Abstract
5′-Guanylylimidodiphosphate (Gpp(NH)-p) stimulates adenylate cyclase [ATP-pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing), EC 4.6.1.1] activity in plasma membranes isolated from frog and salmon erythrocytes, from rat adrenal, hepatic, and fat cells, and from bovine thyroid cells. The nucleotide acts cooperatively with the various hormones (glucagon, secretin, ACTH, thyrotropin, and catecholamines) that stimulate these adenylate cyclase systems with resultant activities that equal or exceed those obtained with hormone plus GTP or with fluoride ion. In the absence of hormones, Gpp(NH)p is a considerably more effective activator than GTP, and, under certain conditions of incubation, stimulates rat fat cell adenylate cyclase to levels of activity (about 20 nmoles of 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate mg protein per min) far higher than reported hitherto for any adenylate cyclase system examined. The nucleotide activates frog erythrocyte adenylate cyclase when the catecholamine receptor is blocked by the competitive antagonist, propranolol, and activates the enzyme from an adrenal tumor cell line which lacks functional ACTH receptors. In contrast, Gpp(NH)p does not stimulate adenylate cyclase in extracts from Escherichia coli B. Gpp(NH)p appears to be a useful probe for investigating the mechanism of hormone and nucleotide action on adenylate cyclase systems in eukaryotic cells.
Keywords: hormones, membranes, cyclic AMP, guanine nucleotides, allosteric regulation
Full text
PDF
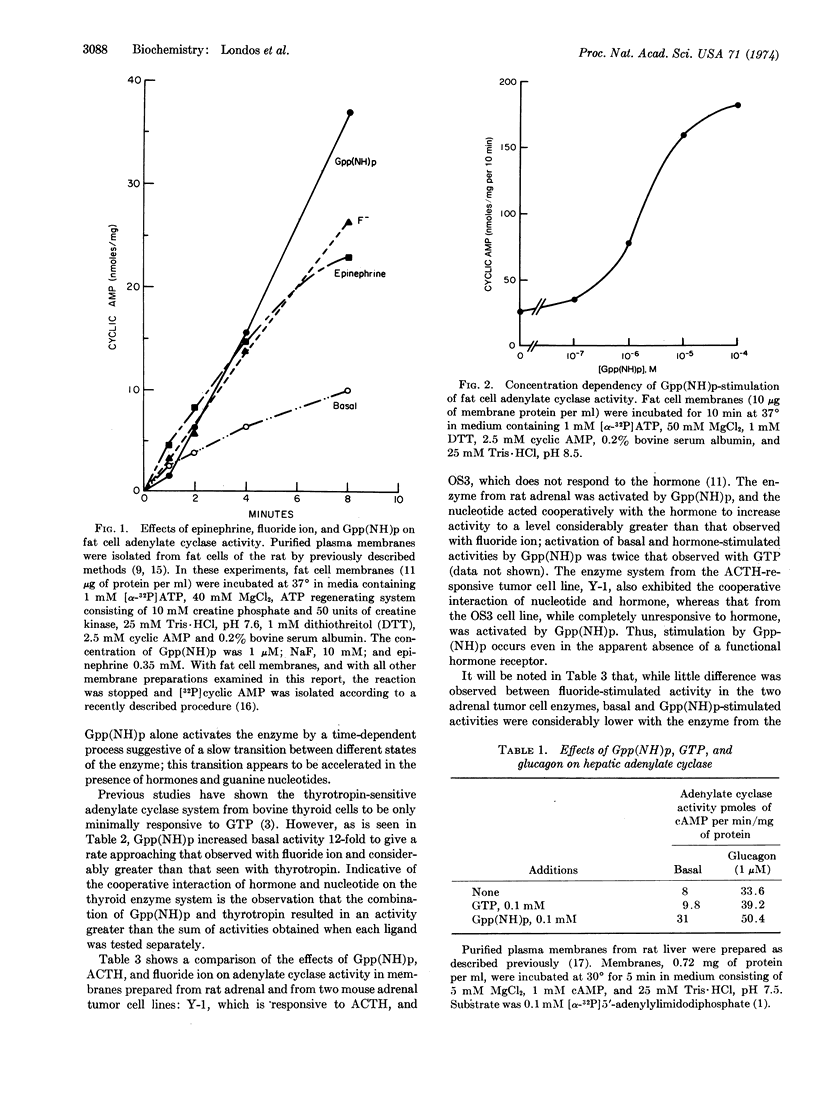
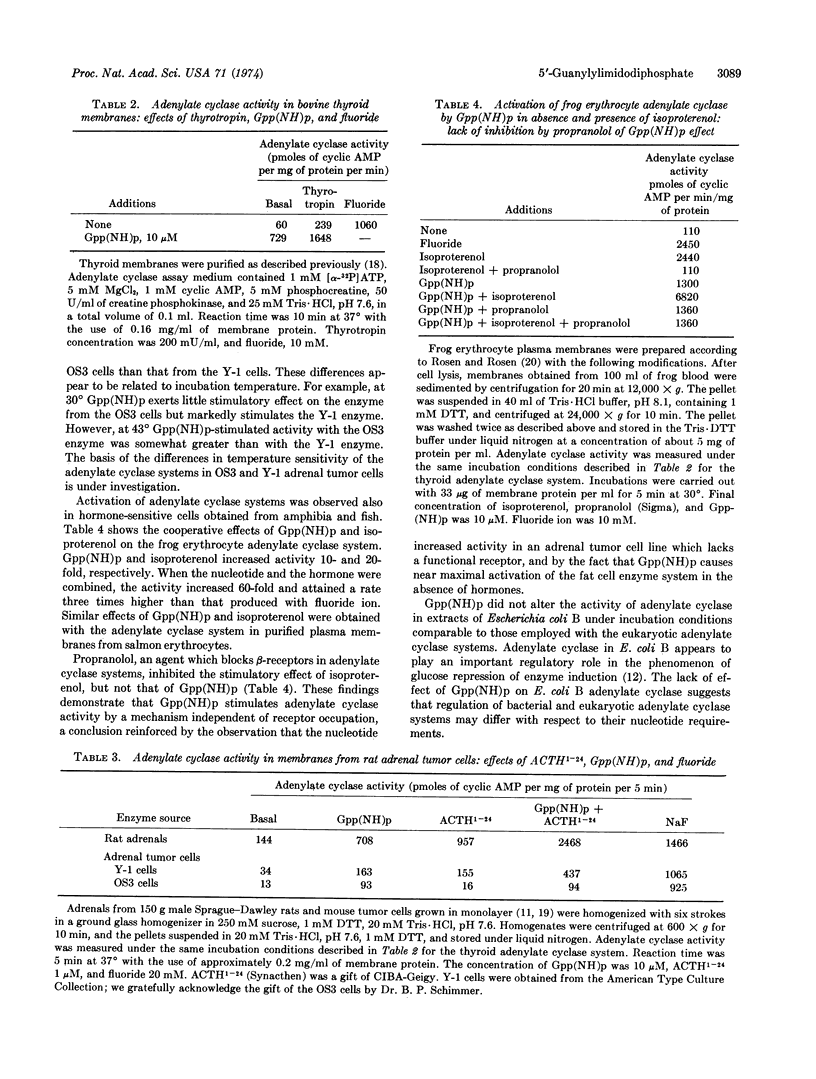

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainslie G. R., Jr, Shill J. P., Neet K. E. Transients and cooperativity. A slow transition model for relating transients and cooperative kinetics of enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7088–7096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Roy C., Jard S. Oxytocin-sensitive adenylate cyclase in frog bladder epithelial cells. Role of calcium, nucleotides, and other factors in hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7073–7081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C. Kinetic aspects of regulation of metabolic processes. The hysteretic enzyme concept. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5788–5799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Birnbaumer L. Glucagon receptors in -cells. Binding of 125 I-glucagon and activation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1211–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. P., Löw H., Rodbell M. Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of guanyl nucleotides on fat cell adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6239–6245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Harwood J. P. Requirement for guanosine triphosphate in the prostaglandin activation of adenylate cyclase of platelet membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2253–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leray F., Chambaut A. M., Hanoune J. Role of GTP in epinephrine and glucagon activation of adenyl cyclase of liver plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1385–1391. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90866-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in bacteria. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):339–344. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Krans H. M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. V. An obligatory role of guanylnucleotides in glucagon action. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1877–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Lin M. C., Salomon Y. Evidence for interdependent action of glucagon and nucleotides on the hepatic adenylate cyclase system. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Rosen S. M. Properties of an adenyl cyclase partially purified from frog erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 May;131(2):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmer B. P. Adenylate cyclase activity in adrenocorticotropic hormone-sensitive and mutant adrenocortical tumor cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3134–3138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H. Activation of thyroid membrane adenylate cyclase by purine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Jones A. B. The purification of bovine thyroid plasma membranes and the properties of membrane-bound adenyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3939–3947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Temple R., Cook G. H. Stimulation of steroid secretion in adrenal tumor cells by choleragen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2741–2744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount R. G., Babcock D., Ballantyne W., Ojala D. Adenylyl imidodiphosphate, an adenosine triphosphate analog containing a P--N--P linkage. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2484–2489. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


