Abstract
In the molecule of the title difluorobenzamide derivative, C10H7F2NO, the angle formed by the least-squares mean line through the prop-2-ynyl group [maximum deviation = 0.011 (3) Å] and the normal to the benzene ring is 59.03 (7)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked via N—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds into layers parallel to the ac plane.
Related literature
For the biological activity of difluorobenzamide derivatives, see: Chang et al. (2002 ▶); Kees et al. (1989 ▶); Ragavan et al. (2010 ▶); Carmellino et al. (1994 ▶); Rauko et al. (2001 ▶). For the crystal structure of a related compound, see: Fun et al. (2010 ▶).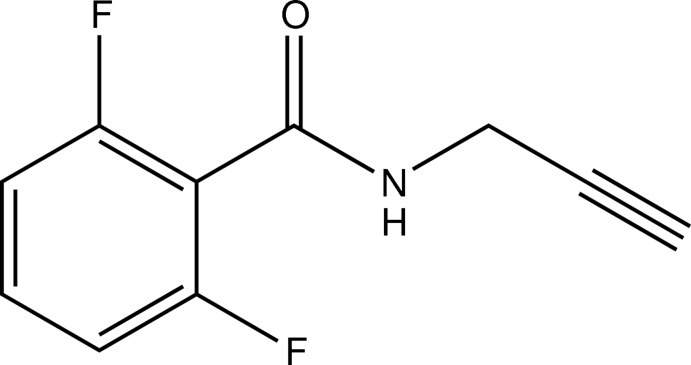
Experimental
Crystal data
C10H7F2NO
M r = 195.17
Monoclinic,
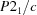
a = 5.0479 (8) Å
b = 19.738 (3) Å
c = 9.2428 (15) Å
β = 91.432 (4)°
V = 920.6 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.12 mm−1
T = 273 K
0.38 × 0.17 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
5388 measured reflections
1669 independent reflections
1283 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.022
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.099
S = 1.03
1669 reflections
135 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813021120/rz5082sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813021120/rz5082Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813021120/rz5082Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.83 (2) | 2.10 (2) | 2.8387 (19) | 147.4 (17) |
| C2—H2A⋯F2ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.394 (2) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 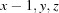 ; (ii)
; (ii) 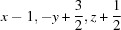 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Comment
Some difluorobenzamide derivatives are known to have excellent antiviral and antiproliferation activities (Chang et al., 2002). They are also well known for their anti-diabetic (Kees et al., 1989), anti-fungal (Carmellino et al., 1994), anti-bacterial (Ragavan et al., 2010) and anti-cancer (Rauko et al., 2001) properties.
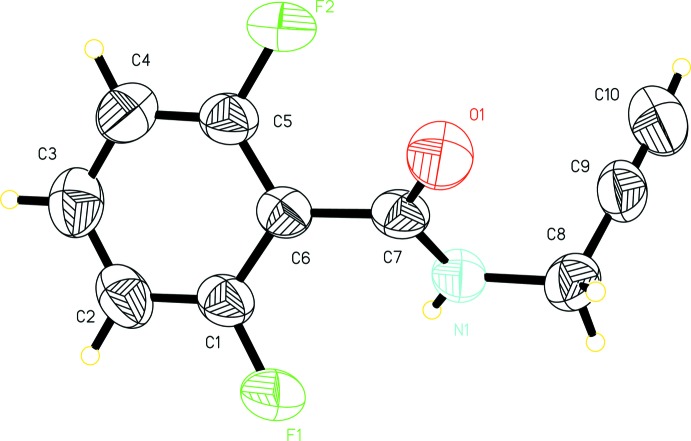
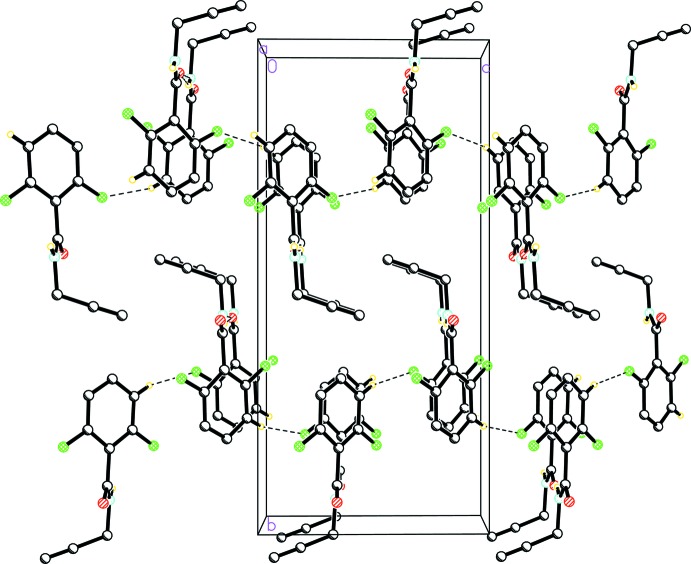
The structure of the title fluorinated benzamide derivative (Fig. 1) is distinctly similar to that of the previously reported compound N-(4-cyanophenyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide (Fun et al., 2010), with the difference that the N-(4-cyanophenyl) moiety is replaced by a prop-2-ynyl chain (C8–C10). The observed distance for the C9—C10 acetylene bond is 1.162 (3) Å. The angle between the least-squares mean line through the prop-2-ynyl group (maximum deviation 0.011 (3) Å for atom C9) and the normal to the benzene ring is 59.03 (7)°. The molecule has no prominent intramolecular non-covalent interactions. In the crystal, molecules are linked via C—H···F (Fig. 2) and N—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) to form layers parallel to the ac plane. No π···π stacking interactions are observed.
