Abstract
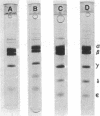
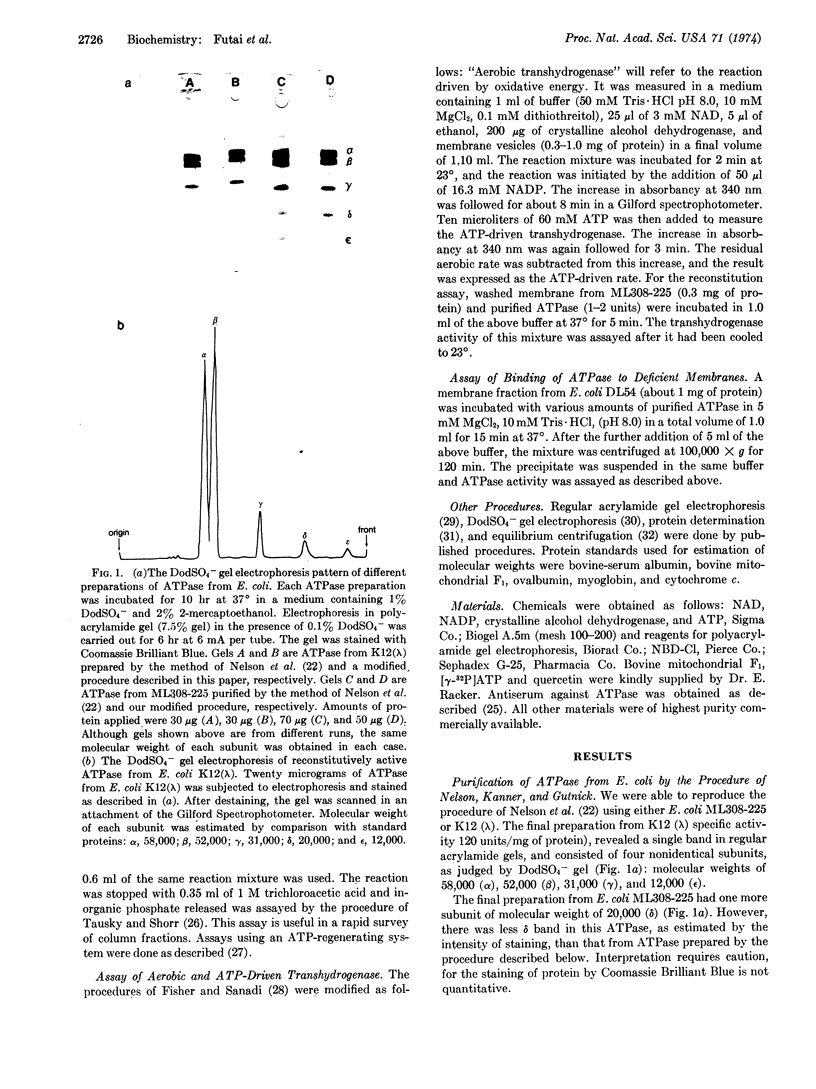
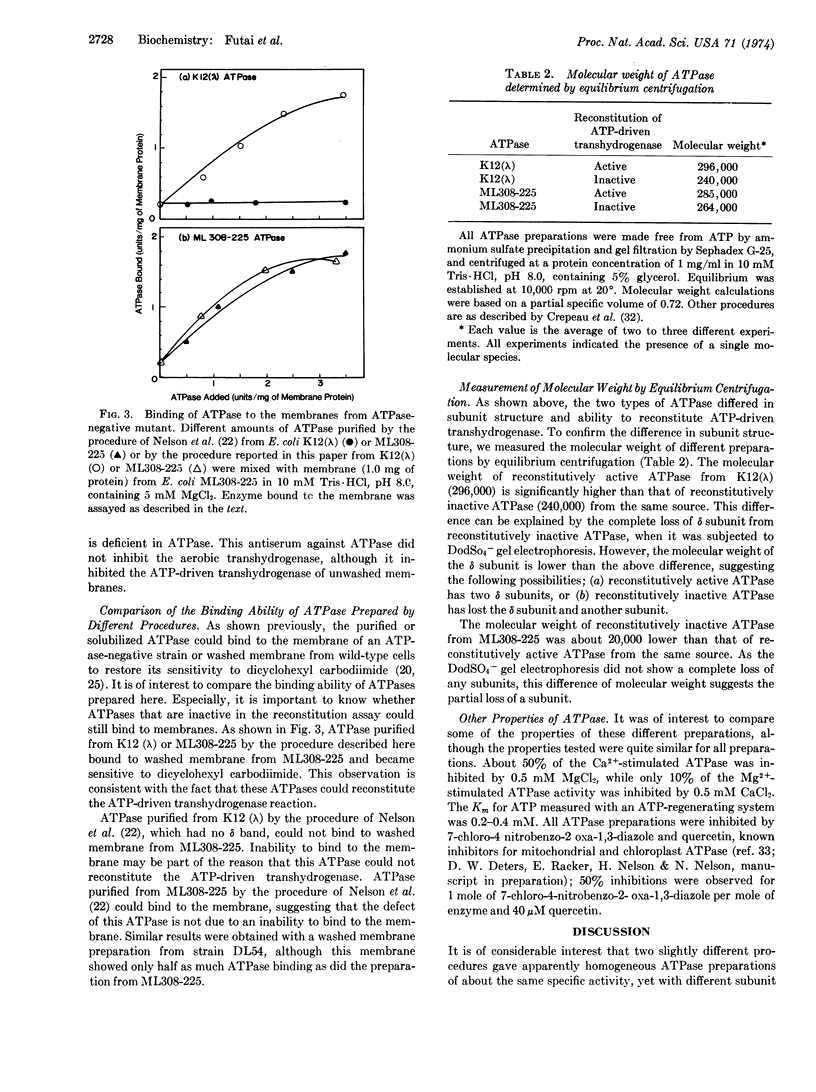
The Mg2+- and Ca2+-stimulated ATPase (EC 3.6.1.3; ATP phosphohydrolase) (bacterial coupling factor) was purified from two strains of E. coli by two different procedures: (a) method of Nelson, Kanner, and Gutnick [Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA (1974) 71, 2720-2724] and (b) a modified procedure described in this paper. The ATPase purified from E. coli K12 (λ) by the first procedure had 4 subunits (α, β, γ, and ε). It did not bind to a deficient membrane, nor did it reconstitute ATP-driven transhydrogenase activity. Our modified procedure (b) yielded 5 subunits (α, β, γ, δ, and ε). This ATPase could bind to a deficient membrane and reconstitute ATP-driven transhydrogenase. This finding suggests that the δ subunit is required for the reaction with the membrane. The molecular weight of the 4-subunit ATPase was significantly lower than that of the 5-subunit ATPase, as judged by equilibrium centrifugation. The specific ATPase activities of both preparations were about the same. These two procedures were also applied to E. coli ML308-225.
Keywords: coupling factor, ATP-driven transhydrogenase
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bragg P. D., Hou C. Purification of a factor for both aerobic-driven and ATP-driven energy-dependent transhydrogenases of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 15;28(3):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80738-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bragg P. D., Hou C. Reconstitution of energy-dependent transhydrogenase in ATPase-negative mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91305-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K-12: the genetic and biochemical characterisations of a strain carrying a mutation in the uncB gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K12. Mutations affecting magnesium ion- or calcium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):75–81. doi: 10.1042/bj1240075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreira J., Leal J. A., Rojas M., Muñoz E. Membrane ATPase of Escherichia coli K 12. Selective solubilization of the enzyme and its stimulation by trypsin in the soluble and membrane-bound states. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 25;307(3):541–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Gibson F., McCann L. Reconstitution of oxidative phosphorylation and the adenosine triphosphate-dependent transhydrogenase activity by a combination of membrane fractions from unCA- and uncB- mutant strains of Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1015–1021. doi: 10.1042/bj1341015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepeau R. H., Edelstein S. J., Rehmar M. J. Analytical ultracentrifugation with absorption optics and a scanner-computer system. Anal Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(1):213–233. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90501-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J. Membrane Mg-(Ca)-Activated Adenosine Triphosphatase of Escherichia coli: Characterization in the Membrane-Bound and Solubilized States. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1203–1212. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1203-1212.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. J., Sanadi D. R. Energy-linked nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide transhydrogenase in membrane particles from Escherchia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 6;245(1):34–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M. Orientation of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli prepared by different procedures. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(1):15–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01870079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutnick D. L., Kanner B. I., Postma P. W. Oxidative phosphorylation in mutants of Escherichia coli defective in energy transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 17;283(2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. L., Kennedy E. P. Energy-transducing adenosine triphosphatase from Escherichia coli: purification, properties, and inhibition by antibody. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):772–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.772-781.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Gutnick D. L. Use of neomycin in the isolation of mutants blocked in energy conservation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):287–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.287-289.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Anraku Y. Membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli. I. Partial purification and properties. J Biochem. 1972 Mar;71(3):387–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Deters D. W., Nelson H., Racker E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing photophosphorylation. 8. Properties of isolated subunits of coupling factor 1 from spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2049–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Kanner B. I., Gutnick D. L. Purification and properties of Mg2+-Ca2+ adenosinetriphosphatase from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2720–2724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULLMAN M. E., PENEFSKY H. S., DATTA A., RACKER E. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. I. Purification and properties of soluble dinitrophenol-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3322–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roisin M. P., Kepes A. The membrane ATPase of Escherichia coli. I. Ion dependence and ATP-ADP exchange reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 20;275(3):333–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roisin M. P., Kepes A. The membrane ATPase of Escherichia coli. I. Release into solution, allotopic properties and reconstitution of membrane-bound ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 30;305(2):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Restoration of active transport in an Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1124-1129.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schairer H. U., Gruber D. Mutants of Escherichia coli K12 defective in oxidative phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 17;37(2):282–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schairer H. U., Haddock B. A. -Galactoside accumulation in a Mg 2+ -,Ca 2+ -activated ATPase deficient mutant of E.coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):544–551. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Shallenberger M. K. Coupling of energy to active transport of amino acids in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUSSKY H. H., SHORR E. A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosphorus. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnock G., Erickson S. K., Ackrell B. A., Birch B. A mutant of Escherichia coli with a defect in energy metabolism. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):507–515. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T. H., Mével-Ninio M., Valentine R. C. Essential role of membrane ATPase or coupling factor for anaerobic growth and anaerobic active transport in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 26;314(3):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]