Abstract
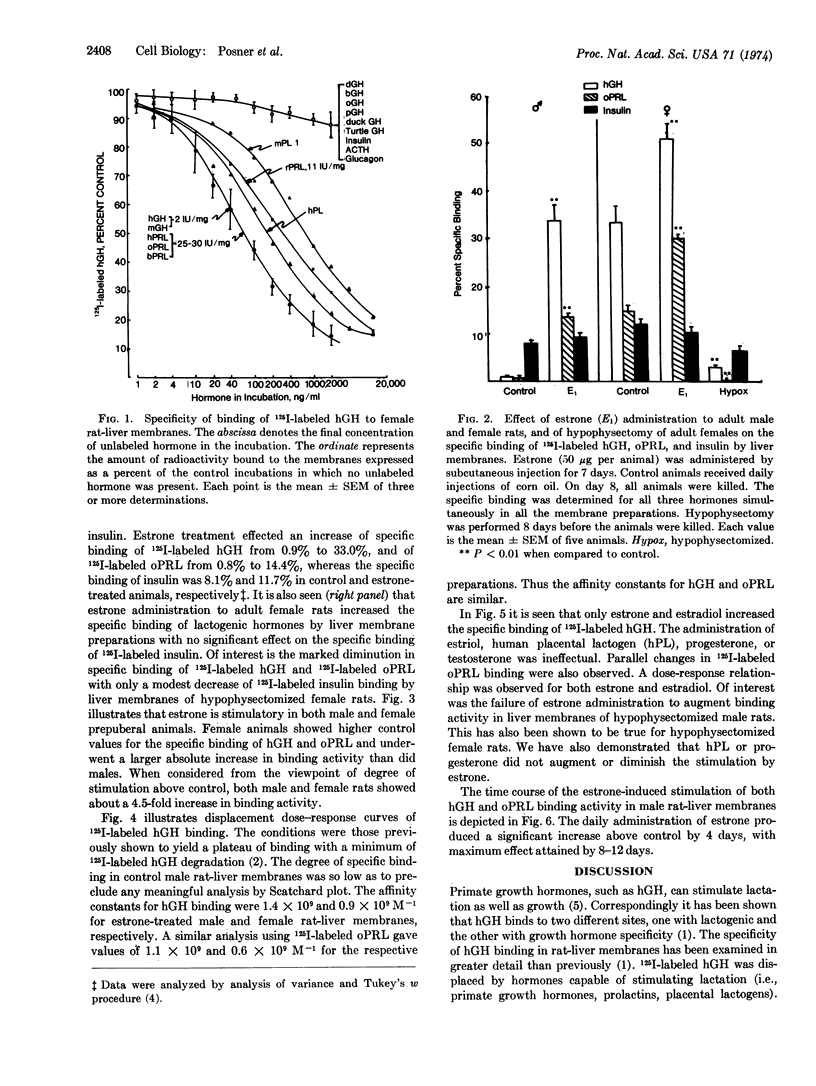
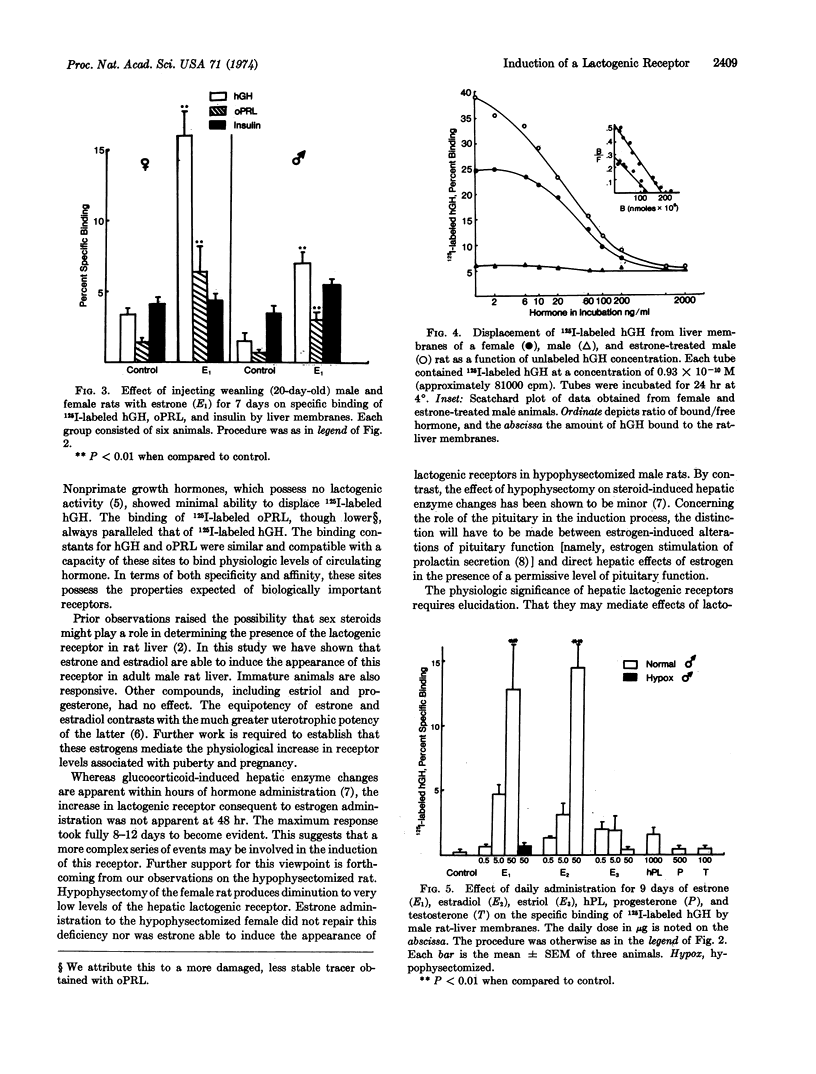
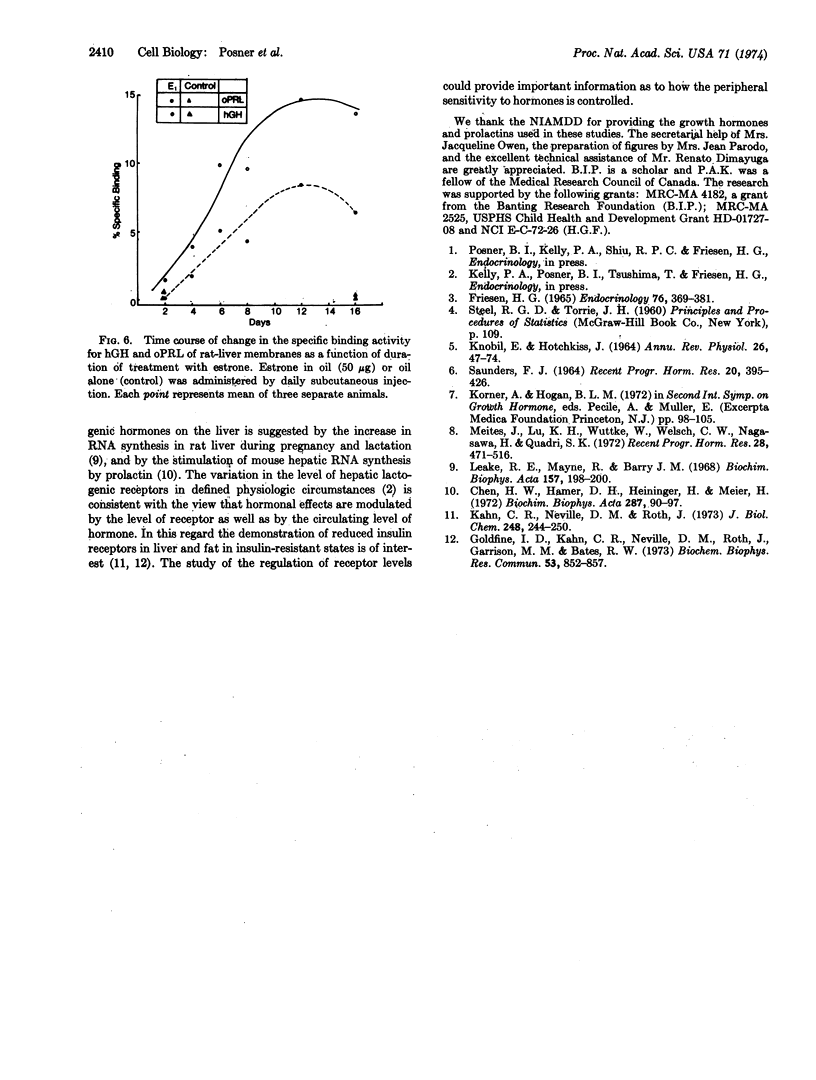
A receptor exists in female rat liver with high specificity for lactogenic hormones. Previous work showed the receptor level increased at the time of puberty in female but not male animals. Pregnancy caused a further substantial increase. Here we show that estrone (50 μg/day) administration to male rats induced a 10- to 30-fold increase in specific binding of ovine prolactin and human growth hormone after 8-12 days with a significant increase first seen after 4 but not 2 days of injection. In females, this regimen increased binding to pregnancy levels. In prepuberal (20-days-old) male and female rats, estrone was also markedly stimulatory. The binding sites for ovine prolactin and human growth hormone were of high affinity in liver membranes from both female and estrone-treated male rats (Ka = 0.6 to 1.4 × 109 M-1).
Estrone and estradiol were equally effective in inducing the lactogenic receptor. Estriol (50 μg/day), progesterone (500 μg/day), human placental lactogen (1 mg/day), and testosterone (100 μg/day) were without influence. Hypophysectomy drastically decreased the levels of lactogenic receptor in mature female rats, and estrogen treatment failed to restore receptor levels to normal. Hypophysectomized male rats were also unresponsive to estrogen. Throughout these studies the specific binding of 125I-labeled insulin remained relatively constant.
This work demonstrates estrogen induction of a lactogenic receptor. The pituitary gland appears to have a critical, though presently undefined, role in the induction process.
Keywords: growth hormone, prolactin, estrone, steroids
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen H. W., Hamer D. H., Heiniger H. J., Meier H. Stimulation of hepatic RNA synthesis in dwarf mice by ovine prolactin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 16;287(1):90–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIESEN H. PURIFICATION OF A PLACENTAL FACTOR WITH IMMUNOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL SIMILARITY TO HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE. Endocrinology. 1965 Mar;76:369–381. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-3-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J., Garrison M. M., Bates R. W. Decreased binding of insulin to its receptors in rats with hormone induced insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):852–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOBIL E., HOTCHKISS J. GROWTH HORMONE. Annu Rev Physiol. 1964;26:47–74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.26.030164.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake R. E., Mayne R., Barry J. M. Increase during lactation of RNA synthesis b isolated liver nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):198–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meites J., Lu K. H., Wuttke W., Welsch C. W., Nagasawa H., Quadri S. K. Recent studies on functions and control of prolactin secretion in rats. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1972;28:471–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