2. Experimental
Prop-2-yn-1-amine (36.3 mmol, 1.0 eq) was dissolved in dichloromethane (20 mL) in a round bottom flask and kept at 0 °C. Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) (145 mmol, 4.0 eq) and 2,6-diflurobenzoyl chloride (54.4 mmol, 1.5 eq) were then added and the mixture stirred for 1.5 h. Progress of the reaction was monitored by thin layer chromatography. On completion of the reaction the mixture was dissolved in water and extracted with diethyl ether (2 × 25 mL). The organic layer was dried with anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated to obtain a crude gummy product. The crude product was finally purified by flash column chromatography by using EtOAc/hexane (3:7 v/v) as eluent to afford the title compound in 77% yield. Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution.
3. Refinement
The amide and acetylenic H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely. All other H atoms were placed at calculated positions and refined as riding, with C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound showing intermolecular hydrogen bonding as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C10H7F2NO | F(000) = 400 |
| Mr = 195.17 | Dx = 1.408 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1280 reflections |
| a = 5.0479 (8) Å | θ = 2.4–22.9° |
| b = 19.738 (3) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| c = 9.2428 (15) Å | T = 273 K |
| β = 91.432 (4)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 920.6 (3) Å3 | 0.38 × 0.17 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 1283 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.022 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.1° |
| phi and ω scans | h = −6→6 |
| 5388 measured reflections | k = −23→22 |
| 1669 independent reflections | l = −10→11 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0397P)2 + 0.172P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1669 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 135 parameters | Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| F1 | 0.4706 (2) | 0.66642 (6) | 0.01184 (13) | 0.0784 (4) | |
| F2 | 1.1590 (2) | 0.68247 (6) | −0.31627 (13) | 0.0808 (4) | |
| O1 | 1.0617 (2) | 0.56728 (6) | −0.15774 (16) | 0.0689 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.6219 (3) | 0.55850 (7) | −0.17077 (17) | 0.0520 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.6337 (3) | 0.70378 (9) | −0.06950 (19) | 0.0533 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.6133 (4) | 0.77291 (10) | −0.0635 (2) | 0.0670 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.4884 | 0.7934 | −0.0055 | 0.080* | |
| C3 | 0.7807 (4) | 0.81150 (10) | −0.1445 (2) | 0.0690 (6) | |
| H3A | 0.7685 | 0.8585 | −0.1419 | 0.083* | |
| C4 | 0.9655 (4) | 0.78117 (10) | −0.2290 (2) | 0.0664 (5) | |
| H4A | 1.0802 | 0.8071 | −0.2835 | 0.080* | |
| C5 | 0.9778 (3) | 0.71209 (9) | −0.2314 (2) | 0.0546 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.8147 (3) | 0.66992 (8) | −0.15372 (17) | 0.0453 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.8430 (3) | 0.59431 (9) | −0.16021 (17) | 0.0475 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.6276 (4) | 0.48497 (9) | −0.1809 (2) | 0.0607 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.4535 | 0.4673 | −0.1599 | 0.073* | |
| H8B | 0.7519 | 0.4674 | −0.1085 | 0.073* | |
| C9 | 0.7041 (4) | 0.46128 (9) | −0.3233 (2) | 0.0621 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.7642 (5) | 0.44382 (12) | −0.4380 (3) | 0.0880 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.475 (4) | 0.5775 (9) | −0.1715 (19) | 0.061 (6)* | |
| H2 | 0.817 (5) | 0.4327 (13) | −0.524 (3) | 0.120 (10)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| F1 | 0.0691 (7) | 0.0792 (8) | 0.0889 (9) | −0.0091 (6) | 0.0395 (6) | −0.0161 (6) |
| F2 | 0.0727 (7) | 0.0810 (8) | 0.0907 (9) | −0.0041 (6) | 0.0418 (7) | −0.0052 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0315 (6) | 0.0655 (8) | 0.1096 (11) | 0.0057 (5) | 0.0013 (6) | −0.0028 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0316 (7) | 0.0521 (9) | 0.0726 (11) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0071 (7) | −0.0047 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0412 (9) | 0.0628 (11) | 0.0559 (11) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0054 (8) | −0.0104 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0674 (13) | 0.0794 (14) | 0.0088 (9) | 0.0033 (10) | −0.0230 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0648 (12) | 0.0532 (11) | 0.0885 (16) | 0.0037 (9) | −0.0073 (11) | −0.0048 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0604 (11) | 0.0634 (12) | 0.0753 (14) | −0.0065 (9) | 0.0039 (10) | 0.0069 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0432 (9) | 0.0629 (11) | 0.0579 (11) | −0.0003 (8) | 0.0070 (8) | −0.0048 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0320 (8) | 0.0553 (10) | 0.0484 (10) | 0.0000 (7) | −0.0021 (7) | −0.0053 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0328 (8) | 0.0571 (10) | 0.0527 (10) | 0.0014 (7) | 0.0052 (7) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0503 (10) | 0.0529 (11) | 0.0794 (14) | −0.0025 (8) | 0.0094 (9) | 0.0042 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0579 (11) | 0.0451 (10) | 0.0835 (16) | 0.0055 (8) | 0.0048 (11) | −0.0031 (10) |
