Abstract
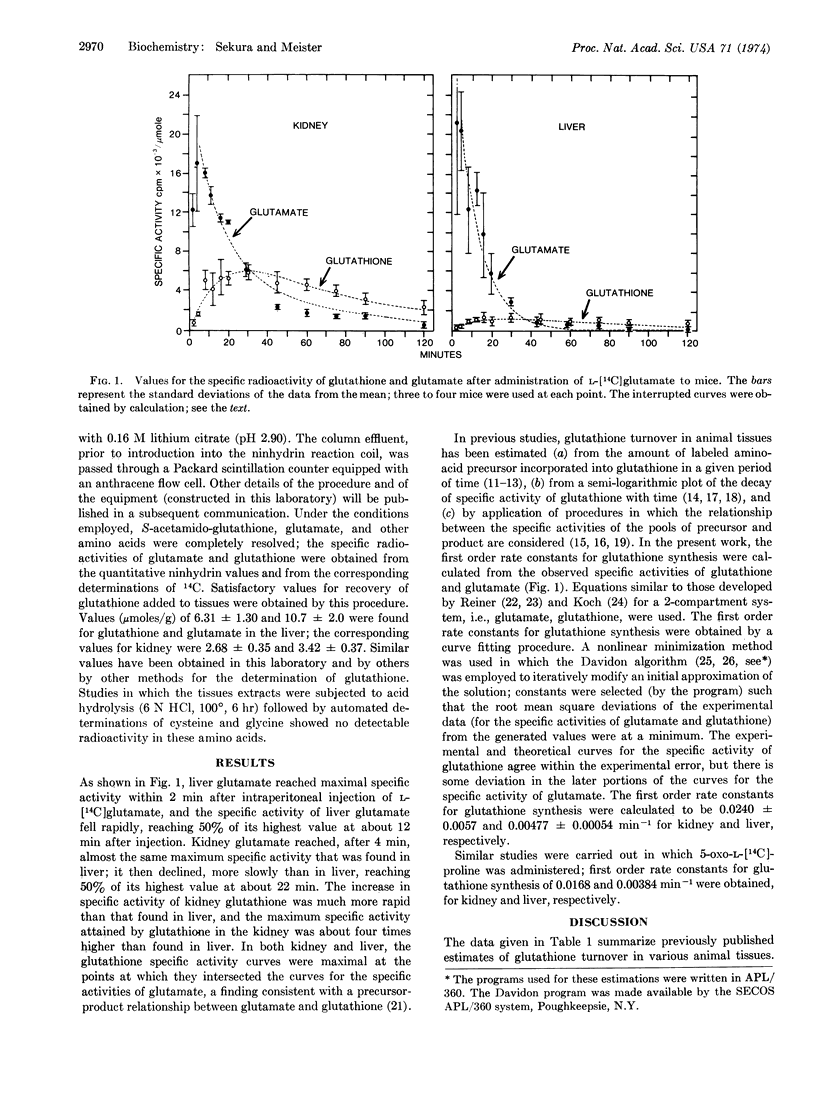
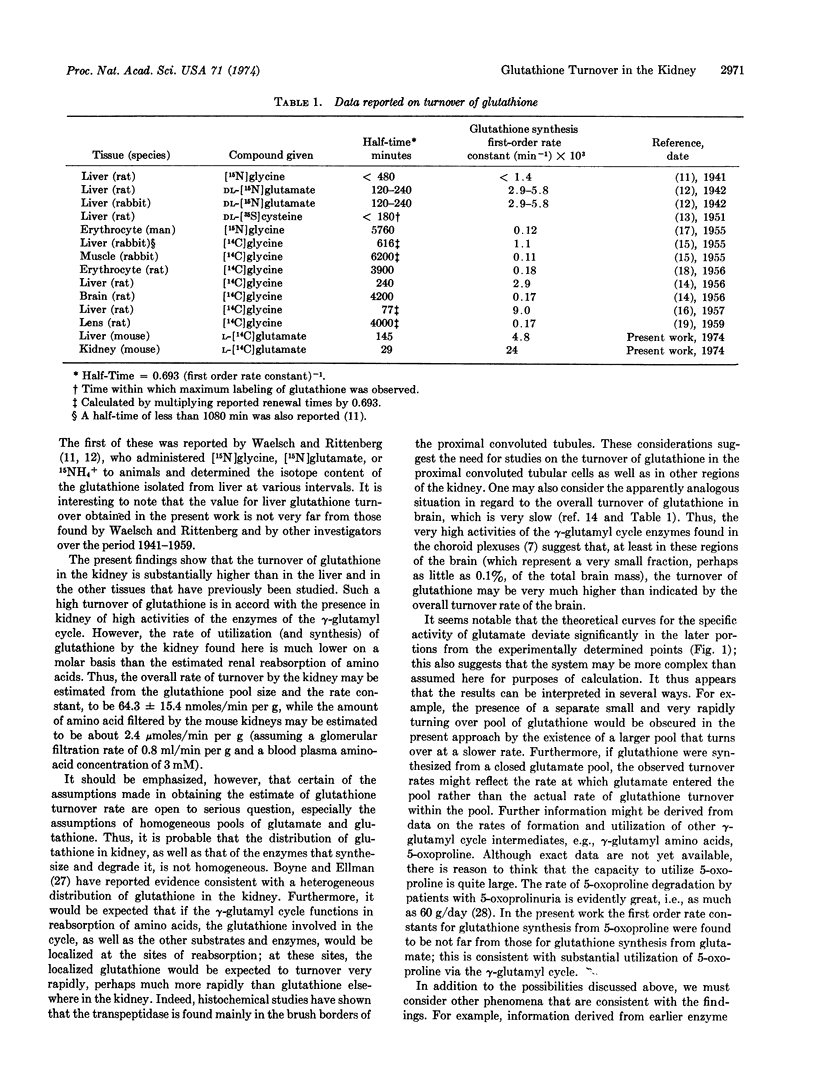
The overall turnover of glutathione in kidney and liver was determined in studies in which L-[14C]glutamate was administered to mice. Turnover was much more rapid (about 5 times greater) in kidney than in liver. Studies were also carried out in which 5-oxo-L-[14C]proline was administered; the first order rate constants for glutathione synthesis from 5-oxoproline in liver and kidney were not far from those found for synthesis of glutathione from glutamate in these tissues. The findings are in accord with the fact that the activities of the enzymes of the γ-glutamyl cycle are much higher in kidney than in liver. The findings of high turnover of glutathione in kidney and the rapid utilization of 5-oxoproline by this organ for glutathione synthesis are consistent with the function of the γ-glutamyl cycle in vivo and the proposed role of γ-glutamyl derivatives in amino-acid transport.
Keywords: 5-oxoproline, pyrrolidone carboxylate, pyroglutamate, γ-glutamyl amino acids, γ-glutamyl-cysteine
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON E. I., MOSHER W. A. Incorporation of S35 from DL-cystine into glutathione and protein in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):717–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyne A. F., Ellman G. L. A methodology for analysis of tissue sulfhydryl components. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):639–653. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIMANT E., LANDSBERG E., LONDON I. M. The metabolic behavior of reduced glutathione in human and avian erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1955 Apr;213(2):769–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS G. W., MORTENSEN R. A. The rate of metabolism of brain and liver glutathione in the rat studied with C14-glycine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Oct;222(2):581–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman G. L., Lysko H. Disulfide and sulfhydryl compounds in TCA extracts of human blood and plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Sep;70(3):518–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIQUES O. B., HENRIQUES S. B., NEUBERGER A. Quantitative aspects of glycine metabolism in the rabbit. Biochem J. 1955 Jul;60(3):409–424. doi: 10.1042/bj0600409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIQUES S. B., HENRIQUES O. B., MANDELBAUM F. R. Incorporation of glycine into glutathione and fibrinogen of rats under adrenaline treatment. Biochem J. 1957 Jun;66(2):222–227. doi: 10.1042/bj0660222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTENSEN R. A., HALEY M. I., ELDER H. A. The turnover of erythrocyte glutathione in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):269–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMILLAN P. J., RYERSON S. J., MORTENSEN R. A. The metabolism of lens glutathione studies with glycine-C14. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Mar;81(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. On the enzymology of amino acid transport. Science. 1973 Apr 6;180(4081):33–39. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4081.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Meister A. The gamma-glutamyl cycle: a possible transport system for amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1248–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINER J. M. The study of metabolic turnover rates by means of isotopic tracers. I. Fundamental relations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Sep;46(1):53–79. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINER J. M. The study of metabolic turnover rates by means of isotopic tracers. II. Turnover in a simple reaction system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Sep;46(1):80–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross L. L., Barber L., Tate S. S., Meister A. Enzymes of the gamma-glutamyl cycle in the ciliary body and lens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2211–2214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Ross L. L., Meister A. The -glutamyl cycle in the choroid plexus: its possible function in amino acid transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1447–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Werf P., Stephani R. A., Meister A. Accumulation of 5-oxoproline in mouse tissues after inhibition of 5-oxoprolinase and administration of amino acids: evidence for function of the gamma-glutamyl cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1026–1029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werf P., Orlowski M., Meister A. Enzymatic conversion of 5-oxo-L-proline (L-pyrrolidone carboxylate) to L-glutamate coupled with cleavage of adenosine triphosphate to adenosine diphosphate, a reaction in the -glutamyl cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2982–2985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werf P., Stephani R. A., Orlowski M., Meister A. Inhibition of 5-oxoprolinase by 2-imidazolidone-4-carboxylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):759–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellner V. P., Sekura R., Meister A., Larsson A. Glutathione synthetase deficiency, an inborn error of metabolism involving the gamma-glutamyl cycle in patients with 5-oxoprolinuria (pyroglutamic aciduria). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2505–2509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



