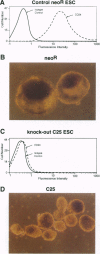
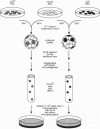
Abstract
We created a "knockout" embryonic stem cell via targeted disruption of the phosphatidylinositol glycan class A (Pig-a) gene, resulting in loss of expression of cell surface glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins and reproducing the mutant phenotype of the human disease paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Morphogenesis of Pig-a- embryoid bodies (EB) in vitro was grossly aberrant and, unlike EB derived from normal embryonic stem cells, Pig-A EB produced no secondary hematopoietic colonies. Chimeric EB composed of control plus Pig-A- cells, however, appeared normal, and hematopoiesis from knock-out cells was reconstituted. Transfer in situ of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins from normal to knock-out cells was demonstrated by two-color fluorescent analysis, suggesting a possible mechanism for these functional effects. Hematopoietic cells with mutated PIG-A genes in humans with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria may be subject to comparable pathophysiologic processes and amenable to similar therapeutic protein transfer.
Full text
PDF


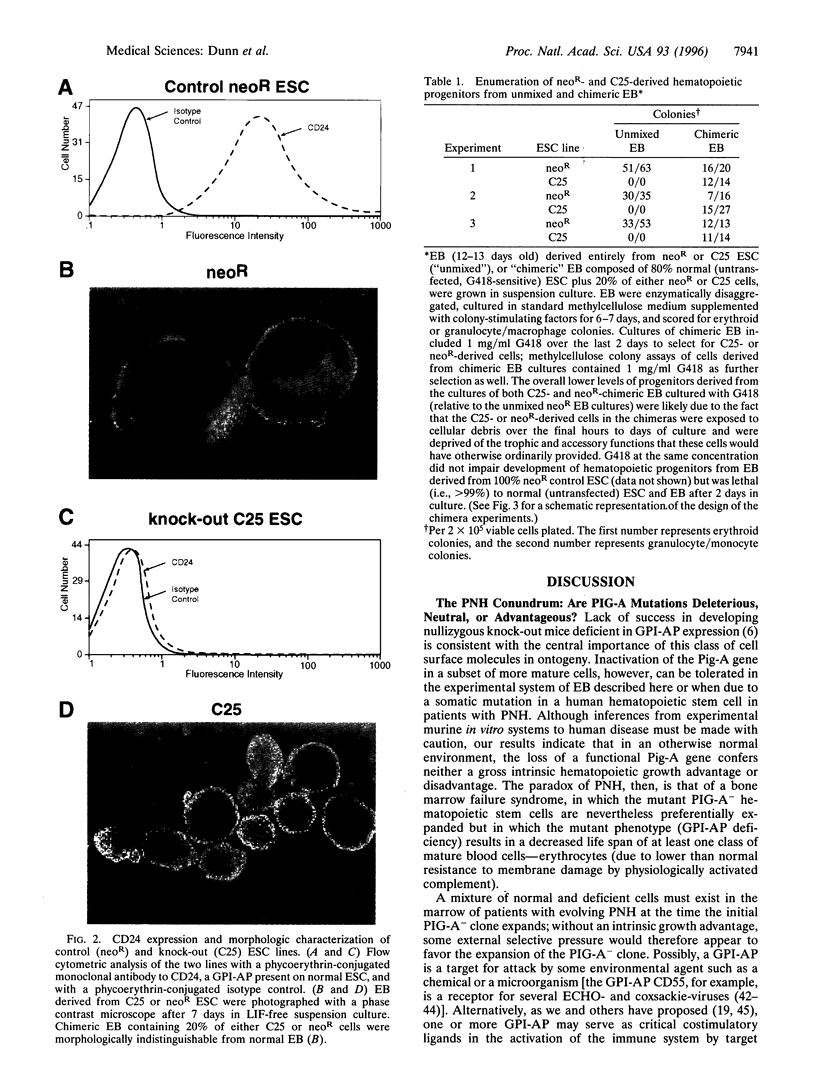
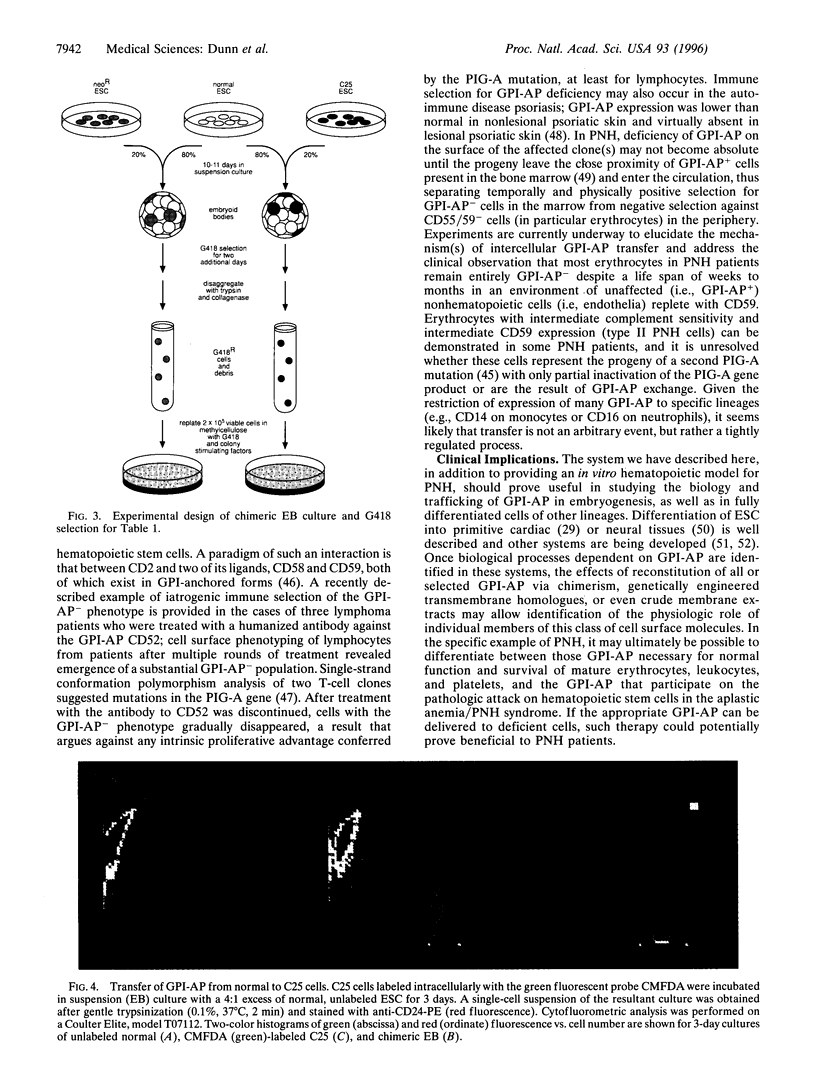

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G. Functional specialization of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Semin Immunol. 1994 Apr;6(2):89–95. doi: 10.1006/smim.1994.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergelson J. M., Chan M., Solomon K. R., St John N. F., Lin H., Finberg R. W. Decay-accelerating factor (CD55), a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored complement regulatory protein, is a receptor for several echoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6245–6248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler M., Mason P. J., Hillmen P., Miyata T., Yamada N., Takeda J., Luzzatto L., Kinoshita T. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH) is caused by somatic mutations in the PIG-A gene. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):110–117. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler M., Mason P., Hillmen P., Luzzatto L. Somatic mutations and cellular selection in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Lancet. 1994 Apr 16;343(8903):951–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkert U., von Rüden T., Wagner E. F. Early fetal hematopoietic development from in vitro differentiated embryonic stem cells. New Biol. 1991 Jul;3(7):698–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J. Protein lipidation in cell signaling. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):221–225. doi: 10.1126/science.7716512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. L., Bouma S. R., Huestis W. H. Cell to vesicle transfer of intrinsic membrane proteins: effect of membrane fluidity. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 30;19(20):4601–4607. doi: 10.1021/bi00561a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Simmons D. L., Hale G., Harrison R. A., Tighe H., Lachmann P. J., Waldmann H. CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):637–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessypris E. N., Clark D. A., McKee L. C., Jr, Krantz S. B. Increased sensitivity to complement or erythroid and myeloid progenitors in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 22;309(12):690–693. