Abstract
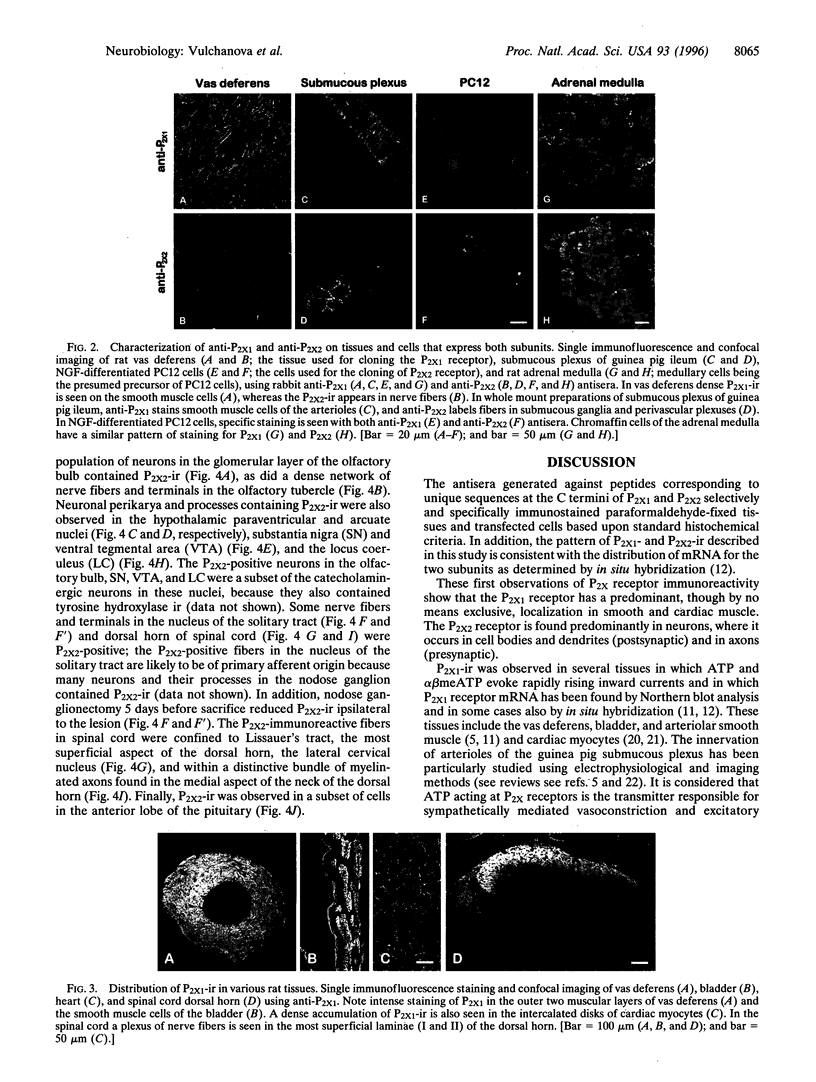
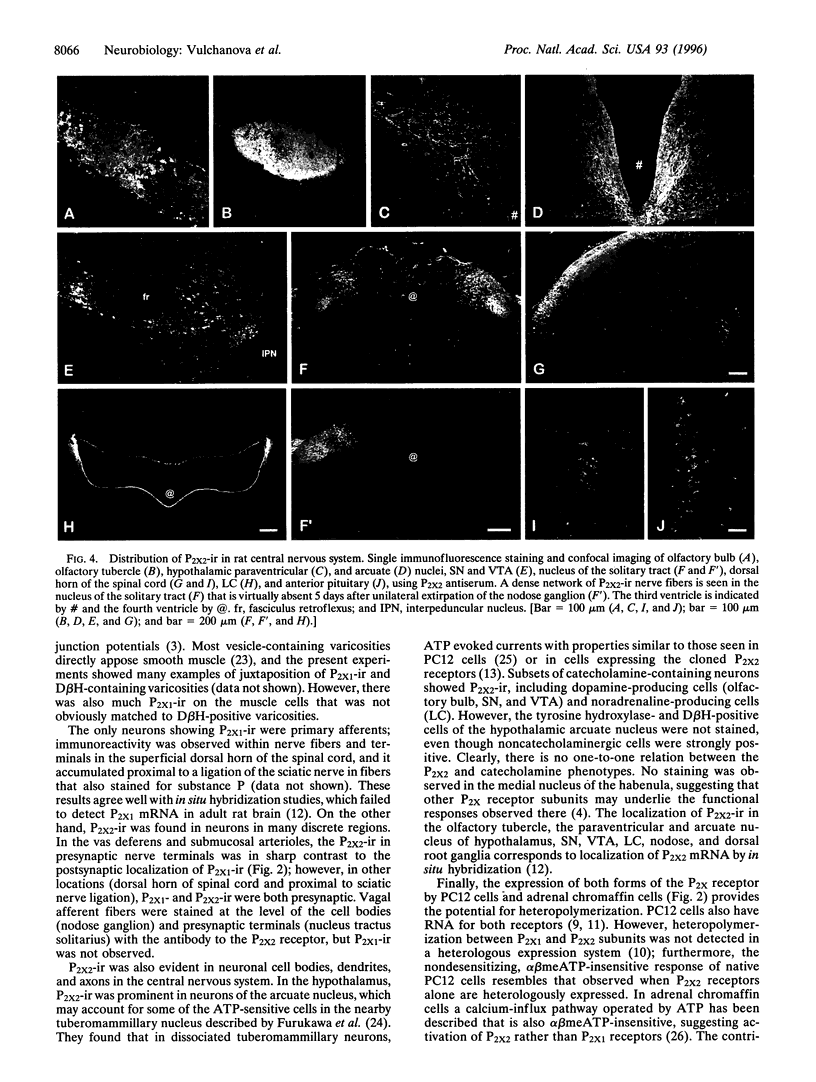
Several P2X receptor subunits were recently cloned; of these, one was cloned from the rat vas deferens (P2X1) and another from pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells differentiated with nerve growth factor (P2X2). Peptides corresponding to the C-terminal portions of the predicted receptor proteins (P2X1 391-399 and P2X2 460-472) were used to generate antisera in rabbits. The specificities of antisera were determined by staining human embryonic kidney cells stably transfected with either P2X1 or P2X2 receptors and by absorption controls with the cognate peptides. In the vas deferens and the ileal submucosa, P2X1 immunoreactivity (ir) was restricted to smooth muscle, whereas P2X2-ir was restricted to neurons and their processes. Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla and PC12 cells contained both P2X1- and P2X2-ir. P2X1-ir was also found in smooth muscle cells of the bladder, cardiac myocytes, and nerve fibers and terminals in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord. In contrast, P2X2-ir was observed in scattered cells of the anterior pituitary, neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate and paraventricular nuclei, and catecholaminergic neurons in the olfactory bulb, the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and locus coeruleus. A plexus of nerve fibers and terminals in the nucleus of the solitary tract contained P2X2-ir. This staining disappeared after nodose ganglionectomy, consistent with a presynaptic function. The location of the P2X1 subunit in smooth muscle is consistent with its role as a postjunctional receptor in autonomic transmission, while in neurons, these receptors appear in both postsynaptic and presynaptic locations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidsson U., Riedl M., Chakrabarti S., Lee J. H., Nakano A. H., Dado R. J., Loh H. H., Law P. Y., Wessendorf M. W., Elde R. Distribution and targeting of a mu-opioid receptor (MOR1) in brain and spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1995 May;15(5 Pt 1):3328–3341. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-03328.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidsson U., Riedl M., Chakrabarti S., Vulchanova L., Lee J. H., Nakano A. H., Lin X., Loh H. H., Law P. Y., Wessendorf M. W. The kappa-opioid receptor is primarily postsynaptic: combined immunohistochemical localization of the receptor and endogenous opioids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5062–5066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Pharmacology and electrophysiology of ATP-activated ion channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Burnstock G. Distribution of [3H]alpha,beta-methylene ATP binding sites in rat brain and spinal cord. Neuroreport. 1994 Aug 15;5(13):1601–1604. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199408150-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J., Wagenbach M. J., Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):519–523. doi: 10.1038/371519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Overview. Purinergic mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro E., Tomé A. R., Miras-Portugal M. T., Rosário L. M. Single-cell fura-2 microfluorometry reveals different purinoceptor subtypes coupled to Ca2+ influx and intracellular Ca2+ release in bovine adrenal chromaffin and endothelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Apr;426(6):524–533. doi: 10.1007/BF00378530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collo G., North R. A., Kawashima E., Merlo-Pich E., Neidhart S., Surprenant A., Buell G. Cloning OF P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels. J Neurosci. 1996 Apr 15;16(8):2495–2507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-08-02495.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Buffa R., Furness J. B., Solcia E. Immunohistochemical localization of polypeptides in peripheral autonomic nerves using whole mount preparations. Histochemistry. 