Abstract
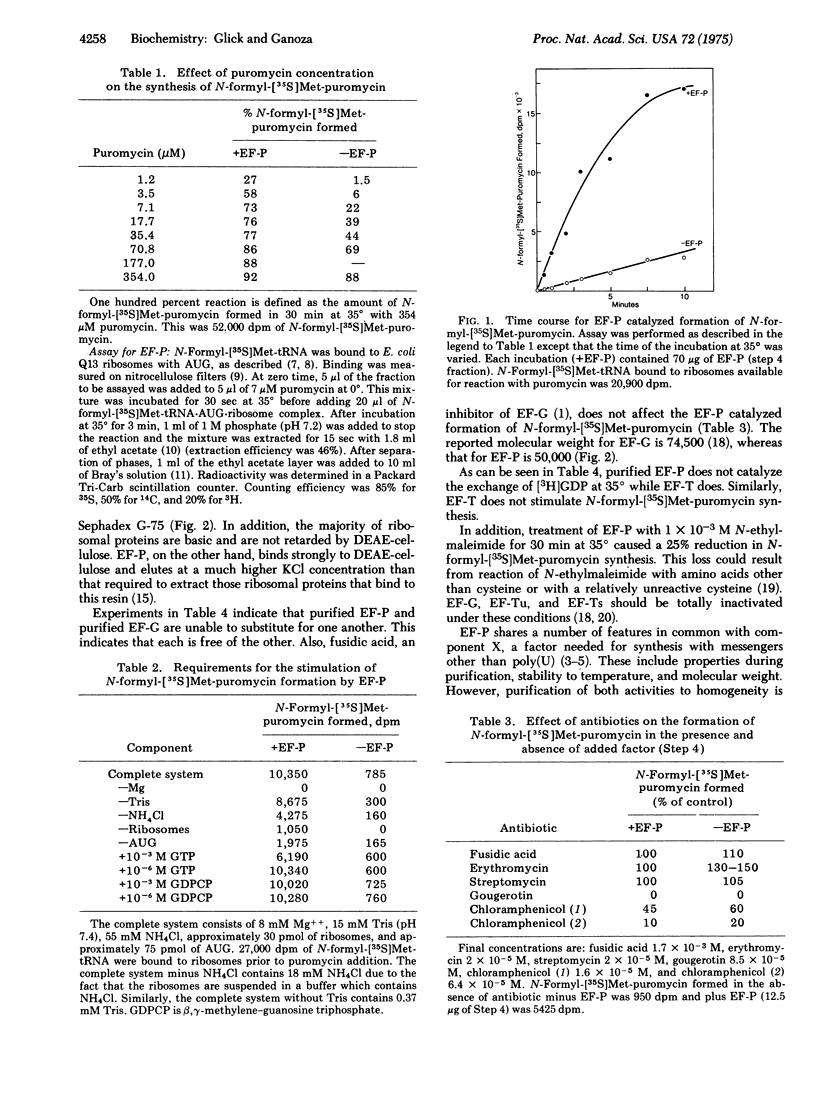
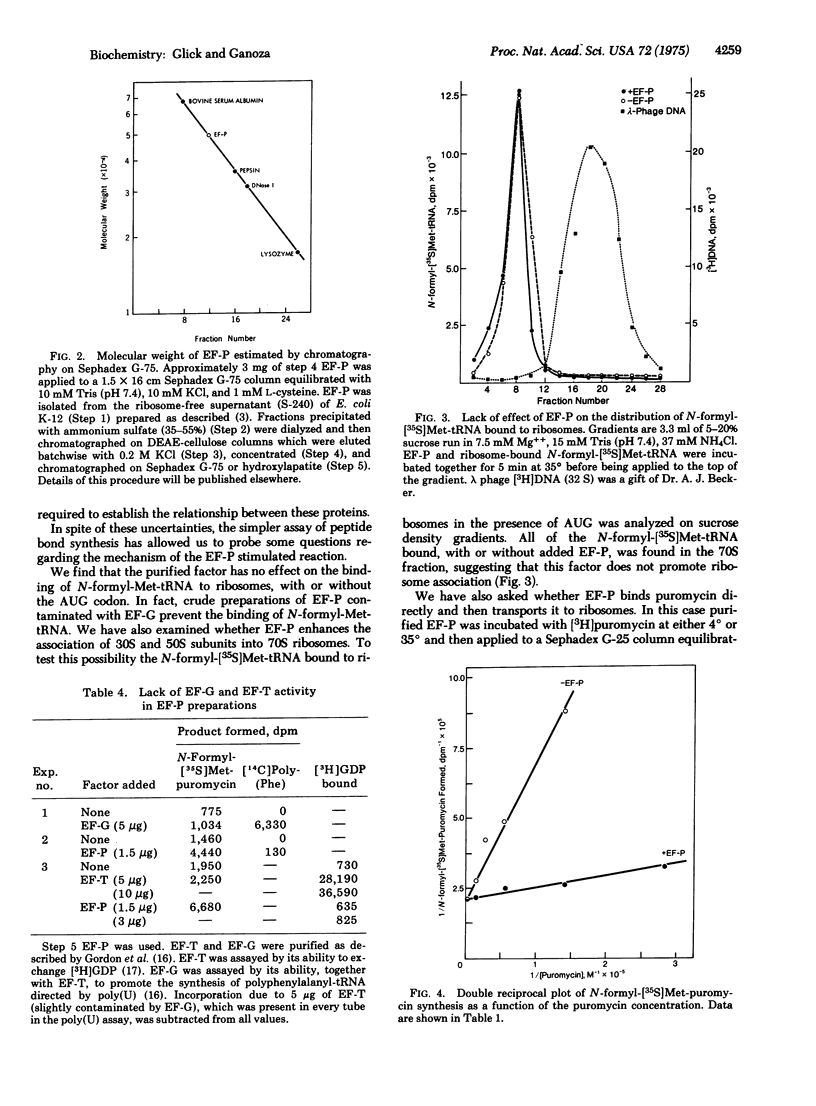
A soluble protein factor was isolated, free of elongation factor (EF)-T and EF-G, based on its ability to stimulate the synthesis of peptide bonds using ribosomal bound 70S-AUG-N-formyl-[35S]methionyl-tRNA complex and added puromycin as substrates. Over 90% of this activity was found in the ribosome-free cytoplasm of Escherichia coli extracts. Otherfeatures such as molecular weight, purification properties, and catalytic activities distinguish this factor from ribosomal proteins and known activators of translation. The factor requires all components needed for peptide bond synthesis and is inhibited by antibiotics known to specifically block the peptidyl transferase activity of ribosomes. The factor increases the binding affinity of the ribosome for the aminoacyl-tRNA analog puromycin about 10-fold. We suggest that this extraribosomal factor modulates the intrinsic activity of ribosomes to catalyze peptide-bond synthesis, and regard it as a new factor required for peptide chain elongation, which we call EF-P.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fahnestock S., Neumann H., Shashoua V., Rich A. Ribosome-catalyzed ester formation. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 9;9(12):2477–2483. doi: 10.1021/bi00814a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Barraclough N. Isolation of a factor that stimulates cleavage of ribosomal bound N-acetyl or N-formyl methionyl tRNA-Met. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Fox J. L. Isolation of a soluble factor needed for protein synthesis with various messenger ribonucleic acids other than poly(U). J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1037–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. P., Ghosh K., Ganoza M. C. Mechanism of polypeptide chain termination. Translation of tandem amber termination codons by an amber suppressor transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5322–5326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick R. B., Brubacher L. J. The reaction between N-ethylmaleimide and ribosomes. A re-examination of some common assumptions. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):319–321. