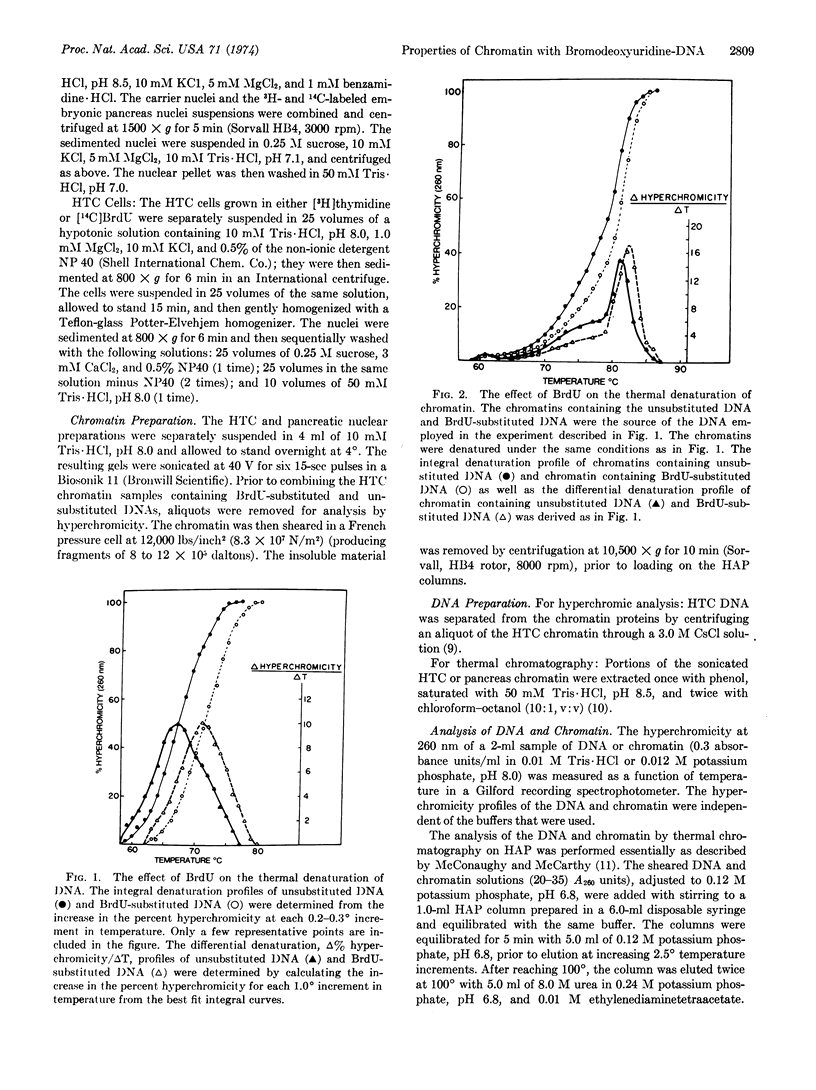
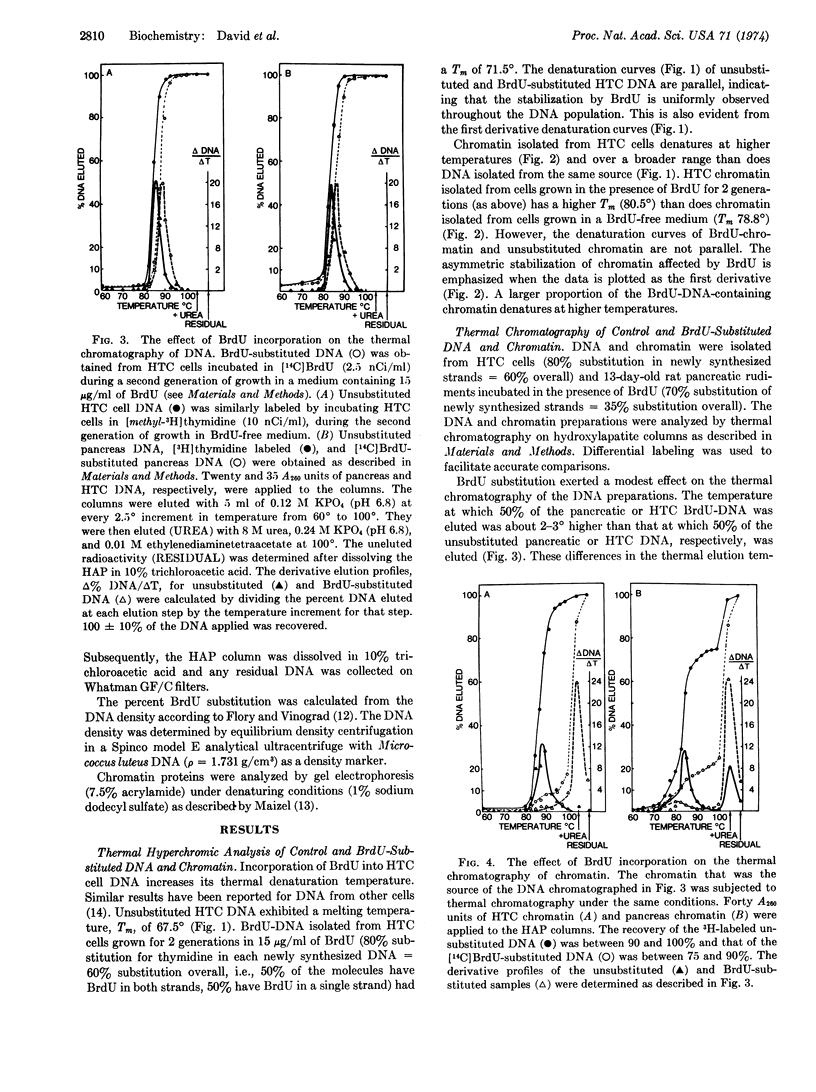
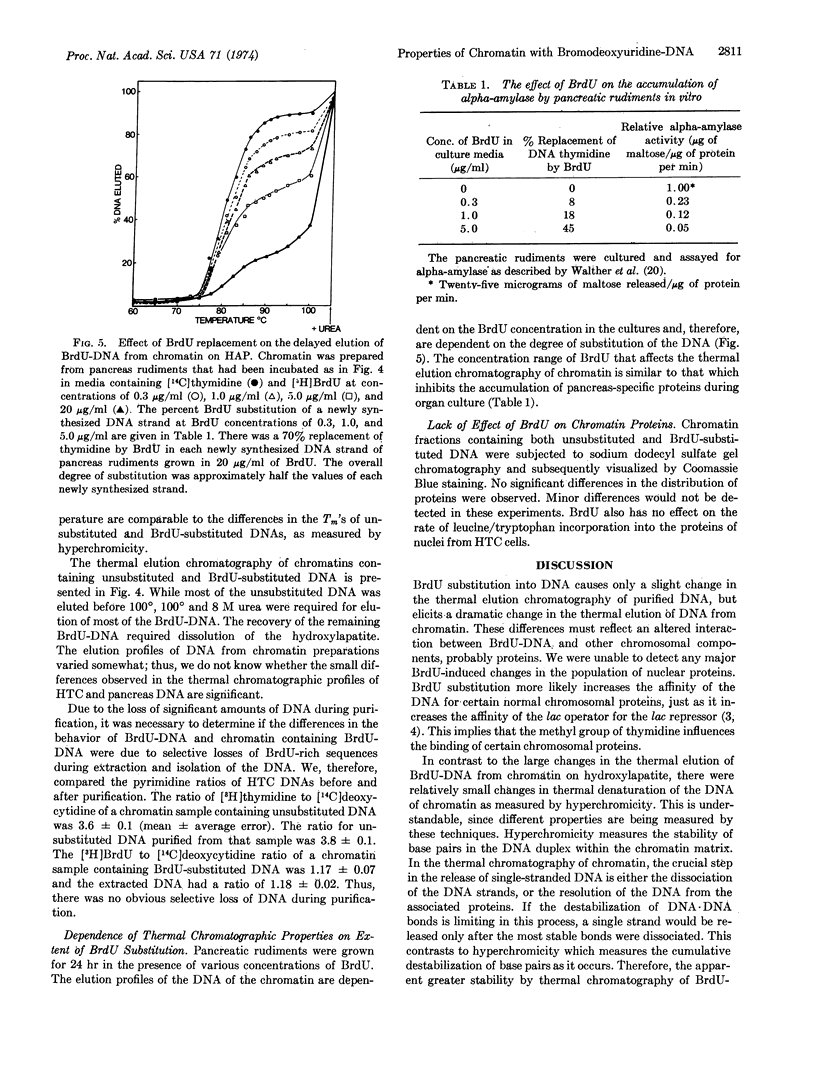
Abstract
The replacement of thymidine by 5-bromodeoxyuridine in DNA leads to a greatly enhanced stability of chromatin from hepatoma tissue culture or embryonic rat pancreas, as measured by thermal chromatography on hydroxylapatite. The increased stability is directly correlated with the degree of bromodeoxyuridine substitution. On the other hand, the incorporation of bromodeoxyuridine into DNA results in a modest stabilization of purified DNA. Substitution of nucleotide also alters slightly the hyperchromicity profile generated during the thermal denaturation of purified DNA and chromatin. The observed changes can best be explained by an altered interaction between the bromodeoxyuridine-DNA and other chromatin components, presumably proteins. These results suggests that the selective effects of bromodeoxyuridine on cytodifferentiation may be due to an increased affinity of regulatory proteins for bromodeoxyuridine-DNA.
Keywords: pancreas, cytodifferentiation, gene expression, chromosome
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler K., Beyreuther K., Fanning E., Geisler N., Gronenborn B., Klemm A., Müller-Hill B., Pfahl M., Schmitz A. How lac repressor binds to DNA. Nature. 1972 Jun 9;237(5354):322–327. doi: 10.1038/237322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. The relationship between glucocorticoid binding and tyrosine aminotransferase induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):709–715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Inhibition of myoblast fusion after one round of DNA synthesis in 5-bromodeoxyuridine. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jan;44(1):134–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory P. J., Jr, Vinograd J. 5-bromodeoxyuridine labeling of monomeric and catenated circular mitochondrial DNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 25;74(2):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUANG R. C., BONNER J. Histone, a suppressor of chromosomal RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1216–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., HSU T. C. Relative stability to thermal denaturation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) preparations containing bromodeoxyuridine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 2;5:120–124. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., Riggs A. D. Lac operator analogues: bromodeoxyuridine substitution in the lac operator affects the rate of dissociation of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2574–2576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., Riggs A. D. Lac repressor binding to operator analogues: comparison of poly(d(A-T)), poly(d(A-BrU)), and poly(d(A-U)). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 17;45(6):1542–1547. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., McCarthy B. J. Fractionation of chromatin by thermal chromatography. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 14;11(6):998–1003. doi: 10.1021/bi00756a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Pictet R. L., Williams R. H., Rutter W. J. Early differentiation of glucagon-producing cells in embryonic pancreas: a possible developmental role for glucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3478–3482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter W. J., Pictet R. L., Morris P. W. Toward molecular mechanisms of developmental processes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:601–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tomkins G. M. Relation of steroid structure to enzyme induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug 28;52(1):57–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen R. H., Tomkins G. M. Differential effect of 5-bromodeoxyuridine on the concentrations of specific enzymes in hepatoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1147–1150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen R. H., Tomkins G. M. Preferential inhibition by 5-bromodeoxyuridine of the synthesis of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 28;56(1):167–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther B. T., Pictet R. L., David J. D., Rutter W. J. On the mechanism of 5-bromodeoxyuridine inhibition of exocrine pancreas differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1953–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Campbell G. L., Holtzer H. Identification of a developmental program using bromodeoxyuridine. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90543-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilt F. H., Anderson M. The action of 5-bromodeoxyuridine on differentiation. Dev Biol. 1972 Jun;28(2):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



