (2) | 2.920 (3) | 165 (3) |
| C7—H7A⋯O1 | 0.98 | 2.33 | 2.938 (4) | 119 |
| C8—H8C⋯O1 | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.109 (4) | 116 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Robert A. Welch Foundation for their support of GCH via the Welch Summer Scholars Program, and Texas Tech University for start-up funds.
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Comment
The title compound tert-butyl N-(thiophene-2-yl)carbamate, C9H13NO2S, (Fig. 1) is a precursor in the synthesis of diimine ligands suitable for metal complex formation. This compound exhibits intramolecular methyl C7—H···O1 and C8—H···O1 interactions [2.938 (4) and 3.109 (4), respectively] in addition to bulky tert -butyl groups. These two features in tandem allow the packing in the crystal to be nearly perpendicular [the angle between adjacent thiophene rings = 74.83 (7)°]. An intermolecular N1—H···O1i hydrogen bond (Table 1) gives a one-dimensional chain which extends along [0 0 1]. The compound was synthesized via a typical Curtius Rearrangement from thiophene-2-carbonyl azide (Binder et al., 1977; Kruse et al., 1989).
2. Experimental
The title compound was prepared by a typical Curtius Rearrangement. Thiophene-2-carbonyl azide (270 mg; 1.77 mmol) was reacted with 1.0 equivalent of tert-butyl alcohol (131 mg; 1.77 mmol) and dissolved in 15 ml of toluene. The solution was heated at 100 °C overnight. Excess solvent and tert-butyl alcohol was removed in vacuo. Crystals suitable for X-ray structure determination were obtained by cooling a toluene solution to -30 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, chloroform-d): δ=6.9(br, 1H, –NH), 6.79(m, 2H, –CH), 6.5(dd, 1H, –CH), 1.5(s, 9H, tBu).
3. Refinement
The NH hydrogen atom was located from the difference-Fourier map and refined isotropically subject to a distance restraint (N—H = 0.98 Å). Carbon-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions (C—H distances are 0.98 Å for methyl H atoms and 0.95 Å for thiophene H atoms) and refined as riding atoms with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(thiophene H atom) or Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(methyl H atom).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C9H13NO2S | Dx = 1.320 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 199.26 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pca21 | Cell parameters from 1327 reflections |
| a = 11.732 (2) Å | θ = 1.0–27.5° |
| b = 8.6513 (17) Å | µ = 0.29 mm−1 |
| c = 9.879 (2) Å | T = 153 K |
| V = 1002.7 (3) Å3 | Rod, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.08 mm |
| F(000) = 424 |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 2112 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1816 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (DENZO and SCALEPACK; Otwinowski & Minor, 1997) | h = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.944, Tmax = 0.977 | k = −11→11 |
| 2112 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.078 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0301P)2 + 0.2397P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2112 reflections | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 125 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 703 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons & Flack, 2004). |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.53 (4) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.13622 (6) | 0.05380 (7) | 0.63359 (7) | 0.02745 (19) | |
| O1 | 0.29399 (16) | 0.2992 (2) | 0.61913 (19) | 0.0273 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.32467 (18) | 0.4564 (2) | 0.80079 (18) | 0.0289 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.23352 (19) | 0.2367 (2) | 0.8305 (2) | 0.0224 (5) | |
| H1N | 0.238 (3) | 0.264 (4) | 0.919 (2) | 0.036 (9)* | |
| C1 | 0.1713 (2) | 0.1041 (3) | 0.7987 (3) | 0.0209 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.1219 (3) | 0.0067 (3) | 0.8902 (3) | 0.0241 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.1317 | 0.0150 | 0.9854 | 0.029* | |
| C3 | 0.0542 (2) | −0.1082 (3) | 0.8269 (3) | 0.0289 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.0137 | −0.1855 | 0.8754 | 0.035* | |
| C4 | 0.0533 (3) | −0.0964 (3) | 0.6907 (3) | 0.0306 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.0115 | −0.1635 | 0.6329 | 0.037* | |
| C5 | 0.2857 (2) | 0.3295 (3) | 0.7389 (3) | 0.0220 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.3798 (2) | 0.5829 (3) | 0.7233 (3) | 0.0250 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.3034 (3) | 0.6385 (4) | 0.6108 (4) | 0.0438 (9) | |
| H7A | 0.2928 | 0.5554 | 0.5446 | 0.066* | |
| H7B | 0.3384 | 0.7280 | 0.5663 | 0.066* | |
| H7C | 0.2292 | 0.6684 | 0.6483 | 0.066* | |
| C8 | 0.4940 (3) | 0.5271 (4) | 0.6722 (4) | 0.0445 (9) | |
| H8A | 0.5384 | 0.4856 | 0.7480 | 0.067* | |
| H8B | 0.5354 | 0.6135 | 0.6310 | 0.067* | |
| H8C | 0.4823 | 0.4458 | 0.6045 | 0.067* | |
| C9 | 0.3945 (3) | 0.7083 (3) | 0.8284 (4) | 0.0459 (9) | |
| H9A | 0.3196 | 0.7408 | 0.8617 | 0.069* | |
| H9B | 0.4337 | 0.7970 | 0.7878 | 0.069* | |
