Abstract
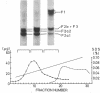
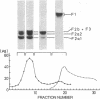
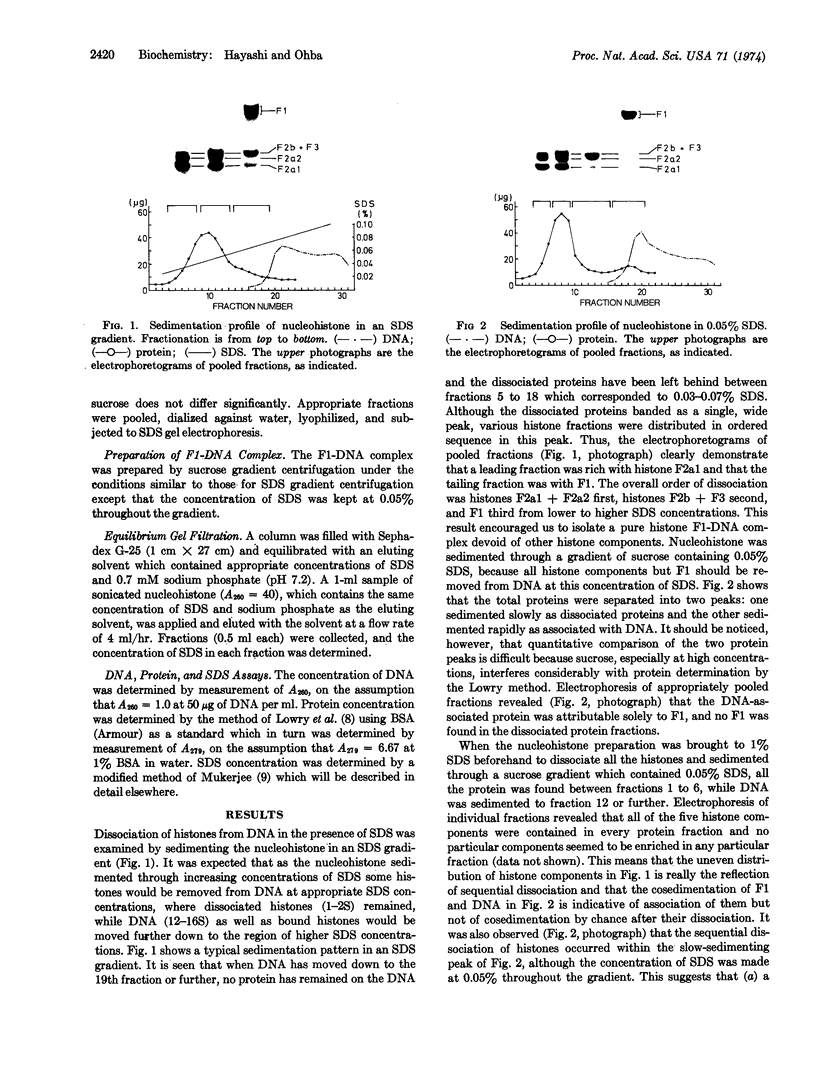
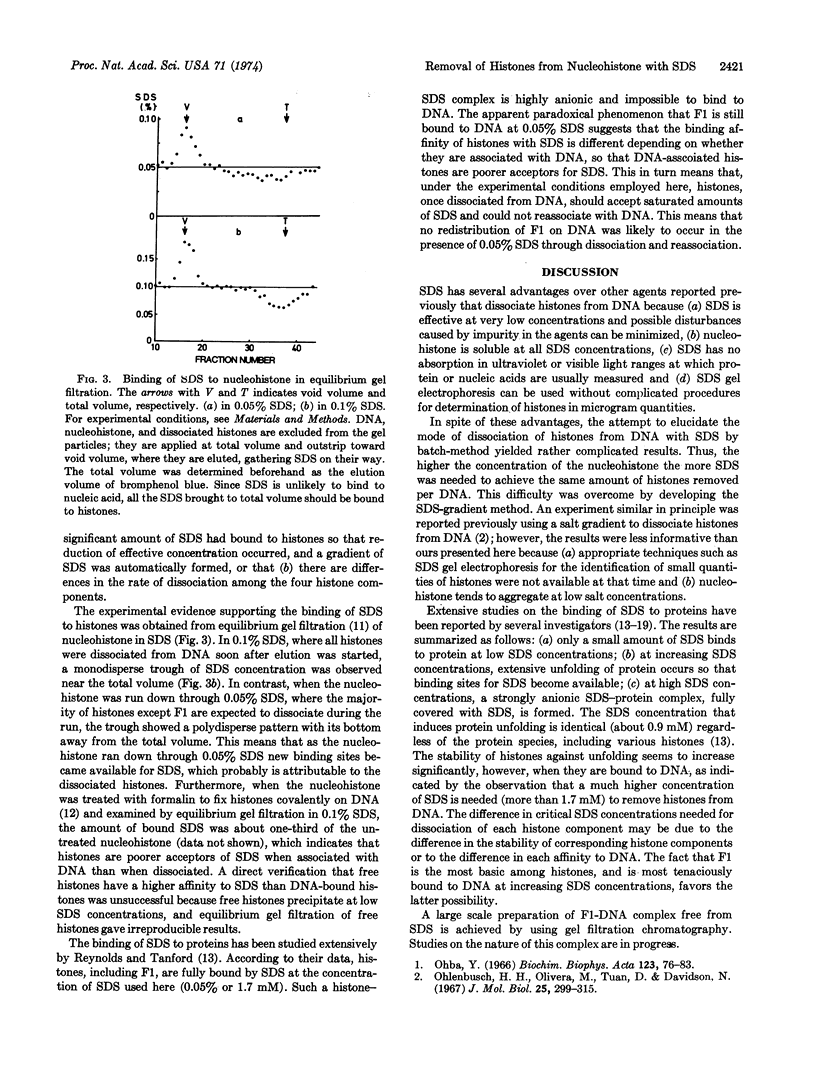
Calf-thymus nucleohistone studied by a newly developed `SDS gradient' centrifugation technique showed that histones dissociate sequentially when treated with increasing concentrations of sodium dodecylsulfate. Histones F2a1 and F2a2 were dissociated first at about 0.03% sodium dodecylsulfate, and F1 was removed lastly by the highest concentration of sodium dodecylsulfate (0.06% or more). A DNA-histone F1 complex, which consisted of DNA and all of the histone F1 and completely lacked other histones, was obtained by sedimenting nucleohistone through 0.05% sodium dodecylsulfate. Results of equilibrium gel filtrations in 0.05% sodium dodecylsulfate revealed that the binding of sodium dodecylsulfate to nucleohistone caused new binding sites to be available for the detergent which presumably was accompanied with dissociation of histones from DNA. This result indicates that no redistribution of histone F1 on DNA should occur in the presence of 0.05% sodium dodecylsulfate.
Keywords: sodium dodecylsulfate-gradient centrifugation, equilibrium gel filtration, histone F1-DNA complex, detergent binding, histone redistribution
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brutlag D., Schlehuber C., Bonner J. Properties of formaldehyde-treated nucleohistone. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3214–3218. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Gel chromatography of proteins in denaturing solvents. Comparison between sodium dodecyl sulfate and guanidine hydrochloride as denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5166–5168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. W., Chamberlin M. J. Measurement of ligand-protein binding interactions in a biphasic aqueous polymer system. Anal Biochem. 1971 May;41(1):83–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirgensons B., Capetillo S. Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on circular dichroism of some nonhelical proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 27;214(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. Stepwise removal of histones from native deoxyribonucleoprotein by titration with acid at low temperature and some properties of the resulting partial nucleoproteins. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):125–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohba Y. Structure of nucleohistone. I. Hydrodynamic behaviour. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 20;123(1):76–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt-Rivers R., Impiombato F. S. The binding of sodium dodecyl sulphate to various proteins. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):825–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1090825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Reynolds J. A., Polet H., Steinhardt J. Binding of large organic anions and neutral molecules by native bovine serum albumin. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2606–2616. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Herbert S., Polet H., Steinhardt J. The binding of divers detergent anions to bovine serum albumin. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):937–947. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Binding of dodecyl sulfate to proteins at high binding ratios. Possible implications for the state of proteins in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):1002–1007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. The gross conformation of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5161–5165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senshu T. Selective extraction of histones with sodium chloride and urea. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Bonner J. Selective dissociation of histones from chromatin by sodium deoxycholate. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):651–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]