Abstract
We demonstrate here that coexpression of ROMK2, an inwardly rectifying ATP-sensitive renal K+ channel (IKATP) with cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) significantly enhances the sensitivity of ROMK2 to the sulfonylurea compound glibenclamide. When expressed alone, ROMK2 is relatively insensitive to glibenclamide. The interaction between ROMK2, CFTR, and glibenclamide is modulated by altering the phosphorylation state of either ROMK2, CFTR, or an associated protein, as exogenous MgATP and the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A significantly attenuate the inhibitory effect of glibenclamide on ROMK2. Thus CFTR, which has been demonstrated to interact with both Na+ and Cl- channels in airway epithelium, modulates the function of renal ROMK2 K+ channels.
Full text
PDF
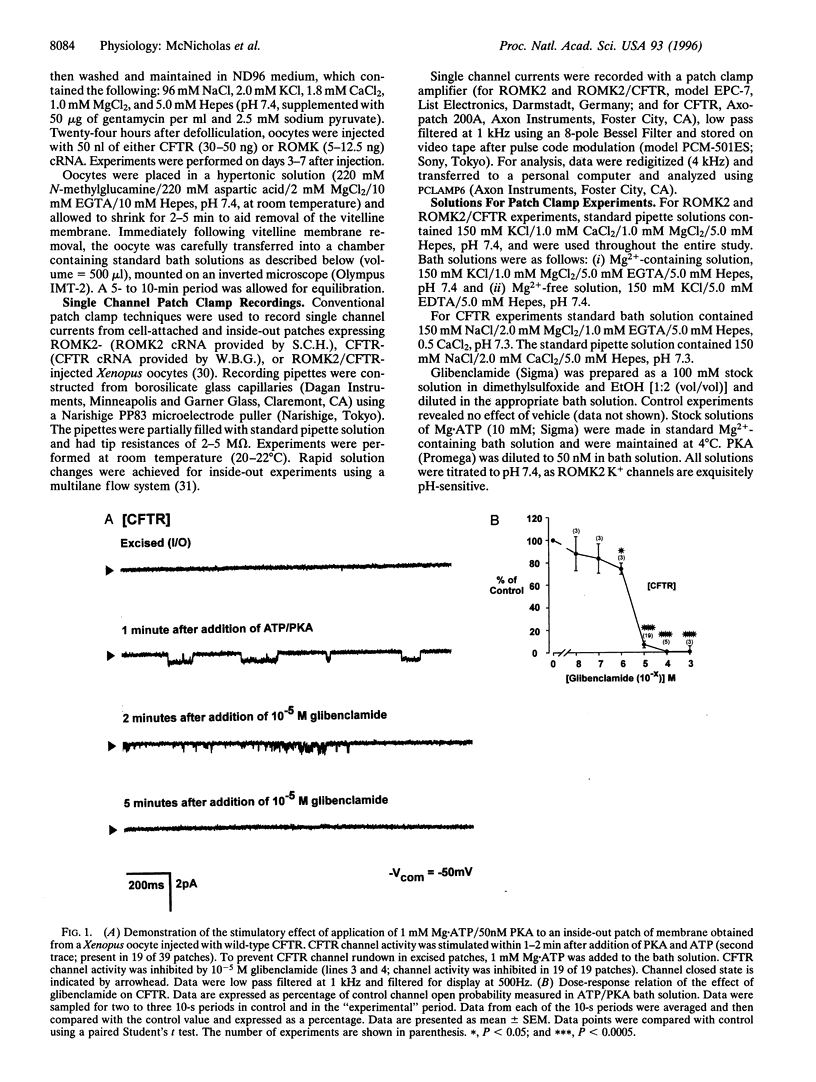

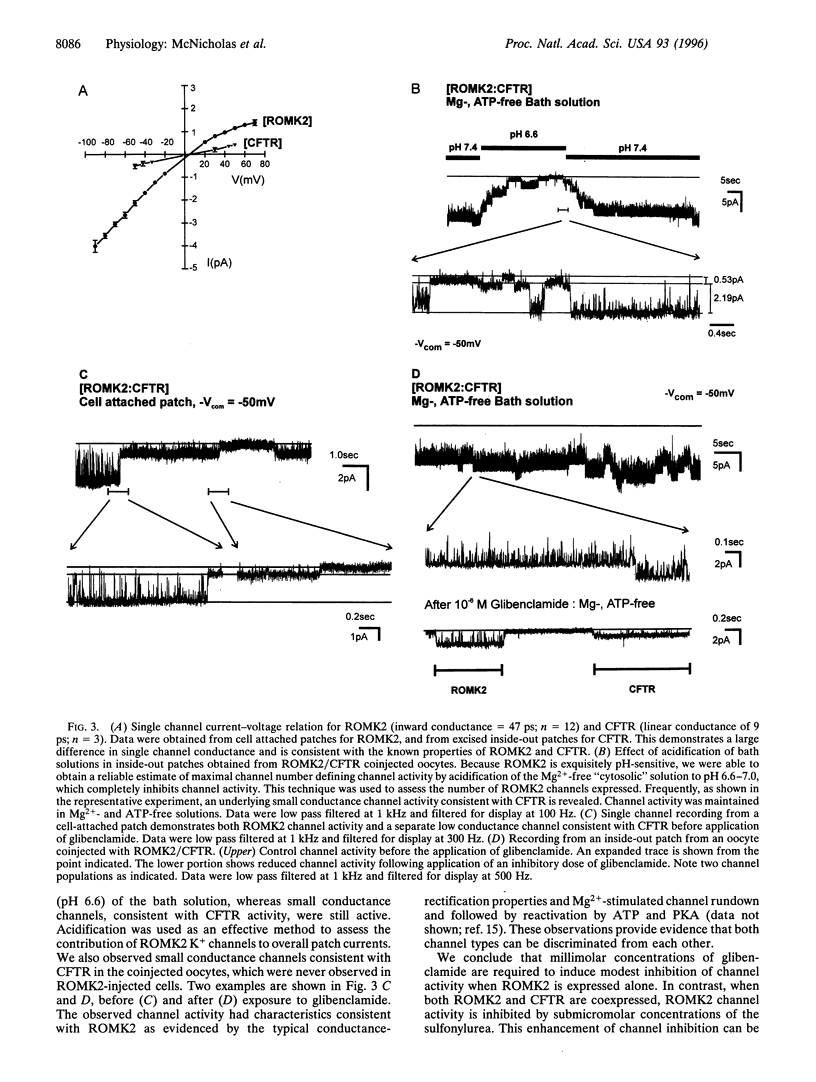
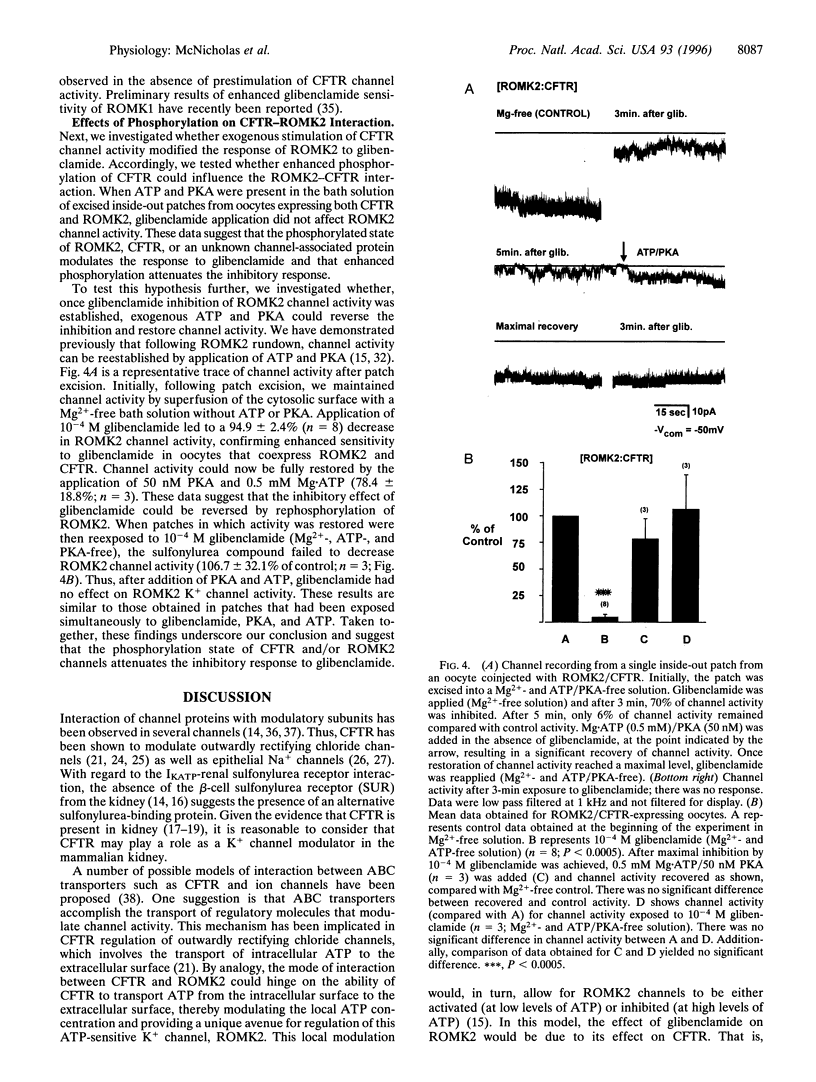

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilar-Bryan L., Nichols C. G., Wechsler S. W., Clement J. P., 4th, Boyd A. E., 3rd, González G., Herrera-Sosa H., Nguy K., Bryan J., Nelson D. A. Cloning of the beta cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science. 1995 Apr 21;268(5209):423–426. doi: 10.1126/science.7716547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barasch J., Kiss B., Prince A., Saiman L., Gruenert D., al-Awqati Q. Defective acidification of intracellular organelles in cystic fibrosis. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):70–73. doi: 10.1038/352070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boim M. A., Ho K., Shuck M. E., Bienkowski M. J., Block J. H., Slightom J. L., Yang Y., Brenner B. M., Hebert S. C. ROMK inwardly rectifying ATP-sensitive K+ channel. II. Cloning and distribution of alternative forms. Am J Physiol. 1995 Jun;268(6 Pt 2):F1132–F1140. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.6.F1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury N. A., Jilling T., Kirk K. L., Bridges R. J. Regulated endocytosis in a chloride secretory epithelial cell line. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C752–C759. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):463–467. doi: 10.1038/367463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I., Maloney P. C., Zeitlin P. L., Guggino W. B., Hyde S. C., Turley H., Gatter K. C., Harris A., Higgins C. F. Immunocytochemical localization of the cystic fibrosis gene product CFTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9262–9266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascal N., Schreibmayer W., Lim N. F., Wang W., Chavkin C., DiMagno L., Labarca C., Kieffer B. L., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Trollinger D. Atrial G protein-activated K+ channel: expression cloning and molecular properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10235–10239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Weston A. H. The pharmacology of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:597–637. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan M., Flotte T., Afione S., Solow R., Zeitlin P. L., Carter B. J., Guggino W. B. Defective regulation of outwardly rectifying Cl- channels by protein kinase A corrected by insertion of CFTR. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):581–584. doi: 10.1038/358581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. E., Clarke L. L., Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J. CFTR and outward rectifying chloride channels are distinct proteins with a regulatory relationship. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):263–268. doi: 10.1038/363263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hyde S. C., Higgins C. F., Valverde M. A., Mintenig G. M., Sepúlveda F. V. Separation of drug transport and chloride channel functions of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90263-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. The ABC of channel regulation. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):693–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K., Nichols C. G., Lederer W. J., Lytton J., Vassilev P. M., Kanazirska M. V., Hebert S. C. Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):31–38. doi: 10.1038/362031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki N., Gonoi T., Clement J. P., 4th, Namba N., Inazawa J., Gonzalez G., Aguilar-Bryan L., Seino S., Bryan J. Reconstitution of IKATP: an inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor. Science. 1995 Nov 17;270(5239):1166–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5239.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. G., Boyles S. E., Wilson J., Boucher R. C. Normalization of raised sodium absorption and raised calcium-mediated chloride secretion by adenovirus-mediated expression of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in primary human cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):1377–1382. doi: 10.1172/JCI117789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapivinsky G., Gordon E. A., Wickman K., Velimirović B., Krapivinsky L., Clapham D. E. The G-protein-gated atrial K+ channel IKACh is a heteromultimer of two inwardly rectifying K(+)-channel proteins. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):135–141. doi: 10.1038/374135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):802–806. doi: 10.1038/364802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas C. M., Wang W., Ho K., Hebert S. C., Giebisch G. Regulation of ROMK1 K+ channel activity involves phosphorylation processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8077–8081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Witzemann V., Takahashi T., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Patch clamp measurements on Xenopus laevis oocytes: currents through endogenous channels and implanted acetylcholine receptor and sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00582635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishige K., Takahashi N., Findlay I., Koyama H., Zanelli J. S., Peterson C., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Mori N., Kurachi Y. Molecular cloning, functional expression and localization of an inward rectifier potassium channel in the mouse brain. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 28;336(3):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80840-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périer F., Radeke C. M., Vandenberg C. A. Primary structure and characterization of a small-conductance inwardly rectifying potassium channel from human hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6240–6244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiebert E. M., Egan M. E., Hwang T. H., Fulmer S. B., Allen S. S., Cutting G. R., Guggino W. B. CFTR regulates outwardly rectifying chloride channels through an autocrine mechanism involving ATP. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D. N., Welsh M. J. Effect of ATP-sensitive K+ channel regulators on cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride currents. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Oct;100(4):573–591. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry A. M., Cuppoletti J., Malinowska D. H. Differential acidic pH sensitivity of delta F508 CFTR Cl- channel activity in lipid bilayers. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 1):C870–C875. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.3.C870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. The G. L. Brown Lecture. Potassium channels, metabolism and muscle. Exp Physiol. 