| H9C | 0.4399 | 0.6685 | 0.9040 | 0.069* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0369 (4) | 0.0261 (3) | 0.0194 (3) | −0.0050 (3) | 0.0003 (3) | −0.0034 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0377 (11) | 0.0268 (9) | 0.0173 (10) | −0.0043 (8) | 0.0014 (9) | −0.0012 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0425 (12) | 0.0258 (10) | 0.0182 (9) | −0.0120 (8) | 0.0029 (9) | 0.0003 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0293 (13) | 0.0232 (11) | 0.0147 (9) | −0.0051 (9) | 0.0006 (10) | −0.0009 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0234 (13) | 0.0211 (12) | 0.0183 (12) | 0.0033 (11) | 0.0000 (11) | −0.0012 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0277 (16) | 0.0226 (13) | 0.0221 (13) | 0.0002 (11) | −0.0017 (11) | 0.0006 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0300 (16) | 0.0227 (14) | 0.0340 (15) | −0.0037 (12) | −0.0002 (13) | 0.0029 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0329 (18) | 0.0259 (15) | 0.0330 (15) | −0.0030 (12) | −0.0029 (14) | −0.0039 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0238 (15) | 0.0227 (14) | 0.0195 (15) | 0.0016 (11) | −0.0023 (11) | −0.0005 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0288 (17) | 0.0228 (14) | 0.0234 (13) | −0.0047 (12) | 0.0053 (11) | 0.0019 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0453 (19) | 0.0306 (15) | 0.056 (2) | −0.0046 (14) | −0.0128 (18) | 0.0135 (16) |
| C8 | 0.0299 (17) | 0.0339 (16) | 0.070 (2) | −0.0022 (13) | 0.0128 (18) | 0.0021 (16) |
| C9 | 0.070 (2) | 0.0327 (17) | 0.0347 (17) | −0.0212 (17) | 0.0122 (17) | −0.0068 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C4 | 1.718 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| S1—C1 | 1.737 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.507 (4) |
| O1—C5 | 1.216 (3) | C6—C8 | 1.511 (4) |
| O2—C5 | 1.337 (3) | C6—C9 | 1.512 (4) |
| O2—C6 | 1.484 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C5 | 1.356 (3) | C7—H7B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C1 | 1.396 (3) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| N1—H1N | 0.90 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.365 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.418 (4) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.350 (4) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| C4—S1—C1 | 90.88 (14) | C7—C6—C8 | 112.6 (3) |
| C5—O2—C6 | 121.3 (2) | O2—C6—C9 | 103.0 (2) |
| C5—N1—C1 | 124.9 (2) | C7—C6—C9 | 110.2 (3) |
| C5—N1—H1N | 117 (2) | C8—C6—C9 | 111.0 (3) |
| C1—N1—H1N | 118 (2) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 125.4 (2) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 111.5 (2) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—S1 | 122.77 (19) | C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 112.2 (3) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 123.9 | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 123.9 | C6—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 113.0 (3) | C6—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 123.5 | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 123.5 | C6—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—S1 | 112.3 (2) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 123.8 | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| S1—C4—H4 | 123.8 | C6—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| O1—C5—O2 | 126.4 (2) | C6—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O1—C5—N1 | 123.9 (2) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O2—C5—N1 | 109.6 (2) | C6—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O2—C6—C7 | 110.9 (2) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O2—C6—C8 | 108.8 (2) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | 177.5 (3) | C1—S1—C4—C3 | −0.9 (3) |
| C5—N1—C1—S1 | −8.9 (4) | C6—O2—C5—O1 | 3.3 (4) |
| C4—S1—C1—C2 | 0.9 (2) | C6—O2—C5—N1 | −176.4 (2) |
| C4—S1—C1—N1 | −173.5 (2) | C1—N1—C5—O1 | −7.8 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 173.6 (2) | C1—N1—C5—O2 | 171.9 (2) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (3) | C5—O2—C6—C7 | 54.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 (4) | C5—O2—C6—C8 | −69.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—S1 | 0.7 (4) | C5—O2—C6—C9 | 172.4 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···O1i | 0.90 (2) | 2.04 (2) | 2.920 (3) | 165 (3) |
| C7—H7A···O1 | 0.98 | 2.33 | 2.938 (4) | 119 |
| C8—H8C···O1 | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.109 (4) | 116 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1/2, y, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZS2273).
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 115–119.
- Arsenyan, P., Petrenko, A. & Belyakov, S. (2008). Tetrahedron Lett. 49, 5255–5257.
- Binder, D., Habison, G. & Noe, C. R. (1977). Synthesis, pp. 255–256.
- Elshaarawy, R. F. & Janiak, C. (2011). Z. Naturforsch. Teil B, 66, 1201–1208.
- Hsu, G. C., Singer, L. M., Cordes, D. B. & Findlater, M. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kruse, L. I., Ladd, D. L., Harrsch, P. B., McCabe, F. L., Mong, S.-M., Faucette, L. & Johnson, R. (1989). J. Med. Chem. 32, 409–417. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Low, J. N., Quesada, A., Santos, L. M. N. B. F., Schröder, B. & Gomes, L. R. (2009). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 39, 747–752.
- Nonius (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Parsons, S. & Flack, H. (2004). Acta Cryst. A60, s61.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302196X/zs2273sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302196X/zs2273Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302196X/zs2273Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



