Abstract
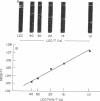
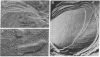
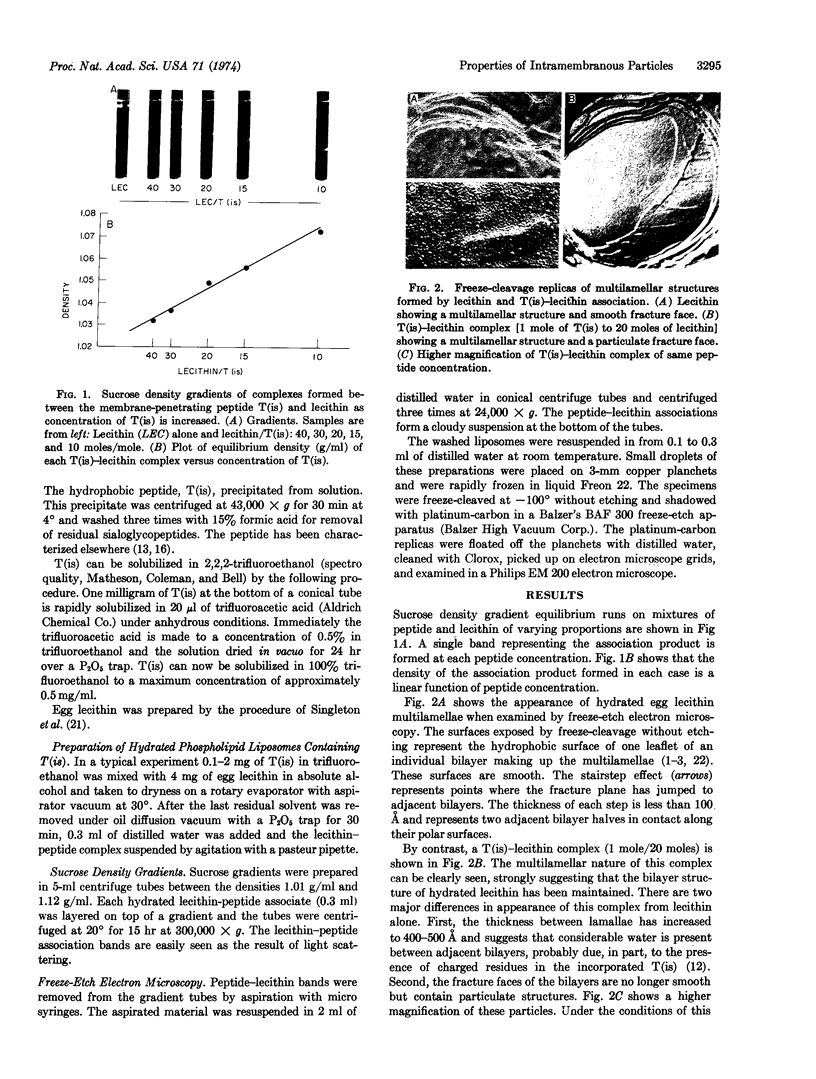
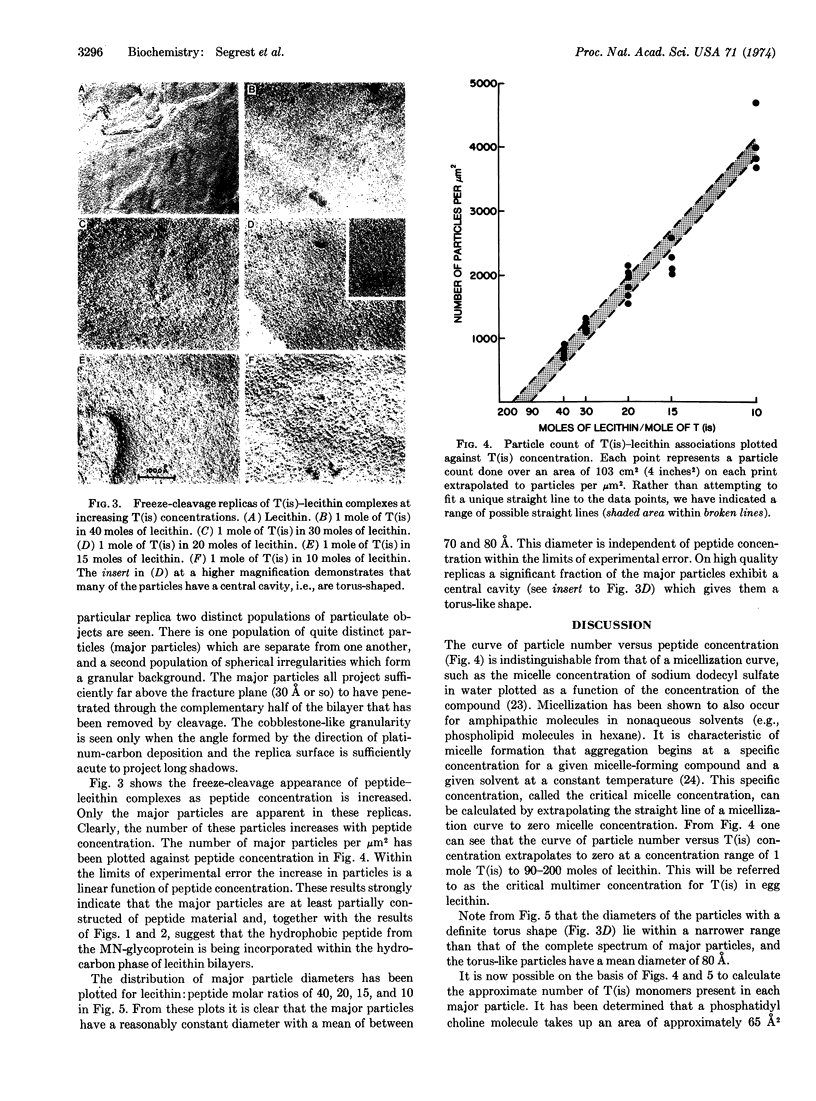
The membrane-penetrating segment of the surface MN-glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte is contained intact within the tryptic peptide T(is). We report here on the association of this peptide with hydrated phospholipid vesicles. Under these conditions 80 Å intramembranous particles, as seen by freeze-etch electron microscopy, are produced that are similar in size to those seen in the native erythrocyte membrane. These particles increase in number as a linear function of T(is) concentration and a plot of particle number versus concentration is compatible with a micelle-like phenomenon; from this curve the critical concentration for the formation of particles is estimated to be approximately one mole of T(is) to 120 moles of lecithin. These data suggest that the membrane-penetrating peptide T(is) is being incorporated, monomerically and multimerically, within the hydrocarbon phase of lecithin bilayers.
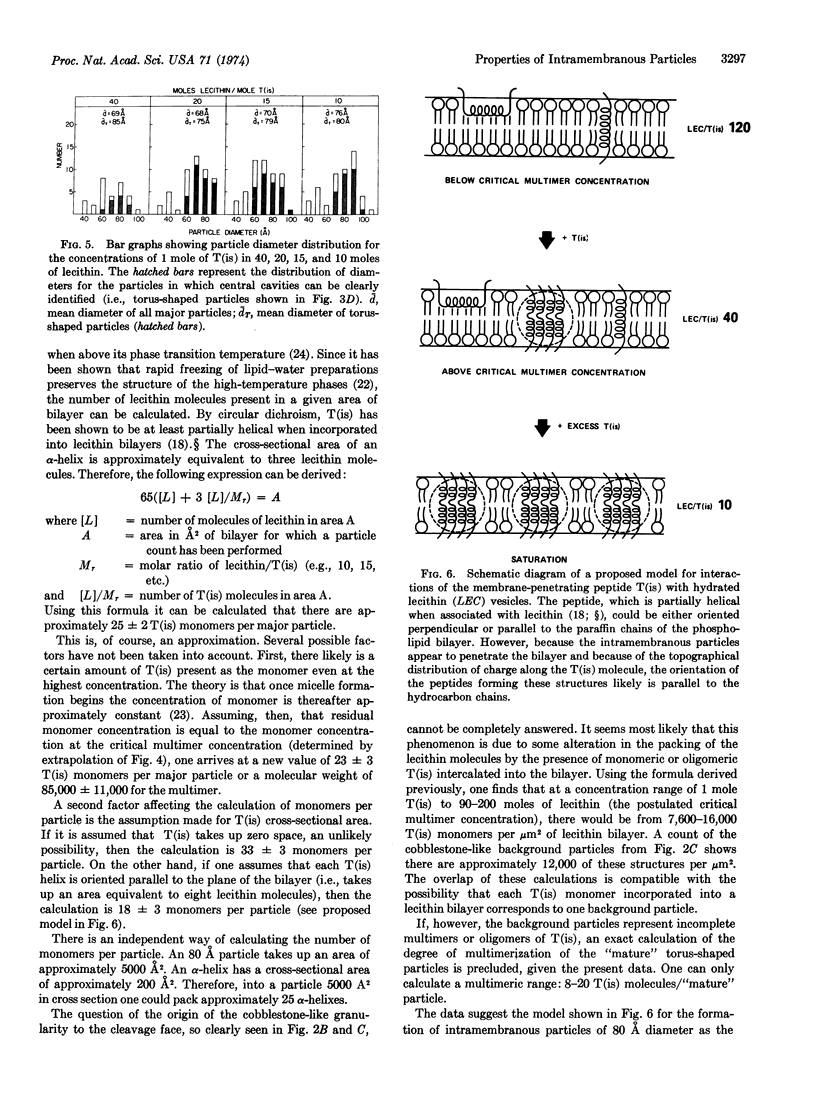
From these data it can be calculated that each intramembranous particle contains between 10 and 20 T(is) monomers. The peptide portion of each particle, therefore, has a molecular weight of 45,000-85,000.
An exact analogy cannot be drawn at this time between the in vivo structure of erythrocyte intramembranous particles and the reconstituted particles described here, although an argument has been constructed to support this possibility. What is clear is that the reconstituted system promises to be useful for further examination of protein-lipid interactions in membranes.
Keywords: electron microscopy, protein-lipid interactions, protein-protein interactions, liposomes, micelles
