Abstract
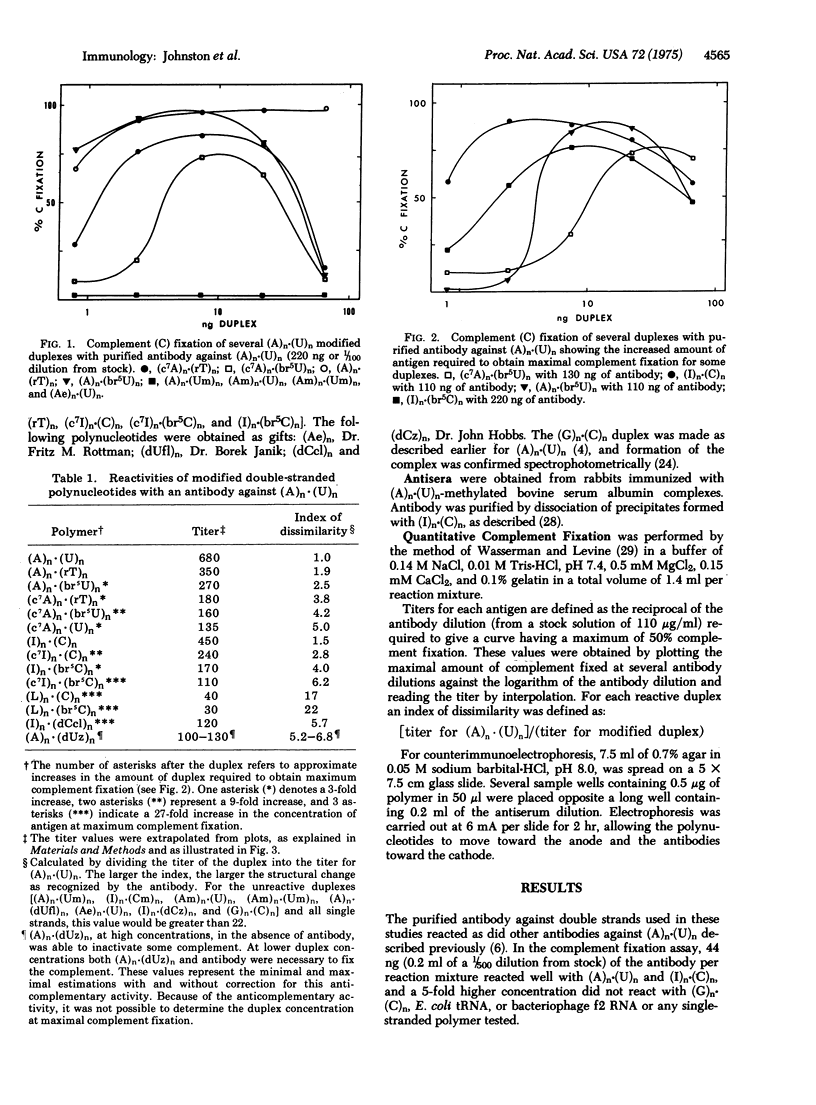
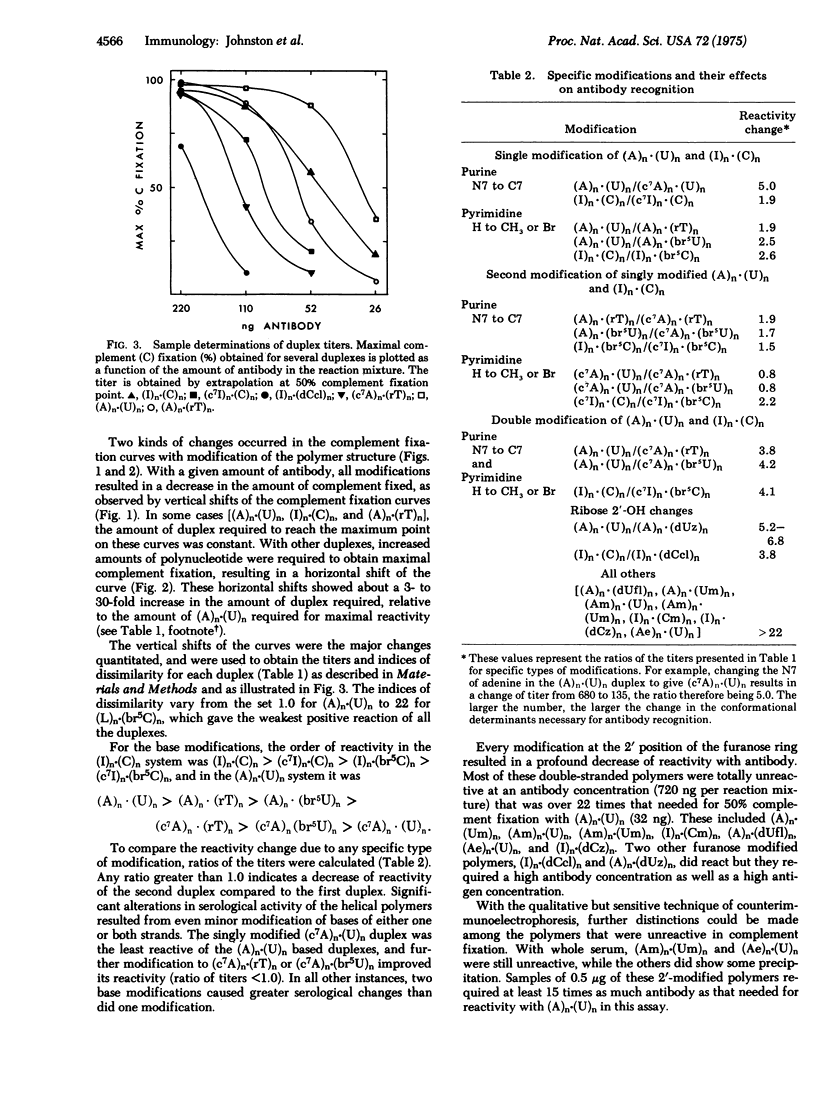
Purified antibody to poly(adenylic acid)-poly(uridylic acid) was used in quantitative microcomplement fixation assays to detect conformational variations among several double-helical polyribonucleotide analogs of poly(adenylic acid)-poly(uridylic acid) or poly(inosinic acid)-poly(cytidylic acid) that had been previously evaluated for their ability to induce interferon. Modification at the furanose 2'-position of one or both strands resulted in a dramatic decrease in serological reactivity. Most modifications of the bases caused smaller serological changes, and no base modification caused complete loss of reactivity. The reaction patterns support the conclusion that the structure of the furanose and the overall conformation of the helix are critical in the formation of antigenic determinants. The backbones of both strands appear to be involved in forming a single antigenic site, and base modifications may alter the steric relationship between the backbones. In addition, the same structural changes that substantially alter recognition by antibody also lead to large changes in the interferon-inducing ability of the nucleic acid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Bond P. J. Structures for Poly(U)-poly(A)-poly(U)triple stranded polynucleotides. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 25;244(134):99–101. doi: 10.1038/newbio244099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Bond P. J. Triple-stranded polynucleotide helix containing only purine bases. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):68–69. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. R., Eckstein F., Hobbs J. B., Sternbach H., Merigan T. C. The antiviral activity of certain thiophosphate and 2'-chloro substituted polynucleotide homopolymer duplexes. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):537–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby C., Chamberlin M. J. The specificity of interferon induction in chick embryo cells by helical RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby C., Stollar B. D., Simon M. I. Interferon induction: DNA-RNA hybrid or double stranded RNA? Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 10;229(6):172–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio229172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Janik B. Antiviral activity of polynucleotides: poly(2'-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridylic acid). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 28;324(1):50–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Rottman F. M., Shugar D. Antiviral activity of polynucleotides: poly 2'-O-ethyladenylic acid and poly 2'-O-ethyluridylic acid. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80758-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E. Synthetic interferon inducers. Top Curr Chem. 1974;52:173–208. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06873-2_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Torrence P. F., De Somer P., Witkop B. Biological, biochemical, and physicochemical evidence for the existence of the polyadenylic-polyuridylic-polyinosinic acid triplex. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2521–2531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Torrence P. F., Witkop B. Interferon induction by synthetic polynucleotides: importance of purine N-7 and strandwise rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):182–186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Torrence P. F., Witkop B., Stewart W. E., 2nd, De Somer P. Interferon induction: tool for establishing interactions among homopolyribonucleotides. Science. 1974 Nov 29;186(4166):835–837. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4166.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Zmudzka B., Shugar D. Antiviral activity of polynucleotides: role of the 2'-hydroxyl and a pyrimidine 5-methyl. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jul 15;24(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GESTELAND R. F., BOEDTKER H. SOME PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF BACTERIOPHAGE R17 AND ITS RIBONUCLEIC ACID. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:496–507. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacour F., Nahon-Merlin E., Michelson M. Immunological recognition of polynucleotide structure. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1973;62:1–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65772-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Rottman F. Influence of increasing 2'-O-methylation on the interferon stimulating capacity of poly(rl)-poly(rC). Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90389-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahon E., Michelson A. M., Lacour F. Antigénicité des complexes de polynucléotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 21;149(1):127–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. F., Stollar B. D. Antibodies to polyadenylate-polyuridylate copolymers as reagents for double strand RNA and DNA-RNA hybrid complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 10;35(1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90490-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward D. L., Herndon W. C., Jr, Schell K. R. Influence of 2'-O-acetylation on the antiviral activity of polyribonucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Doubls-helical polynucleotides: immunochemical recognition of differing conformations. Science. 1970 Aug 7;169(3945):609–611. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3945.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Raso V. Antibodies recognise specific structures of triple-helical polynucleotides built on poly(A) or poly(dA). Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):231–234. doi: 10.1038/250231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Stollar V. Immunofluorescent demonstration of double-stranded RNA in the cytoplasm of Sindbis virus-infected cells. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. The specificity and applications of antibodies to helical nucleic acids. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1975 May;3(1):45–69. doi: 10.3109/10409237509102552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar V., Stollar B. D. Immunochemical measurement of double-stranded RNA of uninfected and arbovirus-infected mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):993–1000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrence P. F., Bobst A. M., Waters J. A., Witkop B. Synthesis and characterization of potential interferon inducers. Poly(2'-azido-2'-deoxyuridylic acid). Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):3962–3972. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrence P. F., De Clercq E., Waters J. A., Witkop B. A potent interferon inducer derived from poly (7-deazainosinic acid). Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4400–4408. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrence P. F., De Clercq E., Waters J. A., Witkop B. Failure of duplexes based on polylaurusin (poly(L), "Polyformycin B") to induce interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):658–664. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90449-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrence P. F., Waters J. A., Buckler C. E., Witkop B. Effect of pyrimidine and ribose modifications on the antiviral activity of synthetic polynucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):890–898. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrence P. F., Witkop B. Polynucleotide duplexes based on poly(7-deazaadenylic acid). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 2;395(1):56–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90233-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Ng M. H., Friedman-Kien A. E., Krawciw T. Induction of interferon synthesis by synthetic double-stranded polynucleotides. J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):648–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.648-650.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



