Abstract
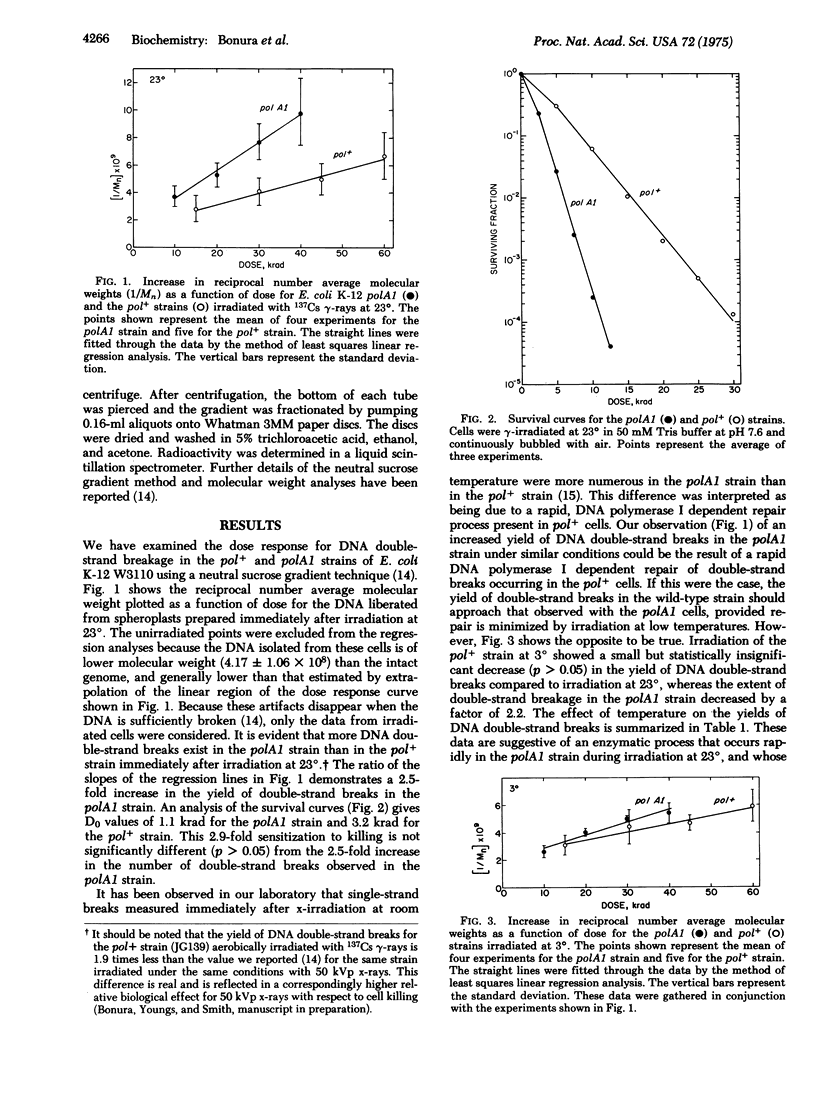
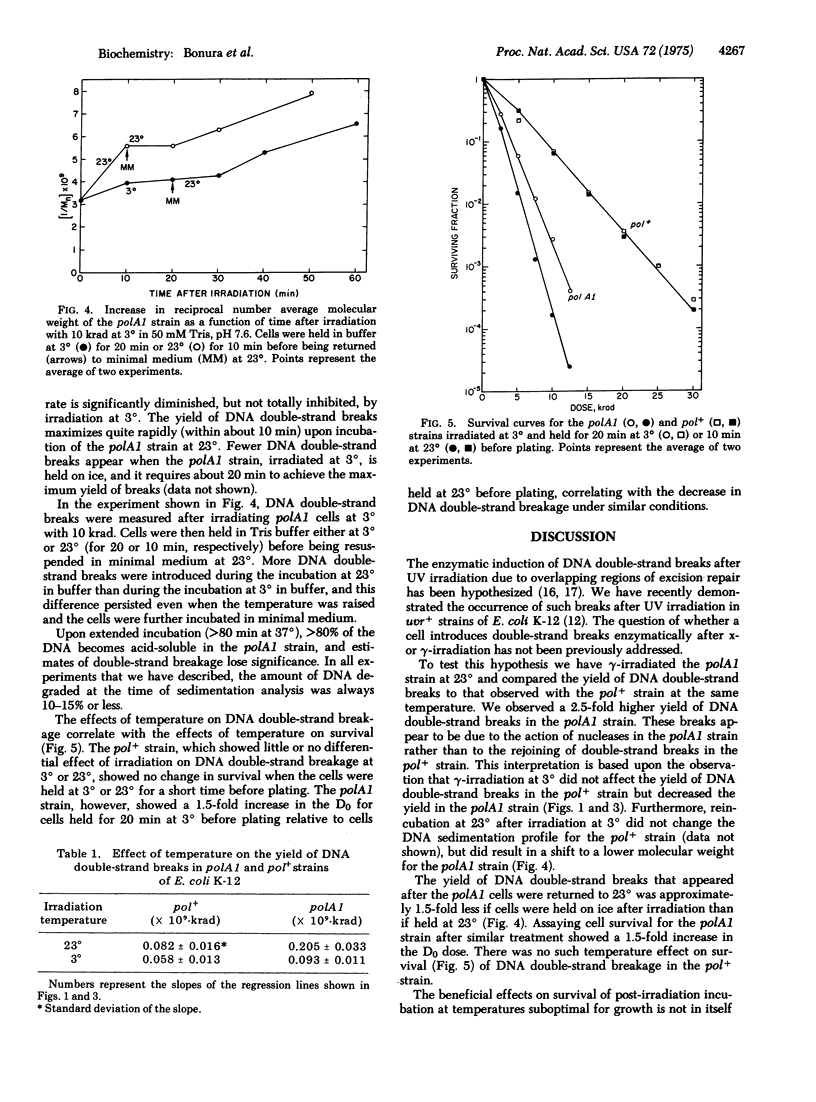
The polA1 mutation increases the sensitivity of E. coli K-12 by killing by gamma-irradiation in air by a factor of 2.9 and increases the yield of DNA double-strand breaks by a factor of 2.5. These additional DNA double-strand breaks appear to be due to the action of nucleases in the polA1 strain rather than to the rejoining of radiation-induced double-strand breaks in the pol+ strain. This conclusion is based upon the observation that gamma-irradiation at 3 degrees did not affect the yield of DNA double-strand breaks in the pol+ strain, but decreased the yield in the polA1 strain by a factor of 2.2. Irradiation of the polA1 strain at 3 degrees followed by incubation at 3 degrees for 20 min before plating resulted in approximately a 1.5-fold increase in the D0. The yield of DNA double-strand breaks was reduced by a factor of 1.5. The pol+ strain, however, did not show the protective effect of the low temperature incubation upon either survival or DNA double-strand breakage. We suggest that the increased yield of DNA double-strand breaks in the polA1 strain may be the result of the unsuccessful exision repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA base damage.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonura T., Smith K. C. Enzymatic production of deoxyribonucleic acid double-strand breaks after ultraviolet irradiation of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):511–517. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.511-517.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonura T., Town C. D., Smith K. C., Kaplan H. S. The influence of oxygen on the yield of DNA double-strand breaks in x-irradiated Escherichia coli K-12. Radiat Res. 1975 Sep;63(3):567–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrell A. D., Feldschreiber P., Dean C. J. DNA-membrane association and the repair of double breaks in x-irradiated Micrococcus radiodurans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 30;247(1):38–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90805-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. K., Hanawalt P. C. Role of DNA polymerase I and the rec system in excision-repair in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1156–1160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry P. M., Cole A. Double strand rejoining in mammalian DNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 26;245(143):100–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugle D. L., Dugle J. R. Gamma-ray induced strand breakage of Bacillus subtilis DNA irradiated in vivo. Can J Microbiol. 1971 May;17(5):575–583. doi: 10.1139/m71-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan A. K., Smith K. C. Dark recovery processes in Escherichia coli irradiated with ultraviolet light. I. Effect of rec mutations on liquid holding recovery. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):365–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.365-373.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan P. V., Cerutti P. A. Excision of damaged thymine residues from gamma-irradiated poly(dA-dT) by crude extracts of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3532–3536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan P. V., Cerutti P. A. Formation and repair of gamma-ray induced thymine damage in Micrococcus radiodurans. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):65–81. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan P. V., Hutchinson F. Neutral sucrose gradient sedimentation of very large DNA from Bacillus subtilis. II. Double-strand breaks formed by gamma ray irradiation of the cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 15;75(3):479–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90455-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harm W. Effects of dose fractionation on ultraviolet survival of Escherichia coli. Photochem Photobiol. 1968 Jan;7(1):73–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1968.tb05831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner L., Hanawalt P. Repair deficiency in a bacterial mutant defective in DNA polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 8;39(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90770-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. DNA-strand scission and loss of viability after x irradiation of normal and sensitized bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama S., Matsuyama A. Possibility of the repair of double-strand scissions in Micrococcus radiodurans DNA caused by gamma-rays. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Nov 8;33(3):418–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90588-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett J. T., Caldwell I., Little J. G. Repair of x-ray damage to the DNA in Micrococcus radiodurans: the effect of 5-bromodeoxyuridine. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):395–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson M. C., Boyle J. M., Setlow R. B. Ultraviolet- and X-ray-induced responses of a deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):61–67. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.61-67.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson M. C., Setlow R. B. Endonucleolytic activity from Micrococcus luteus that acts on -ray-induced damage in plasmid DNA of Escherichia coli minicells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2927–2931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payes B. Enzymatic repair of x-ray-damaged DNA. I. Labeling of the precursor of a malonaldehyde-like material in X-irradiated DNA and the enzymatic excision of labeled lesions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 28;366(3):251–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAPLETON G. E., BILLEN D., HOLLAENDER A. Recovery of x-irradiated bacteria at suboptimal incubation temperatures. J Cell Physiol. 1953 Apr;41(2):345–357. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030410211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Carrier W. L. Endonuclease activity toward DNA irradiated in vitro by gamma rays. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 7;241(110):170–172. doi: 10.1038/newbio241170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinehart J. L., Lin W. S., Cerutti P. A. Gamma-ray induced damage in thymine in mononucleotide mixtures, and in single- and double-stranded DNA. Radiat Res. 1974 May;58(2):166–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town C. D., Smith K. C., Kaplan H. S. DNA polymerase required for rapid repair of x-ray--induced DNA strand breaks in vivo. Science. 1971 May 21;172(3985):851–854. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3985.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins R. J. Does Escherichia coli possess a DNA excision repair system for gamma-ray damage? Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 29;244(139):269–271. doi: 10.1038/newbio244269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngs D. A., Smith K. C. X-ray sensitivity and repair capacity of a polA1 exrA strain of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):121–127. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.121-127.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