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blasie J. K. The location of photopigment molecules in the cross-section of frog retinal receptor disk membranes. Biophys J. 1972 Feb;12(2):191–204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86079-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D. Fracture faces of frozen membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1048–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Major human erythrocyte glycoprotein spans the cell membrane. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):229–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio231229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Leonard R., Tardieu A., Branton D. Lamellar and hexagonal lipid phases visualized by freeze-etching. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;219(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Hubbell W. L. Preparation and properties of phospholipid bilayers containing rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2617–2621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Kahane I., Marchesi V. T. Studies on the major sialoglycoprotein of the human red cell membrane. Isolation and characterization of tryptic glycopeptides. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3131–3138. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R., Branton D. Lipid- and temperature-dependent structural changes in Acholeplasma laidlawii cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 25;323(3):378–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kant J. A., Steck T. L. Cation-impermeable inside-out and right-side-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 1;240(96):26–28. doi: 10.1038/newbio240026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Andrews E. P. Glycoproteins: isolation from cellmembranes with lithium diiodosalicylate. Science. 1971 Dec 17;174(4015):1247–1248. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4015.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Tillack T. W., Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Scott R. E. Chemical characterization and surface orientation of the major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Perrelet A. Membrane-associated particles: increase at sites of pinocytosis demonstrated by freeze-etching. Science. 1973 Aug 31;181(4102):868–869. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4102.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Branton D. Membrane splitting in freeze-ethching. Covalently bound ferritin as a membrane marker. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):598–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Carter R. L., Kidwell W. R. Structural changes in memebranes of synchronized cells demonstrated by freeze-cleavage. Nature. 1971 Oct 13;233(5320):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Marchesi V. T. Structural changes in membranes of transformed lymphocytes demonstrated by freeze-etching. Cell Immunol. 1972 Feb;3(2):301–317. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Marchesi V. T., Guyer R. B., Terry W. Red cell membrane glycoprotein: amino acid sequence of an intramembranous region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):964–969. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Kahane I., Jackson R. L., Marchesi V. T. Major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane: evidence for an amphipathic molecular structure. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):167–183. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillack T. W., Marchesi V. T. Demonstration of the outer surface of freeze-etched red blood cell membranes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):649–653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillack T. W., Scott R. E., Marchesi V. T. The structure of erythrocyte membranes studied by freeze-etching. II. Localization of receptors for phytohemagglutinin and influenza virus to the intramembranous particles. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1209–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]