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309223091202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T. C., Eistetter H., Katz M., Schmidt W., Kemler R. The in vitro development of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines: formation of visceral yolk sac, blood islands and myocardium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Jun;87:27–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn W. C., Menu E., Bothwell A. L., Sims P. J., Bierer B. E. Overlapping but nonidentical binding sites on CD2 for CD58 and a second ligand CD59. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1805–1807. doi: 10.1126/science.1377404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertenstein B., Wagner B., Bunjes D., Duncker C., Raghavachar A., Arnold R., Heimpel H., Schrezenmeier H. Emergence of CD52-, phosphatidylinositolglycan-anchor-deficient T lymphocytes after in vivo application of Campath-1H for refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 1995 Aug 15;86(4):1487–1492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillmen P., Lewis S. M., Bessler M., Luzzatto L., Dacie J. V. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1995 Nov 9;333(19):1253–1258. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511093331904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida Y., Takeda J., Miyata T., Inoue N., Nishimura J., Kitani T., Maeda K., Kinoshita T. Characterization of genomic PIG-A gene: a gene for glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchor biosynthesis and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1994 Jun 1;83(11):3126–3131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G., Kennedy M., Papayannopoulou T., Wiles M. V. Hematopoietic commitment during embryonic stem cell differentiation in culture. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):473–486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooyman D. L., Byrne G. W., McClellan S., Nielsen D., Tone M., Waldmann H., Coffman T. M., McCurry K. R., Platt J. L., Logan J. S. In vivo transfer of GPI-linked complement restriction factors from erythrocytes to the endothelium. Science. 1995 Jul 7;269(5220):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.7541557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. R., Mortensen R. M., Larson C. A., Brent G. A. Thyroid hormone receptor-alpha inhibits retinoic acid-responsive gene expression and modulates retinoic acid-stimulated neural differentiation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Jun;8(6):746–756. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.6.7935490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Dacie J. V. The aplastic anaemia--paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1967 Mar;13(2):236–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan T., Dalrymple S., Barkett M., Lee F. Hematopoietic growth factor receptor genes as markers of lineage commitment during in vitro development of hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1993 Jun 1;81(11):2903–2915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of complement activation on the surface of cells after incorporation of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) into their membranes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1558–1578. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Silber R., Nussenzweig V. Amelioration of lytic abnormalities of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria with decay-accelerating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Rutgers J. L., Knowles D. M., Nussenzweig V. Identification of the complement decay-accelerating factor (DAF) on epithelium and glandular cells and in body fluids. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):848–864. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Takeda J., Iida Y., Yamada N., Inoue N., Takahashi M., Maeda K., Kitani T., Kinoshita T. The cloning of PIG-A, a component in the early step of GPI-anchor biosynthesis. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1318–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.7680492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. G., Humphries R. K., Frank M. M., Young N. Characterization of the hematopoietic defect in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Exp Hematol. 1986 Mar;14(3):222–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi H., Hotta T., Ichikawa A., Kinoshita T., Taguchi R., Kiguchi T., Ikezawa H., Saito H. Peripheral blood cells are predominantly chimeric of affected and normal cells in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: simultaneous investigation on clonality and expression of glycophosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. Blood. 1994 Feb 1;83(3):853–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. M., Nguyen M., Lazarus H. M., Brodsky R. A., Terstappen L. W., Medof M. E. Peripheral blood harvest of unaffected CD34+ CD38- hematopoietic precursors in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1995 Nov 1;86(9):3381–3386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickard K. A., Brown R. D., Wilkinson T., Kronenberg H. The colony forming cell in the myeloproliferative disorders and aplastic anaemia. Scand J Haematol. 1979 Feb;22(2):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin M. R., Landsberger F. R. Trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein transfer to target membranes: a model for the pathogenesis of trypanosomiasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):801–805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risau W., Sariola H., Zerwes H. G., Sasse J., Ekblom P., Kemler R., Doetschman T. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in embryonic-stem-cell-derived embryoid bodies. Development. 1988 Mar;102(3):471–478. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins S. A., Sims P. J. The complement-inhibitory activity of CD59 resides in its capacity to block incorporation of C9 into membrane C5b-9. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3478–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. J., Kimball J., Vining D., Young N. S. Intensive immunosuppression with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine as treatment for severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 1995 Jun 1;85(11):3058–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotoli B., Robledo R., Luzzatto L. Decreased number of circulating BFU-Es in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):157–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R. M., Bruyns E., Snodgrass H. R. Hematopoietic development of embryonic stem cells in vitro: cytokine and receptor gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):728–740. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. E., McIntosh D. P., Dvorak A. M., Liu J., Oh P. Separation of caveolae from associated microdomains of GPI-anchored proteins. Science. 1995 Sep 8;269(5229):1435–1439. doi: 10.1126/science.7660128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafren D. R., Bates R. C., Agrez M. V., Herd R. L., Burns G. F., Barry R. D. Coxsackieviruses B1, B3, and B5 use decay accelerating factor as a receptor for cell attachment. J Virol. 1995 Jun;69(6):3873–3877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3873-3877.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda J., Kinoshita T. GPI-anchor biosynthesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Sep;20(9):367–371. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda J., Miyata T., Kawagoe K., Iida Y., Endo Y., Fujita T., Takahashi M., Kitani T., Kinoshita T. Deficiency of the GPI anchor caused by a somatic mutation of the PIG-A gene in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90250-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Z., Xu Y., Warner C. M. Removal of Qa-2 antigen alters the Ped gene phenotype of preimplantation mouse embryos. Biol Reprod. 1992 Aug;47(2):271–276. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod47.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasiewicz H., Ono K., Yee D., Thompson C., Goridis C., Rutishauser U., Magnuson T. Genetic deletion of a neural cell adhesion molecule variant (N-CAM-180) produces distinct defects in the central nervous system. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1163–1174. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90228-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneker G. T., Das P. K., Meinardi M. M., van Marle J., van Veen H. A., Bos J. D., Asghar S. S. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane proteins are constitutively down-regulated in psoriatic skin. J Pathol. 1994 Feb;172(2):189–197. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Väkevä A., Jauhiainen M., Ehnholm C., Lehto T., Meri S. High-density lipoproteins can act as carriers of glycophosphoinositol lipid-anchored CD59 in human plasma. Immunology. 1994 May;82(1):28–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Clark R., Bautch V. L. Embryonic stem cell-derived cystic embryoid bodies form vascular channels: an in vitro model of blood vessel development. Development. 1992 Feb;114(2):303–316. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward T., Pipkin P. A., Clarkson N. A., Stone D. M., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. Decay-accelerating factor CD55 is identified as the receptor for echovirus 7 using CELICS, a rapid immuno-focal cloning method. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5070–5074. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles M. V. Embryonic stem cell differentiation in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:900–918. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)25057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles M. V., Keller G. Multiple hematopoietic lineages develop from embryonic stem (ES) cells in culture. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):259–267. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles M. V., Keller G. Multiple hematopoietic lineages develop from embryonic stem (ES) cells in culture. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):259–267. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashina M., Ueda E., Kinoshita T., Takami T., Ojima A., Ono H., Tanaka H., Kondo N., Orii T., Okada N. Inherited complete deficiency of 20-kilodalton homologous restriction factor (CD59) as a cause of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 25;323(17):1184–1189. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010253231707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang E., Huestis W. H. Mechanism of intermembrane phosphatidylcholine transfer: effects of pH and membrane configuration. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 16;32(45):12218–12228. doi: 10.1021/bi00096a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. S., Barrett A. J. The treatment of severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 1995 Jun 15;85(12):3367–3377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. S. The problem of clonality in aplastic anemia: Dr Dameshek's riddle, restated. Blood. 1992 Mar 15;79(6):1385–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]