Abstract
Gangliocytic paraganglioma (GP) is a rare histologic type of neuroendocrine tumors. We report a case of pulmonary GP in a 29-year-old male presenting with an asymptomatic endobronchial nodule. Grossly, the tumor showed a 4.0x3.8x3.5 cm well-defined nodule with yellowish cut surface. Microscopically, the tumor was composed of three distinct cellular types: epithelioid cells, ganglion-like cells and spindle cells. Meanwhile, transitional cells, having morphologic features between ganglion-like and epithelioid cells, were also presented. The epithelioid cells arranged in various morphologic architectures, including Zellballen, papillary, cystic and microcystic pattern. The epithelioid cells were positive for AE1/AE3, CAM 5.2, chromogranin A and synaptophysin. Ganglion-like cells showed immunoreactivity for chromogranin A and synaptophysin. A few ganglion-like cells were also positive for AE1/AE3 and/or CAM 5.2. The spindle cells were positive for S-100 protein and neurofilament. The transitional cells showed a similar immunohistochemical profile to the epithelioid cells. The authors believe stem cell theory is a reasonable explanation for the origin of GP. GP probably originate from some kind of mucosa associated stem cell which can differentiate into diverse cellular lineages.
Keywords: Gangliocytic paraganglioma, bronchial, histomorphology, immunohistochemistry, histogenesis
Introduction
GP is a unique neuroendocrine tumor that differs from other neuroendocrine tumors. It was initially reported as ganglioneuroma by Dahl et al in 1957 [1] and first named GP by Kepes et al in 1971 [2]. The exact origin of GP remains unclear till now. It occurs almost exclusively in the second portion of the duodenum, especially in periampullary region. Most cases in duodenum showed the epithelioid cells were positive for pancreatic polypeptide [3]. Therefore, some researchers consider GP as a hamartoma developing in misplaced embryonic pancreatic tissue [4-6]. However, GP has also been described in other locations including jejunum [7], esophagus [8], stomach [6], pancreas [9], appendix [10], nasopharynx [11] and lung [12-15]. Herein we present an additional case of pulmonary GP which displays diverse histological structures. Meanwhile, we would also comment on the origin of GP.
Case report
A 29-year-old asymptomatic male was admitted to our hospital because of a pulmonary mass detected by chest computerized tomographic (CT) scan during his annual physical examination. The CT scan revealed a 38 mm endobronchial mass almost completely obstructing the bronchial lumen of right lower lobe (Figure 1). From the CT scan, suspicious parenchymal involvement of adjacent right middle and lower lobes was demonstrated. Bronchoscopy displayed a mass partly occluding the bronchus. Bronchoscopic biopsy was reported as carcinoid because of positive staining of AE1/AE3, synaptophysin and chromogranin A in epithelioid cells. Subsequent lobectomy of the right middle and lower lobes with the dissection of the mediastinal lymph node was performed.
Figure 1.
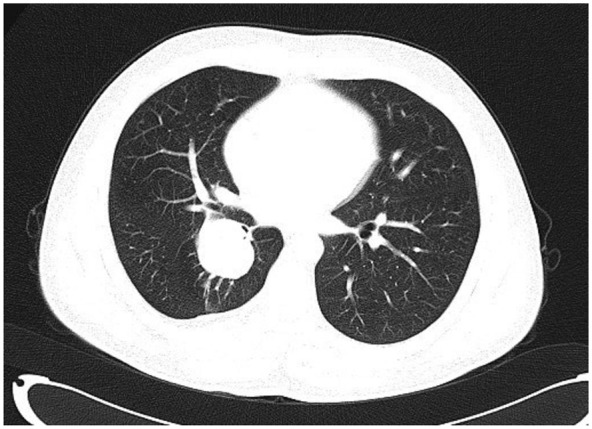
Chest CT scan showing an endobronchial mass almost completely obstructing the bronchial lumen of right lower lobe.