| C10 | 0.1032 (19) | 0.0689 (15) | 0.092 (2) | 0.0121 (12) | 0.0132 (16) | −0.0128 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| F1—C1 | 1.3482 (19) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| F2—C5 | 1.3530 (18) | C4—C5 | 1.365 (3) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2256 (17) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.323 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.384 (2) |
| N1—C8 | 1.455 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.501 (2) |
| N1—H1 | 0.830 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.458 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.370 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.387 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.374 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.162 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C10—H2 | 0.87 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.369 (3) | ||
| C7—N1—C8 | 121.31 (15) | F2—C5—C6 | 117.42 (16) |
| C7—N1—H1 | 120.7 (13) | C4—C5—C6 | 124.38 (16) |
| C8—N1—H1 | 118.0 (13) | C5—C6—C1 | 114.22 (16) |
| F1—C1—C2 | 118.34 (15) | C5—C6—C7 | 121.27 (14) |
| F1—C1—C6 | 118.01 (16) | C1—C6—C7 | 124.49 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 123.65 (17) | O1—C7—N1 | 121.78 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.85 (17) | O1—C7—C6 | 121.24 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.6 | N1—C7—C6 | 116.97 (13) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.6 | N1—C8—C9 | 112.60 (15) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.37 (18) | N1—C8—H8A | 109.1 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.8 | C9—C8—H8A | 109.1 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.8 | N1—C8—H8B | 109.1 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.53 (18) | C9—C8—H8B | 109.1 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.7 | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.8 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.7 | C10—C9—C8 | 178.5 (2) |
| F2—C5—C4 | 118.19 (16) | C9—C10—H2 | 176.4 (19) |
| F1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.19 (17) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.6 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (3) | F1—C1—C6—C7 | −0.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.4 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C7 | 179.05 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (3) | C8—N1—C7—O1 | −0.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—F2 | 179.33 (17) | C8—N1—C7—C6 | 178.68 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.1 (3) | C5—C6—C7—O1 | 41.8 (2) |
| F2—C5—C6—C1 | −179.83 (15) | C1—C6—C7—O1 | −136.53 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.6 (3) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | −137.26 (17) |
| F2—C5—C6—C7 | 1.7 (2) | C1—C6—C7—N1 | 44.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −179.07 (18) | C7—N1—C8—C9 | −75.0 (2) |
| F1—C1—C6—C5 | −178.74 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.83 (2) | 2.10 (2) | 2.8387 (19) | 147.4 (17) |
| C2—H2A···F2ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.394 (2) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) x−1, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RZ5082).
References
- Bruker (2000). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Carmellino, M. L., Pagani, G., Pregnolato, M., Terreni, M. & Pastoni, F. (1994). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 29, 743–751.
- Chang, Y. Y., Chung, Y. H., Lee, C. W., Lee, H. D., Lee, J. S., Park, W. J. & Yang, W. Y. (2002). Patent AU2002345403.
- Fun, H.-K., Goh, J. H., Gowda, J., Khader, A. M. & Kalluraya, B. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o3192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kees, K. L., Cheeseman, R. S., Prozialeck, D. H. & Steiner, K. E. (1989). J. Med. Chem., 32, 11–13. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ragavan, R. V., Vijayakumar, V. & Kumari, S. N. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43, 1173–1180. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rauko, P., Novotny, L., Dovinova, I., Hunakova, L., Szekeres, T. & Jayaram, H. N. (2001). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 12, 387–394. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813021120/rz5082sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813021120/rz5082Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813021120/rz5082Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report