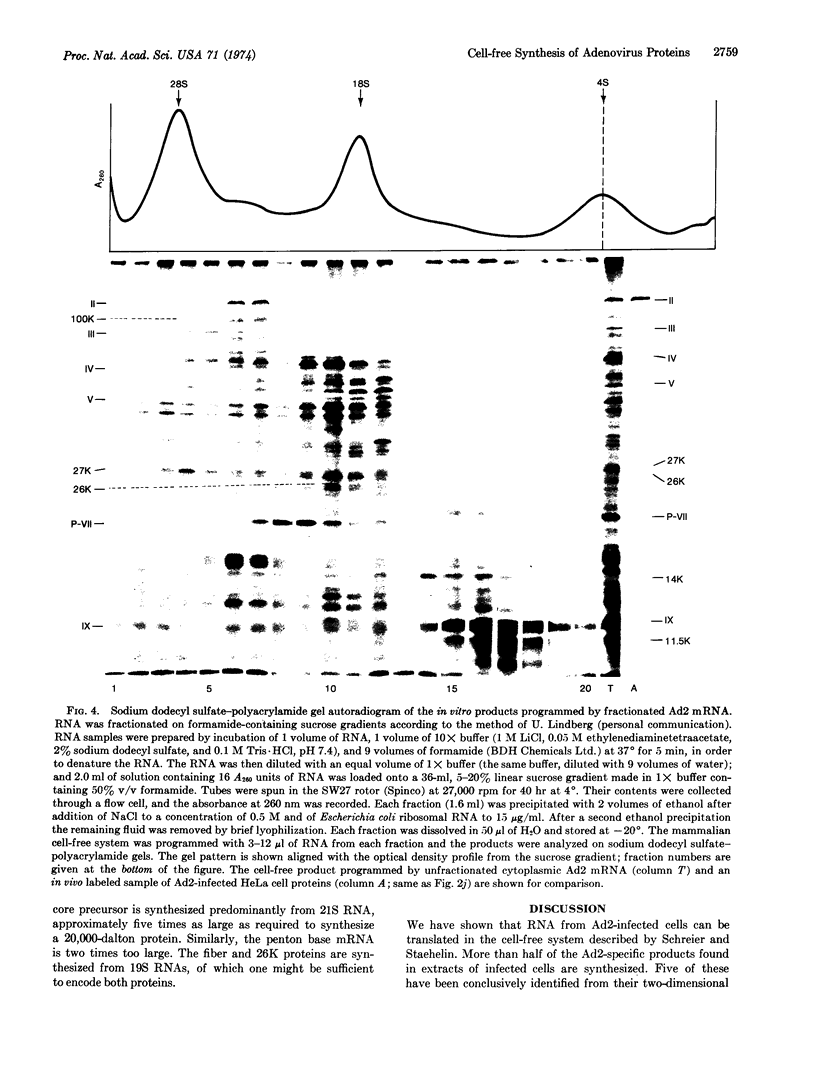
Abstract
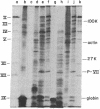
Cytoplasmic RNA extracted from human tissue culture cells infected with adenovirus type 2 was used to program protein synthesis in a cell-free system derived from mammalian cells. Analysis of the protein product by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed ten adenovirus-specific polypeptides. Five of these were further identified by analysis of tryptic peptides. Translation of RNA fractionated by sedimentation through sucrose gradients containing formamide demonstrated seven size classes of RNA, each of which programmed the synthesis of only one or two virus-specific polypeptides. Six of the virus-specific polypeptides were translated from RNAs much larger than expected for the size of the polypeptide.
Keywords: sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, fingerprint analysis, formamide
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi M., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. VI. Early and late glycopolypeptides. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):345–361. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., Mosteller R. D., Hardesty B. The mechanism of sodium fluoride and cycloheximide inhibition of hemoglobin biosynthesis in the cell-free reticulocyte system. J Mol Biol. 1966 Oct 28;21(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Persson T., Philipson L. Isolation and characterization of adenovirus messenger ribonucleic acid in productive infection. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):909–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.909-919.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Osborn M., Berns A. J., Bloemendal H. Translation of two messenger RNAs from lens in a cell free system from Krebs II ascites cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 1;236(61):5–7. doi: 10.1038/newbio236005a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M., Korner A. Mammalian cell-free protein synthesis directed by viral ribonucleic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):328–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo C. K., Raskas H. J. A reconstituted system for in vitro synthesis of adenovirus 2 proteins. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):487–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90285-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Gardner J., Green M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication, XIX. Resolution of late viral RNA species in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):557–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Pettersson U. Structure and function of virion proteins of adenoviruses. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1973;18:1–55. doi: 10.1159/000393160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Shekel J. J., Machado R., Pereira H. G. Phosphorylated polypeptides in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):931–934. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E. The initiation of protein synthesis directed by the RNA from encephalomyocarditis virus. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 1;33(2):301–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan D., Aviv H., Leder P. Purification and properties of biologically active messenger RNA for a myeloma light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1967–1971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J. M., Ginsberg H. S. Synthesis in vitro of type 5 adenovirus capsid proteins. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):973–980. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.973-980.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]