Abstract
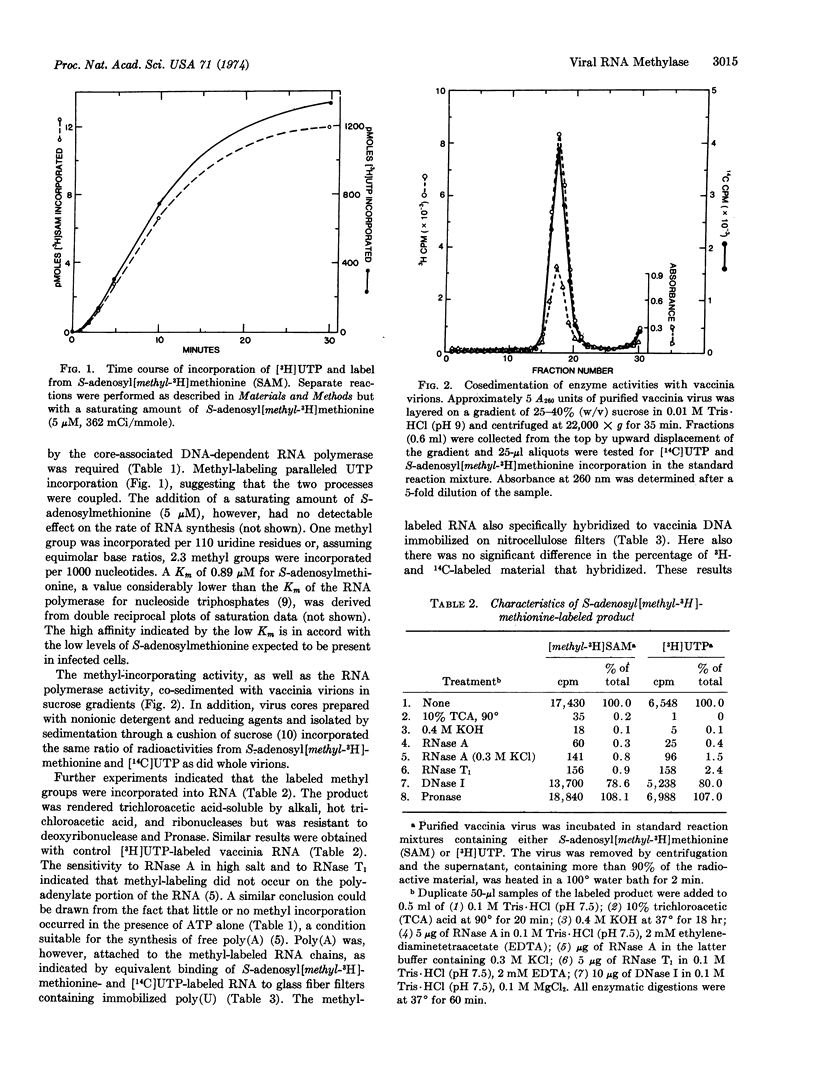
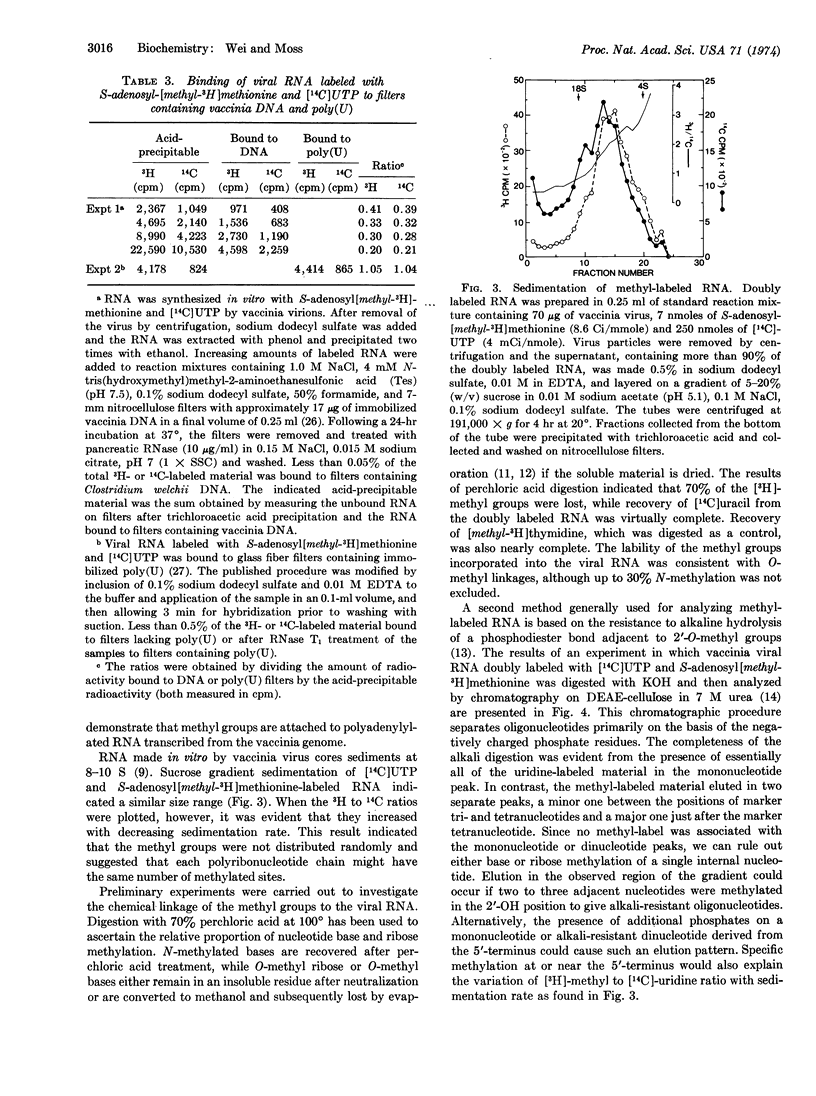
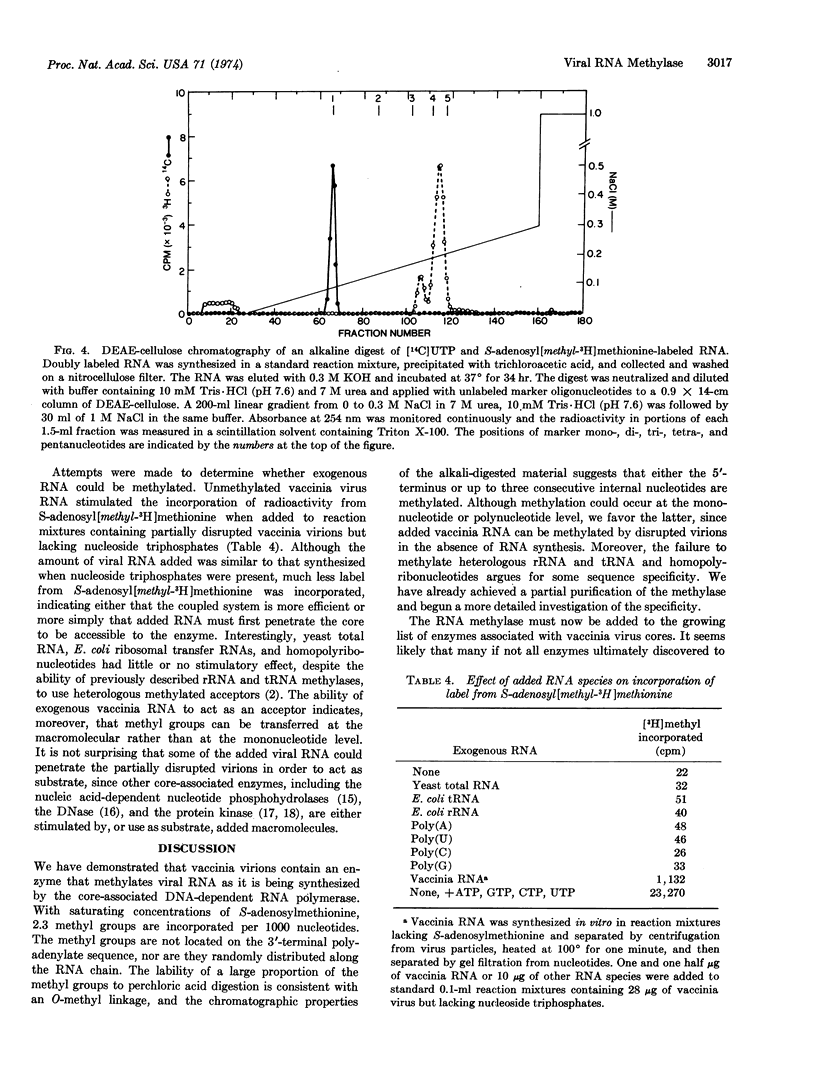
Purified vaccinia virions contain an enzyme that incorporates methyl groups from S-adenosylmethionine into viral RNA synthesized by the core-associated DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. This incorporation, by partially disrupted virions, was dependent on the presence of all four ribonucleoside triphosphates and Mg++ and was inhibited by actinomycin D. At saturation, 2.3 methyl groups were incorporated per 1000 nucleotides. The methyl-labeled RNA product was sensitive to alkali and ribonucleases and hybridized to filters containing immobilized poly(U) or vaccinia DNA. The methyl groups were not located on the 3′-terminal polyadenylate sequence, nor were they randomly distributed along the RNA chain. The lability of a large portion of the methyl groups to perchloric acid digestion was consistent with an O-methyl linkage, and the chromatographic properties of the alkali-digested material suggested that either the 5′-terminus or up to three consecutive internal nucleotides were methylated. Methylation probably occurs at the macromolecular level, since added vaccinia RNA was a suitable substrate. The failure of heterologous rRNA and tRNA species as well as homopolyribonucleotides to act as substrate suggested that a specific sequence might be required.
Keywords: RNA methylase, methyl transferase, S-adenosylmethionine, poxvirus
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskin F., Dekker C. A. A rapid and specific assay for sugar methylation in ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5447–5449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. M., Attardi G. Methylation of nucleic acids in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 26;20(3):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Dorson J. W., Bollum F. J. Terminal riboadenylate transferase: a poly A polymerase in purified vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):203–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.203-208.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The preparation and characteristics of highly purified radioactively labelled poxvirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:290–301. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K., Merigan T. C. Concerning the mechanism of action of interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):558–565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungwirth C., Horak I., Bodo G., Lindner J., Schultze B. The synthesis of poxvirus-specific RNA in interferon-treated cells. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. R., McAuslan B. R. Poxvirus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):134–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J., Beeson J. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in vaccinia virus. I. The mechanism of synthesis and release of RNA in vaccinia cores. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J., Beeson J. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in vaccinia virus. II. Synthesis of polyriboadenylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Moss B. Vaccinia virus structural polypeptide derived from a high-molecular-weight precursor: formation and integration into virus particles. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):717–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.717-726.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman J., Moss B. Protein kinase activity from vaccinia virions: solubilization and separation into heat-labile and heat-stable components. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):684–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.684-689.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Axelrod D. SV40 gene activity during lytic infection and in a series of SV40 transformed mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1203–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz D. H., Esteban M. Interferon inhibits viral protein synthesis in L cells infected with vaccinia virus. Nature. 1972 Aug 18;238(5364):385–388. doi: 10.1038/238385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis by the vaccinia virion. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1028–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1028-1037.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N., Paoletti E. Polyadenylate polymerase from vaccinia virions. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):59–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio245059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Salzman N. P. Sequential protein synthesis following vaccinia virus infection. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1016–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1016-1027.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Paoletti E., Grace J. T., Jr RNA polymerase activity in purified infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2280–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent nucleotide phosphohydrolase activity in purified vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):866–868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.866-868.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Protein kinase and specific phosphate acceptor proteins associated with vaccinia virus cores. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):417–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.417-424.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo B. G., Dales S. Two deoxyribonuclease activities within purified vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):820–827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHATKIN A. J. ACTINOMYCIN D AND VACCINIA VIRUS INFECTION OF HELA CELLS. Nature. 1963 Jul 27;199:357–358. doi: 10.1038/199357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman N. P., Sebring E. D. Sequential formation of vaccinia virus proteins and viral deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.16-23.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Methylated messenger RNA synthesis in vitro by purified reovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3204–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R., Jurale C., Kates J. Detection of polyadenylic acid sequences in viral and eukaryotic RNA(polu(U)-cellulose columns-poly(U) filters-fiberglass-HeLa cells-bacteriophage T4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):417–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



