Abstract
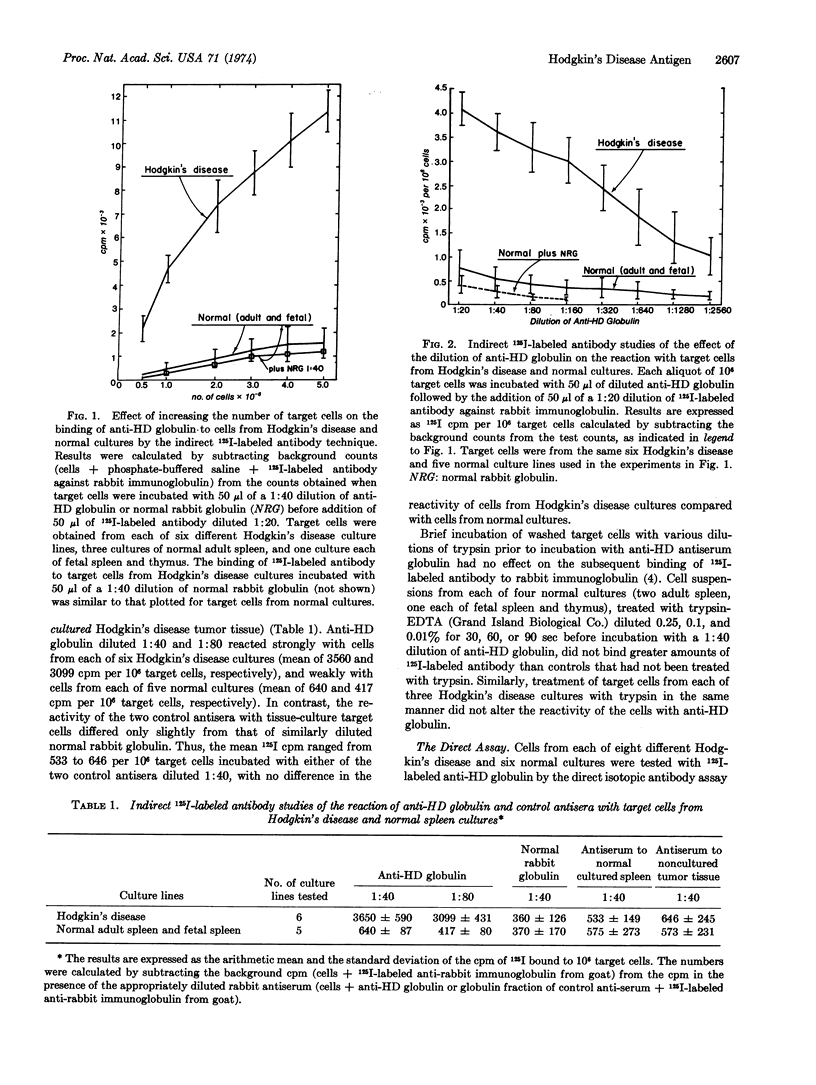
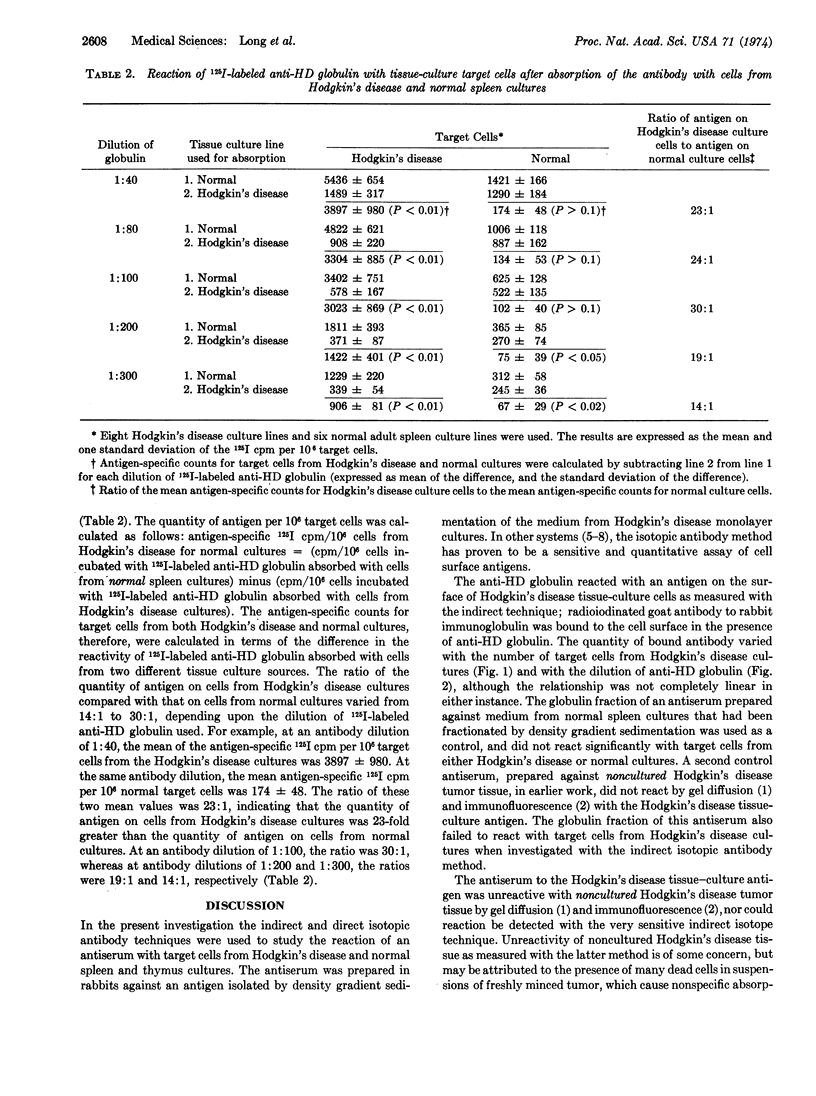
An antiserum was prepared in rabbits against an antigen obtained by density gradient sedimentation of centrifuged medium from monolayer cultures of spleens involved by Hodgkin's disease. The antiserum was tested by isotopic antibody techniques with cells from each of eight cultures derived from spleens involved by Hodgkin's disease, four cultures derived from normal adult spleen, and one culture each of fetal spleen and thymus. By an indirect radioiodine-labeled antibody assay, anti-Hodgkin's disease globulin reacted with an antigen on the surface of cells from the Hodgkin's disease cultures, the quantity of which was related to the number of target cells and the amount of antibody used. This Hodgkin's disease tissue-culture antigen did not react with a rabbit antiserum against fractionated medium from a normal spleen culture, nor against noncultured Hodgkin's disease tumor tissue. The tumor specificity of the Hodgkin's disease tissue-culture antigen was assessed by a direct technique using 125I-labeled anti-Hodgkin's disease globulin absorbed with either cultured Hodgkin's disease cells or with cultured normal cells. By this method the quantity of antigen on cells from Hodgkin's disease cultures was 15- to 30-fold greater than that on cells from normal cultures.
The Hodgkin's disease tissue-culture antigen is intimately associated with the propagation of the tumor in monolayer cultures, but its identity has not been established: it could be a viral component, a tumor or fetal antigen, or a normal tissue constituent.
Keywords: cell culture, direct and indirect radioimmunolabeling
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boone C. W., Church E. C., McAllister R. M. Testing by the "paired-label" antibody binding technique for feline leukemia virus-induced cell surface antigens (FeLV-CSA) on the surface of human rhabdomyosarcoma cells releasing RD-114 virus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M. A., Sibal L. R., Wivel N. A., Cowles C. A., O'Conner T. E. Some characteristics of an isolated group antigen common to most strains of murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden R. V., Oroszlan S. Group-specific antigens of RNA tumor viruses as markers for subinfectious expression of the RNA virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):1021–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder F. H., McKhann C. F. Demonstration of cellular antigens on sarcoma cells by an indirect 125-I-labeled antibody technique. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Feb;40(2):231–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hehlmann R., Kufe D., Spiegelman S. Viral-related RNA in Hodgkins' disease and other human lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1727–1731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufe D. W., Peters W. P., Spiegelman S. Unique nuclear DNA sequences in the involved tissues of Hodgkin's and Burkitt's lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3810–3814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. C., Aisenberg A. C., Zamecnik M. V., Zamecnik P. C. A tumor antigen in tissue cultures derived from patients with Hodgkin's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1540–1544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. C., Aisenberg A. C., Zamecnik P. C. An antigen in Hodgkin's disease tissue cultures: fluorescent antibody studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Warner N. L., Lewis H., Sprent J. Quantitative features of a sandwich radioimmunolabeling technique for lymphocyte surface receptors. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):405–428. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks F. C., Ting C. C., Hammond W. G., Herberman R. B. An isotopic antiglobulin technique for measuring antibodies to cell-surface antigens. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):842–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. E., Kasnic G., Jr, Draycott C., Ben T. Activation of viruses in human tumors by 5-iododeoxyuridine and dimethyl sulfoxide. Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):198–199. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. E., Kasnic G., Jr, Draycott C., Feller W., Golden A., Mitchell E. Activation in vitro, by 5-iododeoxyuridine, of a latent virus resembling C-type virus in a human sarcoma cell line. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Jan;48(1):273–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarro G. Appearance in trypsinized normal cells of reactivity with antibody presumably specific for malignant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):325–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Zeve V., Aaronson S. A. Cell culture techniques in the search for cancer viruses of man. In Vitro. 1971 Mar-Apr;6(5):355–361. doi: 10.1007/BF02619073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Zeve V., Aaronson S. A. Viruses in cell culture derived from human tumour patients. Nature. 1970 Jun 13;226(5250):1047–1049. doi: 10.1038/2261047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