Grossly, the tumor showed a 4.0x3.8x3.5 cm well-defined nodule with yellowish cut surface. Histological examination of the tumor revealed an apparently well-defined but nonencapsulated neoplasm which did not involve the lung parenchyma. The tumor consisted of three distinct cellular elements. The first, uniform epithelioid cells had round to oval-shaped nuclei with granular chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli, and eosinophilic to clear cytoplasm. They arranged in various histological structures, including Zellballen (Figure 2A), papillary (Figure 2B), cystic (Figure 2C), and microcystic pattern (Figure 2D). The second, large ganglion-like cells were characterized by abundant amphophilic cytoplasm, large round-shaped nuclei, and prominent nucleoli. They were dispersed within the nests of epithelioid cells and the background filled with spindle cells. The third, spindle cells were located in the periphery of the epithelioid cells. Additionally, transitional cells, having morphologic features between ganglion-like and epithelioid cells, were also presented (Figure 2E). They were larger than epithelioid cells but smaller than ganglion-like cells. Cellular atypia, mitotic activity and necrosis were not detected. Regional lymph nodes were not invaded.
Figure 2.
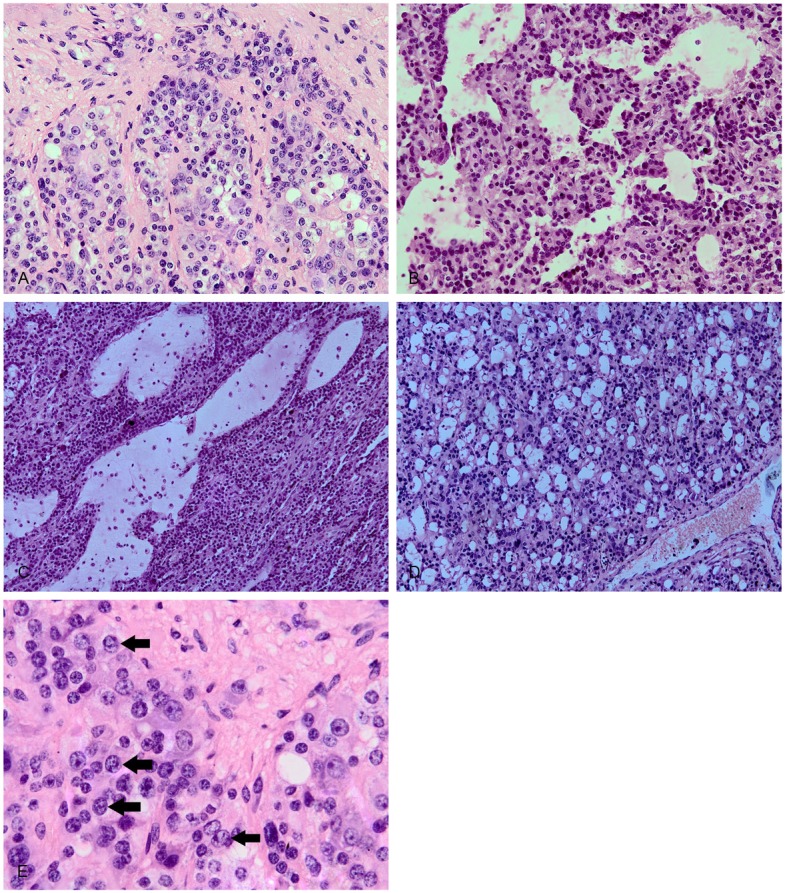
Histopathological features. The epithelioid cells arranging in various histological structures, including Zellballen (A), papillary (B), cystic (C), and microcystic pattern (D). The transitional cells, larger than epithelioid cells but smaller than ganglion-like cells, having morphologic features between ganglion-like and epithelioid cells (E).
Immunohistochemically, all of the components showed immunoreactivity for neuron specific enolase. The epithelioid cells were positive for AE1/AE3 (Figure 3A), CAM 5.2, chromogranin A (Figure 3B) and synaptophysin (Figure 3C), but negative for neurofilament. A number of these cells were weakly positive for S-100 protein. Ganglion-like cells showed immunoreactivity for chromogranin A and synaptophysin. They were negative for neurofilament. Some of ganglion-like cells were also reactive for S-100 protein. Interestingly, we observed a few AE1/AE3 and/or CAM 5.2 positive ganglion-like cells (Figure 3D). Besides neuron specific enolase, the spindle cells were positive for S-100 protein (Figure 3E) and neurofilament, but negative for other markers. The transitional cells showed a similar immunohistochemical profile to the epithelioid cells.
Figure 3.
