Abstract
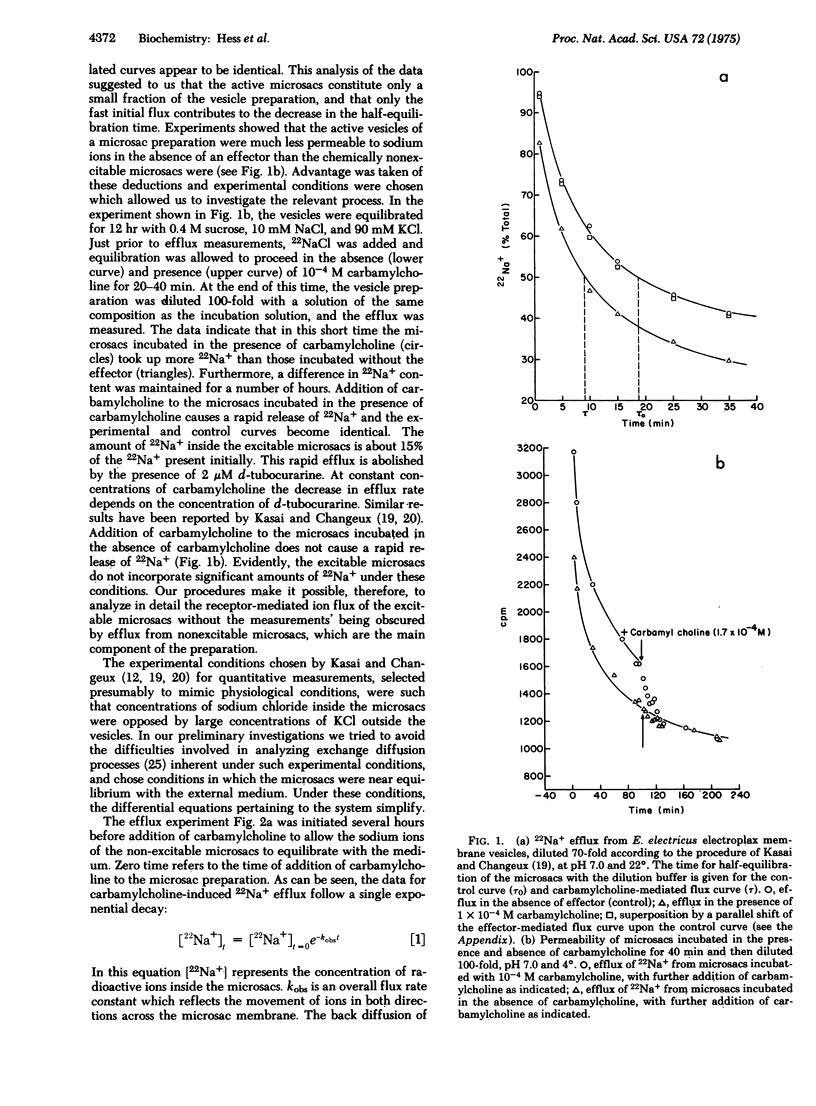
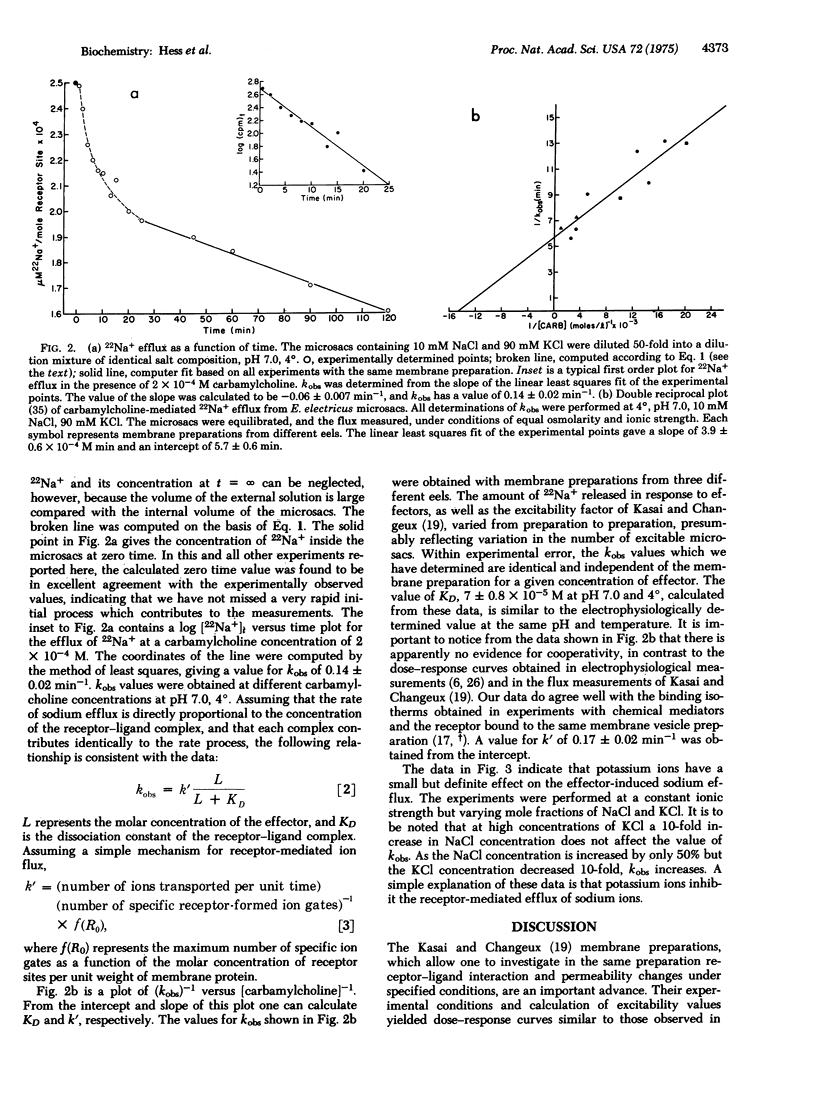
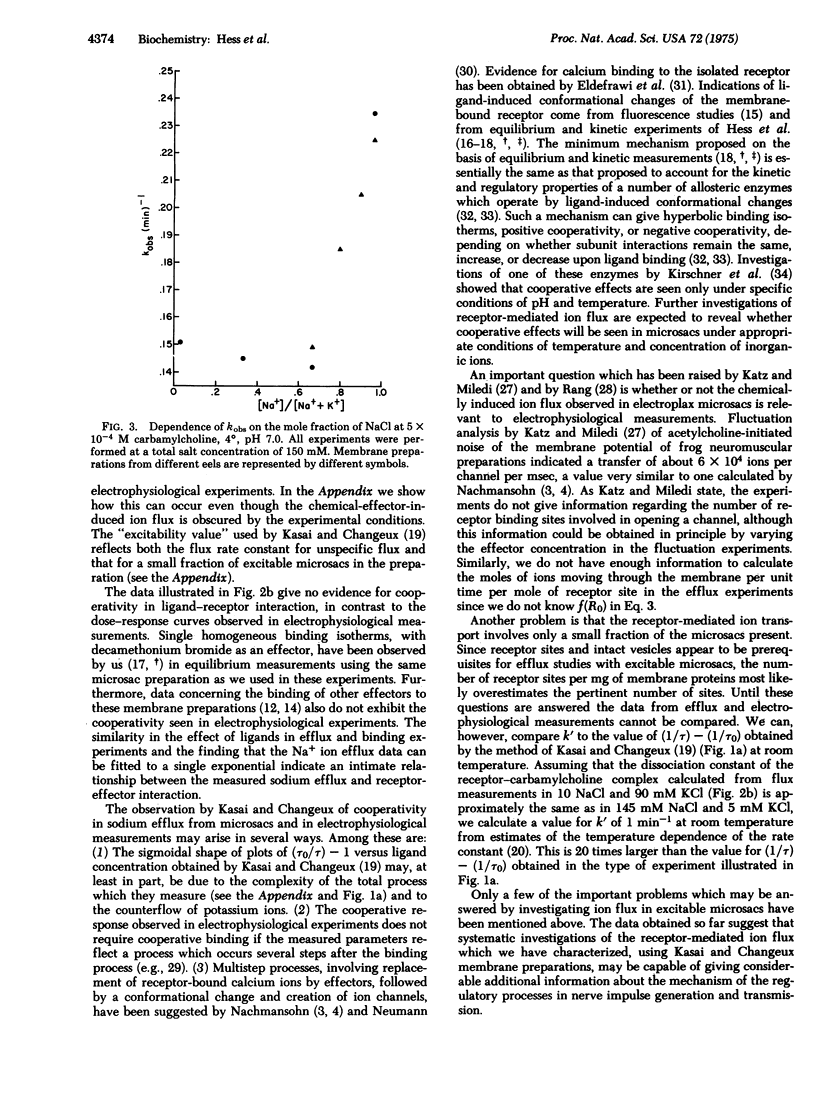
The kinetics of acetylcholine-receptor-mediated sodium efflux from electroplax microsacs of electrophorus electricus has been analyzed. This led to the discovery that only a small fraction of the observed efflux is affected by chemical effectors such as carbamylcholine. Experimental conditions were chosen so that the receptor-mediated flux could be analyzed without the measurements' being obscured by efflux from the nonexcitable microsacs. Near equilibrium the efflux follows a single exponential decay. The apparent first order rate constant for sodium-22 efflux was determined as a function of effector concentration and is considerably higher than previously estimated. The process does not show cooperativity under the experimental conditions, in agreement with the binding isotherms of effectors and the same membrane preparation. The presence of potassium ions inhibits the receptor-mediated sodium flux. It is suggested that interaction of inorganic ions with the receptor may play an important role in the cooperative effects observed in electrophysiological experiments.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biesecker G. Molecular properties of the cholinergic receptor purified from Electrophorus electricus. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4403–4409. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulger J. E., Hess G. P. Evidence for separate initiation and inhibitory sites in the regulation of membrane potential of electroplax. I. Kinetic studies with alpha-bungarotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):677–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W. Purification and characterization of acetylcholine receptor-I from Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2113–2117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Podleski T. R. On the excitability and cooperativity of the electroplax membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):944–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Changeux J. P. Interaction of a fluorescent ligand with membrane-bound cholinergic receptor from Torpedo marmorata. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4855–4864. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefawi M. E., Eldefawi A. T., Penfield L. A., O'Brien R. D., Van Campen D. Binding of calcium and zinc to the acetylcholine receptor purified from Torpedo California. Life Sci. 1975 Mar 15;16(6):925–935. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T., O'Brien R. D. Binding of five cholinergic ligands to housefly brain and Torpedo electroplax. Relationship to acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;7(1):104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J. L., Donner D. B., Hess G. P. Half-of-the-sites reactivity of the membrane-bound Electrophorus electricus acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):1072–1080. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGMAN H. B., PODLESKI T. R., BARTELS E. APPARENT DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS BETWEEN CARBAMYLCHOLINE, DELTA-TUBOCURARINE AND THE RECEPTOR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 24;75:187–193. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90597-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes G. G., Wu C. W. Kinetics of allosteric enzymes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):1–33. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess G. P., Bulger J. E., Fu J. J., Hindy E. F., Silberstein R. J. Allosteric interactions of the membrane-bound acetylcholine reception: kinetic studies with alpha-bungarotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):1018–1027. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Cowburn D. The affinity-labeling of partially purified acetylcholine receptor from electric tissue of Electrophorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3636–3640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner K., Eigen M., Bittman R., Voigt B. The binding of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide to yeast d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: temperature-jump relaxation studies on the mechanism of an allosteric enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1661–1667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klett R. P., Fulpius B. W., Cooper D., Smith M., Reich E., Possani L. D. The acetylcholine receptor. I. Purification and characterization of a macromolecule isolated from Electrophorus electricus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6841–6853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y. Chemistry and pharmacology of polypeptide toxins in snake venoms. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:265–286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. Negative co-operativity in clustered receptors as a possible basis for membrane action. J Theor Biol. 1974 Apr;44(2):367–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(74)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamee M. G., McConnell H. M. Transmembrane potentials and phospholipid flip-flop in excitable membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):2951–2958. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier J. C., Sealock R., Olsen R., Changeux J. P. Purification and properties of the cholinergic receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus electric tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):371–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHMANSOHN D. Metabolism and function of the nerve cell. Harvey Lect. 1953;49:57–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Acetylcholine receptors. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 Jul;7(3):283–399. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOFFENIELS E., NACHMANSOHN D. An isolated single electroplax preparation. I. New data on the effect of acetylcholine and related compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. II. Effect of cholinergic agonists and antagonists on the binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):15–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