1980 Feb;65(2):157–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00493164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. ATP receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):144–147. doi: 10.1038/359144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Derkach V., Surprenant A. ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):503–505. doi: 10.1038/357503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Lewis C., Buell G., Valera S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Pharmacological characterization of heterologously expressed ATP-gated cation channels (P2x purinoceptors). Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):178–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Ishibashi H., Akaike N. ATP-induced inward current in neurons freshly dissociated from the tuberomammillary nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Mar;71(3):868–873. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.3.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C., Neidhart S., Holy C., North R. A., Buell G., Surprenant A. Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):432–435. doi: 10.1038/377432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomneth R., Martin T. F., DasGupta B. R. Botulinum neurotoxin light chain inhibits norepinephrine secretion in PC12 cells at an intracellular membranous or cytoskeletal site. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1413–1421. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luff S. E., McLachlan E. M., Hirst G. D. An ultrastructural analysis of the sympathetic neuromuscular junctions on arterioles of the submucosa of the guinea pig ileum. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Mar 22;257(4):578–594. doi: 10.1002/cne.902570407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Humphrey P. P. Distribution and characterisation of [3H]alpha,beta-methylene ATP binding sites in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;348(6):608–617. doi: 10.1007/BF00167237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A., Inoue K. Comparison of adenosine triphosphate- and nicotine-activated inward currents in rat phaeochromocytoma cells. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:647–660. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren R., Smith G. P. A method for selective section of vagal afferent or efferent axons in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 2):R1136–R1141. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.267.4.R1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., Buell G., North R. A. P2X receptors bring new structure to ligand-gated ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 1995 May;18(5):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93907-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera S., Hussy N., Evans R. J., Adami N., North R. A., Surprenant A., Buell G. A new class of ligand-gated ion channel defined by P2x receptor for extracellular ATP. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):516–519. doi: 10.1038/371516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessendorf M. W., Appel N. M., Molitor T. W., Elde R. P. A method for immunofluorescent demonstration of three coexisting neurotransmitters in rat brain and spinal cord, using the fluorophores fluorescein, lissamine rhodamine, and 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin-3-acetic acid. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Dec;38(12):1859–1877. doi: 10.1177/38.12.1701460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J. S., Christie A., Levy M. N., Scarpa A. Modulation by extracellular ATP of two distinct currents in rat myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 1):C1411–C1417. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.6.C1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H. Signalling via ATP in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Oct;17(10):420–426. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]