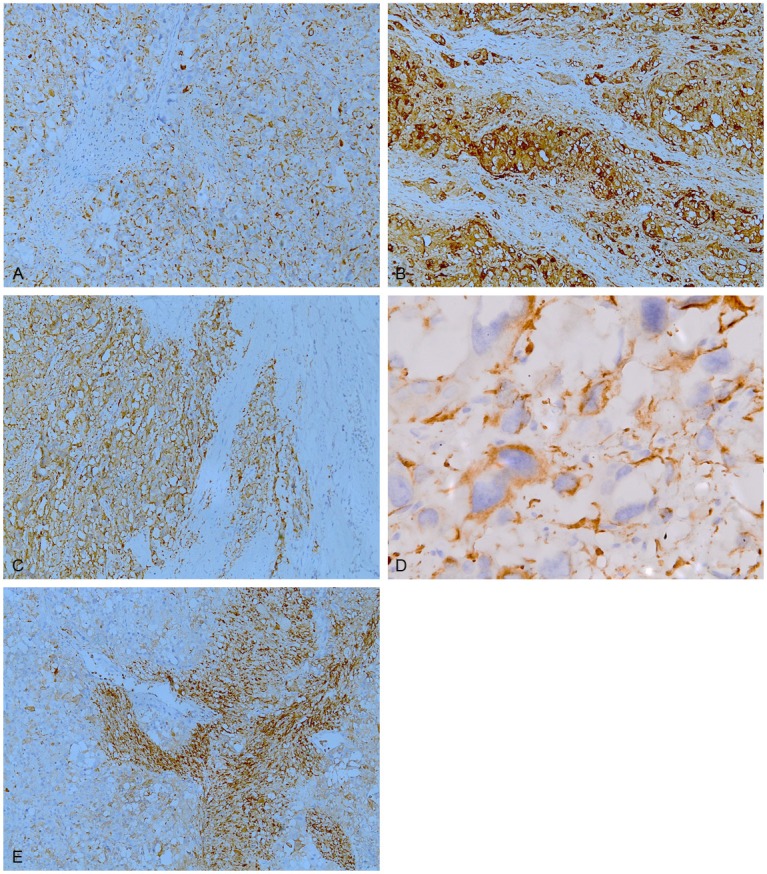
Immunohistochemical staining of GP. The epithelioid cells were positive for AE1/AE3 (A), chromogranin A (B) and synaptophysin (C). A few CAM 5.2 positive ganglion-like cells were also identified (D). The spindle cells were positive for S-100 protein (E).
Discussion
GP is a rare epithelioid tumor with distinctive feature that differs from other neuroendocrine tumors. It spans all age groups (15-84) with an median of 52.3 years, occurs with a slight male predominance (M:F ratio, 114:76) [3], The most common location of GPs is duodenum (90%), especially in periampullary region [3]. Two of the most common symptoms of duodenal GP were gastrointestinal bleeding and abdominal pain [3]. Recently, some extra-duodenal cases have also been described. To our knowledge, excluding the present case, there have been 4 cases of pulmonary GP reported in the English literature (Table 1). All of the 5 cases occurred in adults, and they appear to affect middle-aged and old male more commonly. Of the 5 cases, 4 were located in bronchus. This data indicated bronchus may be a common location of pulmonary GP. The initial clinical manifestation of pulmonary GP could be chest pain, pneumonia or Cushing’s syndrome [12-14]. In the current case, the patient was asymptomatic.
Table 1.
Clinical feature of pulmonary gangliocytic paraganglioma
| Case no. | Sex/Age (yr) | Size (mm) | Location | Clinical presentation | Treatment | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 [12] | M/75 | 16 | Bifurcation of the right middle and lower lobe bronchus | Right anterior chest pain | Lobectomy of the right middle and lower lobes with dissection of the mediastinal | NA |
| 2 [13] | F/54 | 9 | Right lower lobe bronchus | Right lower lobe pneumonia | Bronchoscopic resection | Recurrent was confirmed 6 months later |
| Further bronchoscopic and laser therapy | No evidence of tumor additional 4 months later | |||||
| 3 [14] | M/55 | 8 | Left inferior pulmonary ligament | Cushing’s syndrome | NA | NA |
| 4 [15] | M/61 | NA | Right lower lobe bronchus | NA | Lobectomy of the right lower lobe | NA |
| Present case | M/29 | 40 | Right lower lobe bronchus | Asymptomatic | Lobectomy of the right middle and lower lobes with dissection of the mediastinal | No evidence of tumor 7 months later |
F, female; M, male; NA, not available.