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haralson M. A., Spremulli L. L., Shive W., Ravel J. M. Occurrence of initiation factor 2 in the postribosomal fraction and identification of an initiation inhibitor as elongation factor G. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Ono M., Yamamoto M., Endo H., Kamiya T. Elongation factor T altered in a temperature-sensitive Escherichia coli mutant. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 25;244(134):107–109. doi: 10.1038/newbio244107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Bursztyn H. Initiation of protein synthesis II. A convenient assay for the ribosome-dependent synthesis of N-formyl-C14-methionylpuromycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Lee H., Ochoa S. Inhibition of polypeptide chain initiation in Escherichia coli by elongation factor G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2928–2931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Hachmann J., Weissbach H. The reactions of the sulfhydryl groups on the elongation factors Tu and Ts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90460-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Zamir A. Enhancement of peptidyl transferase activity by antibiotics acting on the 50 S ribosomal subunit. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 25;87(1):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90564-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Marcker K. A. Ribosome-catalysed reaction of puromycin with a formylmethionine-containing oligonucleotide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Staehelin T., Celma M. L., Vazquez D. The peptidyl transferase activity of ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:357–368. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Peptidyl-puromycin synthesis on polyribosomes from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):624–628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. VI. Oligopeptide synthesis and translocation on ribosomes in the presence and absence of soluble transfer factors. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1533–1539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocchini-Valentini G. P., Felicetti L., Rinaldi G. M. Mutants of Escherichia coli blocked in protein synthesis: mutants with an altered G factor. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:463–468. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



