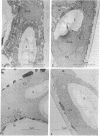
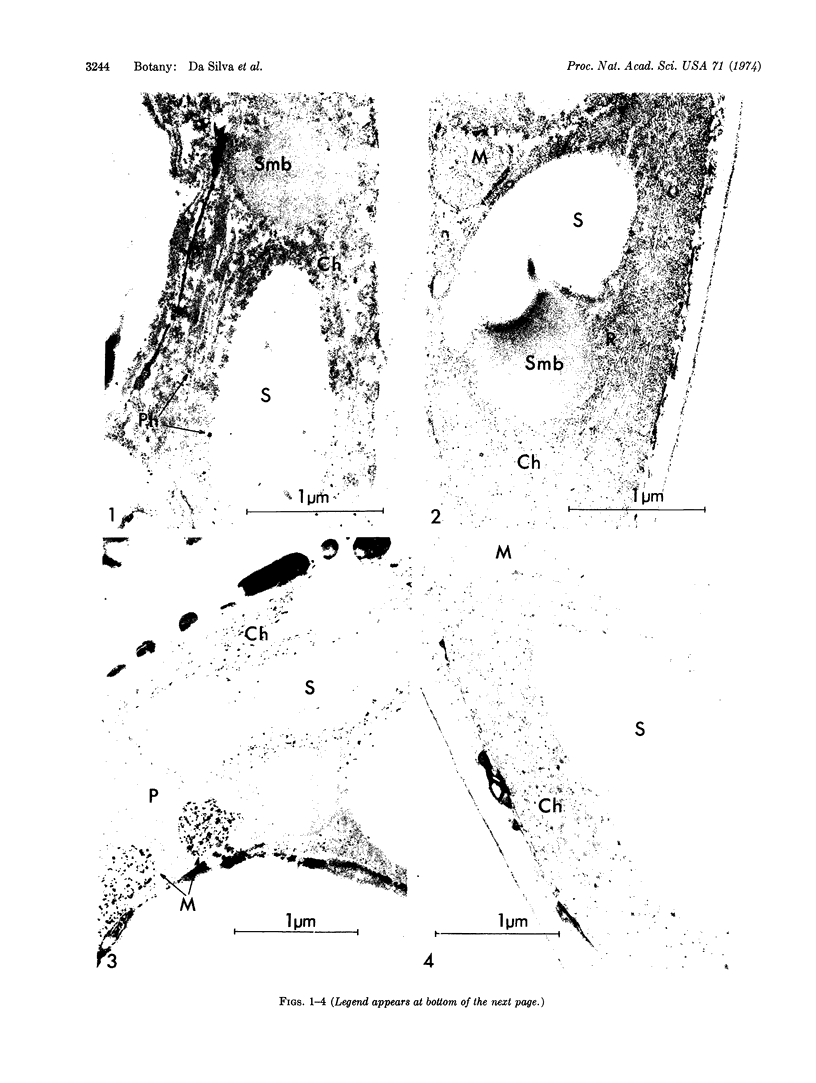
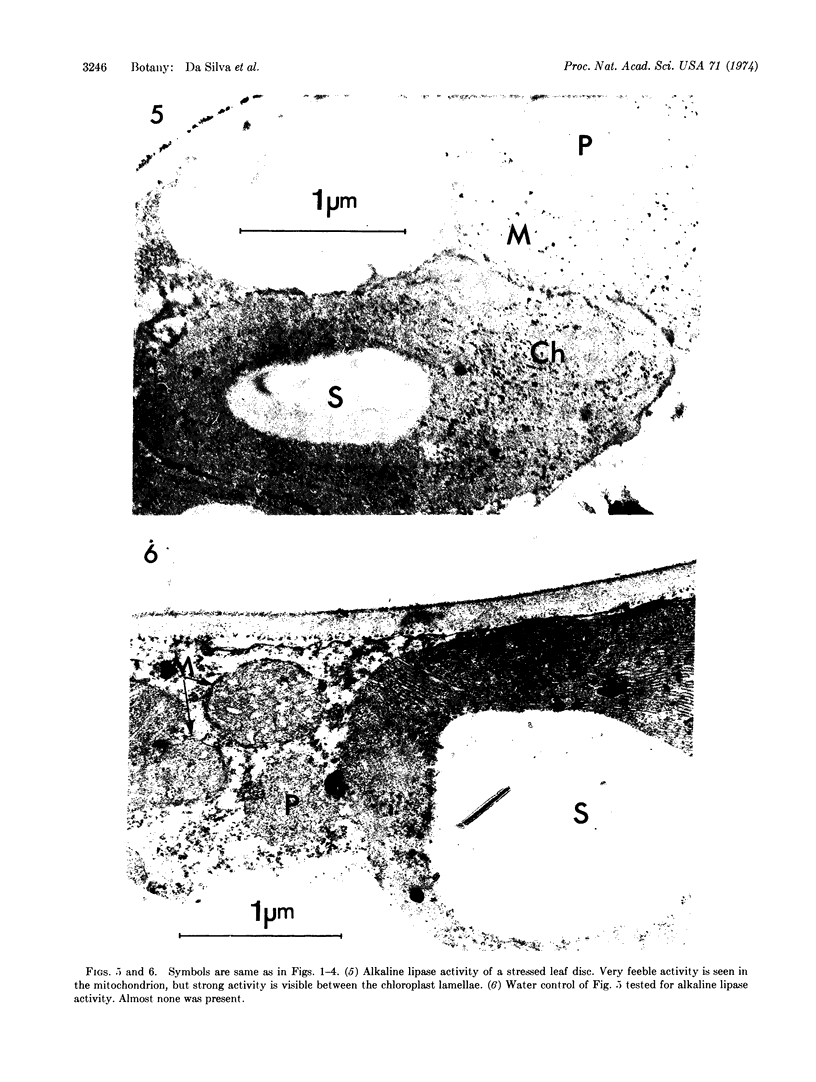
Abstract
Water stress induced by floating discs cut from cotton leaves (Gossypium hirsutum L. cultivar Stoneville) on a polyethylene glycol solution (water potential, -10 bars) was associated with marked alteration of ultrastructural organization of both chloroplasts and mitochondria. Ultrastructural organization of chloroplasts was sometimes almost completely destroyed; peroxisomes seemed not to be affected; and chloroplast ribosomes disappeared. Also accompanying water stress was a sharp increase in activity of acid phosphatase [orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (acid optimum), EC 3.1.3.2], and acid and alkaline lipase [glycerol ester hydrolase EC 3.1.1.3] within chloroplasts. Only acid lipase activity was detected inside mitochondria of stressed discs. These alterations in cell organization and enzymology may account for at least part of the previously reported effects of water stress on the CO2 compensation point, photochemical reactions, and photorespiration.
Keywords: acid phosphatase, acid lipase, alkaline lipase
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bamberger E. S., Park R. B. Effect of hydrolytic enzymes on the photosynthetic efficiency and morphology of chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1966 Dec;41(10):1591–1600. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.10.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. S., Bowen B. L. Inhibition of oxygen evolution in chloroplasts isolated from leaves with low water potentials. Plant Physiol. 1970 May;45(5):612–615. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.5.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. L., Okayama S. The photoreduction of C-550 in chloroplasts and its inhibition by lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 6;245(1):237–239. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champigny M. L., Miginiac-Maslow M. Relations entre l'assimilation photosynthétique de CO 2 et la photophosphorylation des chloroplastes isolés. I. Stimulation de la fixation de CO 2 par l'antimycine A, antagoniste de son inhibition par le phosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 15;234(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D., Sarid S., Katchalski E. The role of water stress in the inactivation of messenger RNA of germinating wheat embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1378–1383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantopoulos G., Kenyon C. N. Release of free fatty acids and loss of hill activity by aging spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1968 Apr;43(4):531–536. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.4.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry K. E. Some factors affecting the Hill reaction activity in cotton chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1970 Apr;45(4):465–469. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.4.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON J. S., TREVELYAN W. E. PHOSPHOLIPID BREAKDOWN IN BAKER'S YEAST DURING DRYING. Nature. 1963 Dec 21;200:1189–1190. doi: 10.1038/2001189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao T. C. Rapid Changes in Levels of Polyribosomes in Zea mays in Response to Water Stress. Plant Physiol. 1970 Aug;46(2):281–285. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantai K. E. Some effects of hydrolytic enzymes on coupled and uncoupled electron flow in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1970 May;45(5):563–566. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.5.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty R. E., Jagendorf A. T. Chloroplast damage due to enzymatic hydrolysis of endogenous lipids. Plant Physiol. 1965 Jul;40(4):725–735. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B. E. Carbowax 6000 compared with mannitol as a suppressant of cucumber hypocotyl elongation. Plant Physiol. 1970 Apr;45(4):507–509. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Bell D. T., Koeppe D. E. The effects of water stress on some membrane characteristics of corn mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1971 Aug;48(2):229–231. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata F., Yokota S., Nagata T. Electron microscopic demonstration of lipase in the pancreatic acinar cells of mice. Histochemie. 1968 May 7;13(3):215–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00303755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Murata F. Supplemental studies on the method for electron microscopic demonstration of lipase in the pancreatic acinar cells of mice and rats. Histochemie. 1972;29(1):8–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00305696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegenthaler P. A. Aging of the photosynthetic apparatus. IV. Similarity between the effects of aging and unsaturated fatty acids on isolated spinach chloroplasts as expressed by volume changes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 17;275(2):182–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]