Microscopically, GP has three characteristic components: epithelioid cells, ganglion-like cells, and spindle cells. The portion of this three components varies widely from case to case [6,16], which pose a challenge for pathologists to make a definite diagnosis especially in a small biopsy. We can assume, if this tumor display a predominance of one or two of above components, various differential diagnoses, including carcinoid, paraganglioma, carcinoma, schwannoma or ganglioneuroma, should be considered. In this case, the epithelioid cells arranged in various histological structures, including Zellballen, papillary, cystic and microcystic pattern. The Zellballen structure showed variable nest like carcinoid or paraganglioma. The papillary structure was first mentioned by Burke and Helwig [6]. This structure brought us to think of pulmonary sclerosing haemangioma which is almost exclusively located in lung parenchyma. Of the 100 cases of pulmonary sclerosing hemangioma reported by Devouassoux-Shisheboran et al, only one was described as an endobronchial polyp [17]. However, pulmonary GP appears not to involve adjacent lung parenchyma [14]. The cystic pattern has not been mentioned in the literature. However, some authors had described pseudoglandular structures which seemed to have some similarity to the microcystic structure we described [18-20].
The transitional cells have been described in duodenal and pulmonary GPs [13,18,21]. We observed similar cells in this case. In fact, epithelioid cells and ganglion-like cells have some similar immunohistochemical and ultrastructural features [5,16,18]. In this case, a small number of ganglion-like cells were positive for AE1/AE3 and/or CAM 5.2 which should not stain ganglion cell. Therefore, ganglion-like cells and epithelioid cells appear to come from a same progenitor.
The histogenesis of GP is widely divergent. It was difficult to elucidate the 3 components observed in a single tumor, because they are of different embryologic origins, epithelioid component originating from entoderm and the other two from neuroectoderm. Taylor and Helwig suggested that GP arose from multipotential cells of embryonic celiac ganglion [22]. Reed et al preferred an origin from pluripotent stem cells residing at the base of intestinal glands [23]. Then the hypothesis of pancreatic origin was popular. In consideration of the consistent location in the duodenum and immunoreactivity for pancreatic polypeptide, Perrone et al suggested this lesion represented a hamartomatous process derived from the ventral primordium of the pancreas [5]. However, there are several problems the pancreatic hypothesis can not solve. First, it can not provide a reasonable explanation for those extra-duodenal cases. Secondly, pancreatic polypeptide is not a specific marker for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Carcinoids of the rectum, colon, lung and bile duct also showed reactivity for pancreatic polypeptide [24-26]. Thirdly, although GP is composed of endodermal and ectodermal tissues, the cases with lymph node or distant metastasis argue against the theory of hamartoma [3,27]. Recently, Ogata et al. reported a case of duodenal GP with glandular component [28] which belongs to endodermal tissue. This unique case delivered a powerful support to stem cell origin but a rebuttal to the pancreatic hypothesis. Reviewing all the sites involved in the literature, we can find GP tends to a mucosa associated tumor. Therefore GP probably originates from some kind of mucosa associated stem cell which can differentiate into diverse cellular lineages. Considering the transitional cells and the similarity between ganglion-like cells and epithelioid cells, we speculate ganglion-like cells and epithelioid cells come from a common cellular lineage.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to this article to declare.
References
- 1.Dahl EV, Waugh JM, Dahlin DC. Gastrointestinal ganglioneuromas; brief review with report of a duodenal ganglioneuroma. Am J Pathol. 1957;33:953–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kepes JJ, Zacharias DL. Gangliocytic paragangliomas of the duodenum. A report of two cases with light and electron microscopic examination. Cancer. 1971;27:61–7. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197101)27:1<61::aid-cncr2820270111>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Okubo Y, Wakayama M, Nemoto T, Kitahara K, Nakayama H, Shibuya K, Yokose T, Yamada M, Shimodaira K, Sasai D, Ishiwatari T, Tsuchiya M, Hiruta N. Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of gangliocytic paraganglioma. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:187. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Guarda LA, Ordonez NG, del Junco GW, Luna MA. Gangliocytic paraganglioma of the duodenum: an immunocytochemical study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983;78:794–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Perrone T, Sibley RK, Rosai J. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma. An immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study and a hypothesis concerning its origin. Am J Surg Pathol. 1985;9:31–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Burke AP, Helwig EB. Gangliocytic paraganglioma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989;92:1–9. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/92.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Aung W, Gallagher HJ, Joyce WP, Hayes DB, Leader M. Gastrointestinal haemorrhage from a jejunal gangliocytic paraganglioma. J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:84–5. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Weinrach DM, Wang KL, Blum MG, Yeldandi AV, Laskin WB. Multifocal presentation of gangliocytic paraganglioma in the mediastinum and esophagus. Hum Pathol. 2004;35:1288–91. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2004.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tomic S, Warner T. Pancreatic somatostatin-secreting gangliocytic paraganglioma with lymph node metastases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:607–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.van Eeden S, Offerhaus GJ, Peterse HL, Dingemans KP, Blaauwgeers HL. Gangliocytic paraganglioma of the appendix. Histopathology. 2000;36:47–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2000.00881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sinkre P, Lindberg G, Albores-Saavedra J. Nasopharyngeal gangliocytic paraganglioma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2001;125:1098–100. doi: 10.5858/2001-125-1098-NGP. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hironaka M, Fukayama M, Takayashiki N, Saito K, Sohara Y, Funata N. Pulmonary gangliocytic paraganglioma: case report and comparative immunohistochemical study of related neuroendocrine neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25:688–93. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200105000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kee AR, Forrest CH, Brennan BA, Papadimitriou JM, Glancy RJ. Gangliocytic paraganglioma of the bronchus: a case report with follow-up and ultrastructural assessment. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:1380–5. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200310000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Palau MA, Merino MJ, Quezado M. Corticotropin-producing pulmonary gangliocytic paraganglioma associated with Cushing’s syndrome. Hum Pathol. 2006;37:623–6. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2005.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gucer H, Mete O. Endobronchial Gangliocytic Paraganglioma: Not All Keratin-Positive Endobronchial Neuroendocrine Neoplasms are Pulmonary Carcinoids. Endocr Pathol. 2013 doi: 10.1007/s12022-013-9258-7. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hamid QA, Bishop AE, Rode J, Dhillon AP, Rosenberg BF, Reed RJ, Sibley RK, Polak JM. Duodenal gangliocytic paragangliomas: a study of 10 cases with immunocytochemical neuroendocrine markers. Hum Pathol. 1986;17:1151–7. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Devouassoux-Shisheboran M, Hayashi T, Linnoila RI, Koss MN, Travis WD. A clinicopathologic study of 100 cases of pulmonary sclerosing hemangioma with immunohistochemical studies: TTF-1 is expressed in both round and surface cells, suggesting an origin from primitive respiratory epithelium. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:906–16. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200007000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Inai K, Kobuke T, Yonehara S, Tokuoka S. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma with lymph node metastasis in a 17-year-old boy. Cancer. 1989;63:2540–5. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890615)63:12<2540::aid-cncr2820631231>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Barbareschi M, Frigo B, Aldovini D, Leonardi E, Cristina S, Falleni M. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma. Report of a case and review of the literature. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989;416:81–9. doi: 10.1007/BF01606473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dookhan DB, Miettinen M, Finkel G, Gibas Z. Recurrent duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma with lymph node metastases. Histopathology. 1993;22:399–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Scheithauer BW, Nora FE, LeChago J, Wick MR, Crawford BG, Weiland LH, Carney JA. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma. Clinicopathologic and immunocytochemical study of 11 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986;86:559–65. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.5.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Taylor HB, Helwig EB. Benign nonchromaffin paragangliomas of the duodenum. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1962;335:356–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00957029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Reed RJ, Caroca PJ Jr, Harkin JC. Gangliocytic paraganglioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1977;1:207–16. doi: 10.1097/00000478-197709000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Federspiel BH, Burke AP, Sobin LH, Shekitka KM. Rectal and colonic carcinoids. A clinicopathologic study of 84 cases. Cancer. 1990;65:135–40. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900101)65:1<135::aid-cncr2820650127>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ishida T, Yokoyama H, Sugio K, Kaneko S, Sugimachi K, Hara N, Ohta M. Carcinoid tumor of the lung: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical studies. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1992;18:180–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Maitra A, Krueger JE, Tascilar M, Offerhaus GJ, Angeles-Angeles A, Klimstra DS, Hruban RH, Albores-Saavedra J. Carcinoid tumors of the extrahepatic bile ducts: a study of seven cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:1501–10. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200011000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rowsell C, Coburn N, Chetty R. Gangliocytic paraganglioma: a rare case with metastases of all 3 elements to liver and lymph nodes. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2011;15:467–71. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2010.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ogata S, Horio T, Sugiura Y, Aiko S, Aida S. Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma with regional lymph node metastasis and a glandular component. Pathol Int. 2011;61:104–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