1992 Jan;77(1):1–25. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutts M. J., Canessa C. M., Olsen J. C., Hamrick M., Cohn J. A., Rossier B. C., Boucher R. C. CFTR as a cAMP-dependent regulator of sodium channels. Science. 1995 Aug 11;269(5225):847–850. doi: 10.1126/science.7543698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Takahashi K., Ikeda M., Hayakawa H., Ogawa A., Kawaguchi Y., Sakai O. Cloning of a pH-sensitive K+ channel possessing two transmembrane segments. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):642–645. doi: 10.1038/367642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano M., Noma A. The ATP-sensitive K+ channel. Prog Neurobiol. 1993 Jul;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(93)90039-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T., Ishii T., Horio Y., Morishige K., Takahashi N., Yamada M., Yamashita T., Kiyama H., Sohmiya K., Nakanishi S. A novel ATP-dependent inward rectifier potassium channel expressed predominantly in glial cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):16339–16346. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.16339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd-Turla K. M., Rusvai E., Náray-Fejes-Tóth A., Fejes-Tóth G. CFTR expression in cortical collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1996 Jan;270(1 Pt 2):F237–F244. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1996.270.1.F237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., Schwab A., Giebisch G. Regulation of small-conductance K+ channel in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):F494–F502. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.3.F494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., White S., Geibel J., Giebisch G. A potassium channel in the apical membrane of rabbit thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F244–F253. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Giebisch G. Dual effect of adenosine triphosphate on the apical small conductance K+ channel of the rat cortical collecting duct. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Jul;98(1):35–61. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H., Tate S. S., Palmer L. G. Primary structure and functional properties of an epithelial K channel. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 1):C809–C824. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.3.C809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



