Abstract
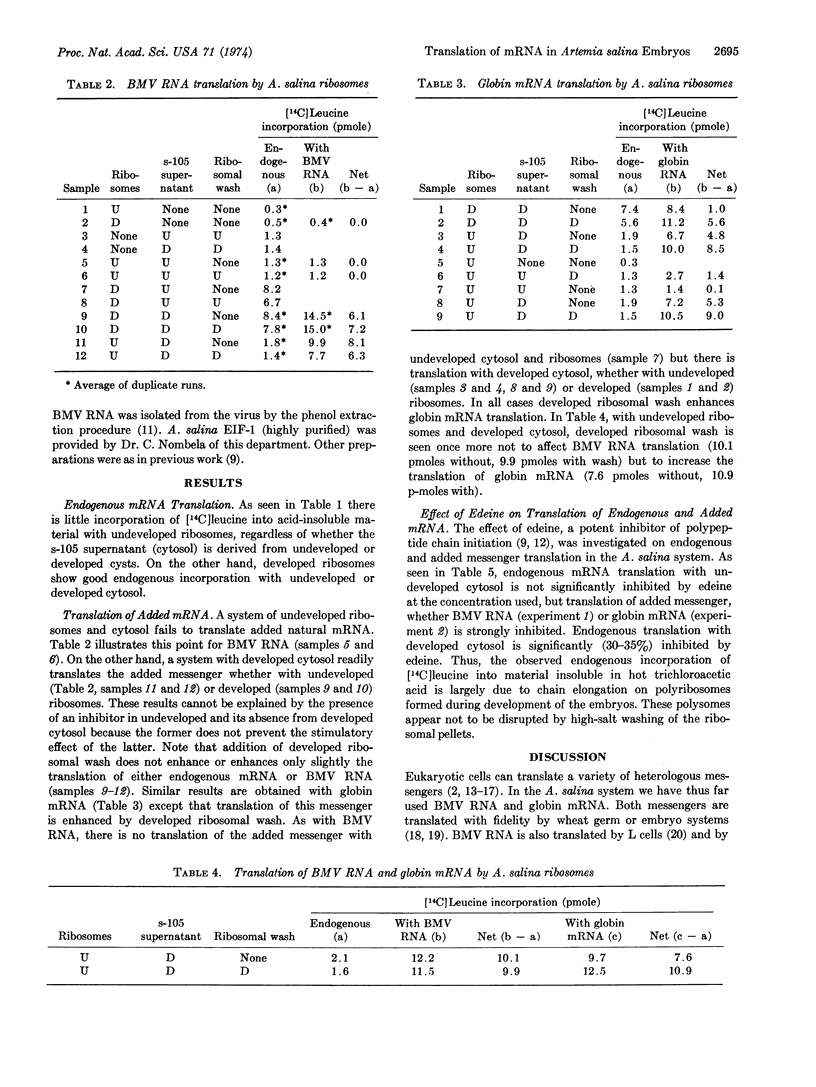
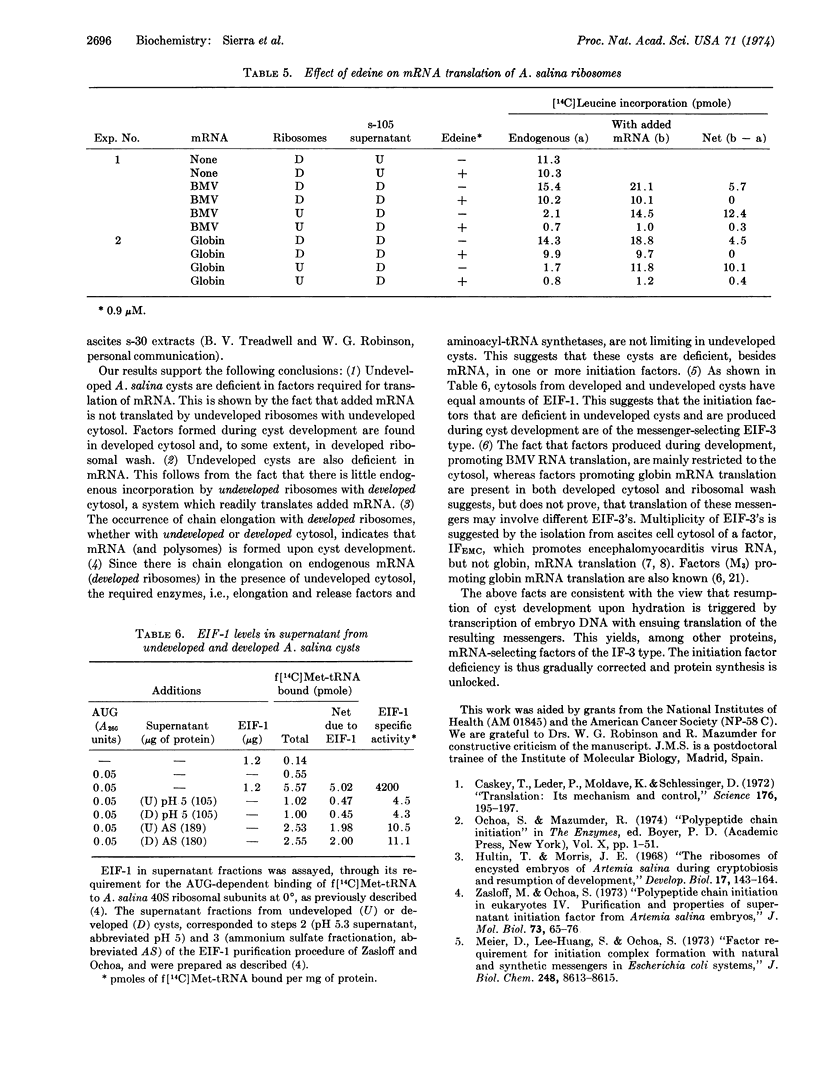
Cell-free preparations from encapsulated Artemia salina embryos readily translate poly(U), but there is no endogenous protein synthesis or translation of added natural mRNA until development resumes upon incubation in saline. High-salt-washed 80S ribosomes and highspeed supernatant (cytosol) were prepared from undeveloped eggs and from eggs allowed to develop to a stage prior to hatching. Endogenous protein synthesis occurs only with ribosomes from developed embryos, whether with undeveloped or developed cytosol. This is mainly elongation of preformed polypeptide chains, for it is largely resistant to edeine, an inhibitor of chain initiation. Edeinesensitive translation of added natural mRNA occurs with both developed and undeveloped ribosomes but requires developed cytosol. Translation of brome mosaic virus RNA is not much, if at all, further stimulated by high-saltwash of developed ribosomes, but that of globin mRNA is markedly enhanced. Levels of the chain initiation factor EIF-1 are the same before and after development. These results are consistent with the view that resumption of developemtn is triggered by transcription, with ensuing translation of the resulting messengers to yield, among other proteins, mRNA-recognizing initiation factors of the IF-3 type which are partly free in the cytosol and partly ribosome-bound. The data also suggest that different factors may be involved in the translation of brome mosaic virus RNA and globin mRNA by this system.
Keywords: cytes, brine shrimp eggs, eukaryotic initiation factors, elongation factors, brome mosaic virus RNA
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball L. A., Minson A. C., Shih D. S. Synthesis of plant virus coat proteins in an animal cell-free system. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 19;246(155):206–208. doi: 10.1038/newbio246206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockstahler L. E., Kaesberg P. Isolation and properties of RNA from bromegrass mosaic virus. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey T., Leder P., Moldave K., Schlessinger D. Translation: its mechanism and control. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):195–197. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin T., Morris J. E. The ribosomes of encysted embryos of Artemia salina during cryptobiosis and resumption of development. Dev Biol. 1968 Feb;17(2):143–164. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Osborn M., Berns A. J., Bloemendal H. Translation of two messenger RNAs from lens in a cell free system from Krebs II ascites cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 1;236(61):5–7. doi: 10.1038/newbio236005a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Pragnell I. B., Osborn M., Arnstein H. R. Stimulation by reticulocyte initiation factors of protein synthesis in a cell-free system from Krebs II ascites cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 16;287(1):113–123. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier D., Lee-Huang S., Ochoa S. Factor requirements for initiation complex formation with natural and synthetic messengers in Escherichia coli systems. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8613–8615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Lebleu B., Revel M. Discrimination between messenger ribonucleic acids by a mammalian translation initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2139–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picciano D. J., Prichard P. M., Merrick W. C., Shafritz D. A., Graf H., Crystal R. G., Anderson W. F. Isolation of protein synthesis initiation factors from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):204–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Kaesberg P. Translation of brome mosaic viral ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system derived from wheat embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1799–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szer W., Kurylo-Borowska Z. Interactions of edeine with bacterial ribosomal subunits. Selective inhibition of aminoacyl-tRNA binding sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 15;259(3):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaquero C., Reibel L., Delaunay J., Schapira G. Translation of globulin mRNA among eukaryotes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):1171–1177. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90815-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigle D. T. Purification of a messenger-specific initiation factor from ascites-cell supernatant. Eur J Biochem. 1973 May;35(1):11–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigle D. T., Smith A. E. Specificity in initiation of protein synthesis in a fractionated mammalian cell-free system. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 4;242(118):136–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio242136a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. A supernatant factor involved in initiation complex formation with eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. Polypeptide chain initiation in eukaryotes. IV. Purification and properties of supernatant initiation factor from Artemia salina embryos. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jan;73(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



