Abstract
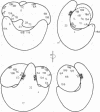
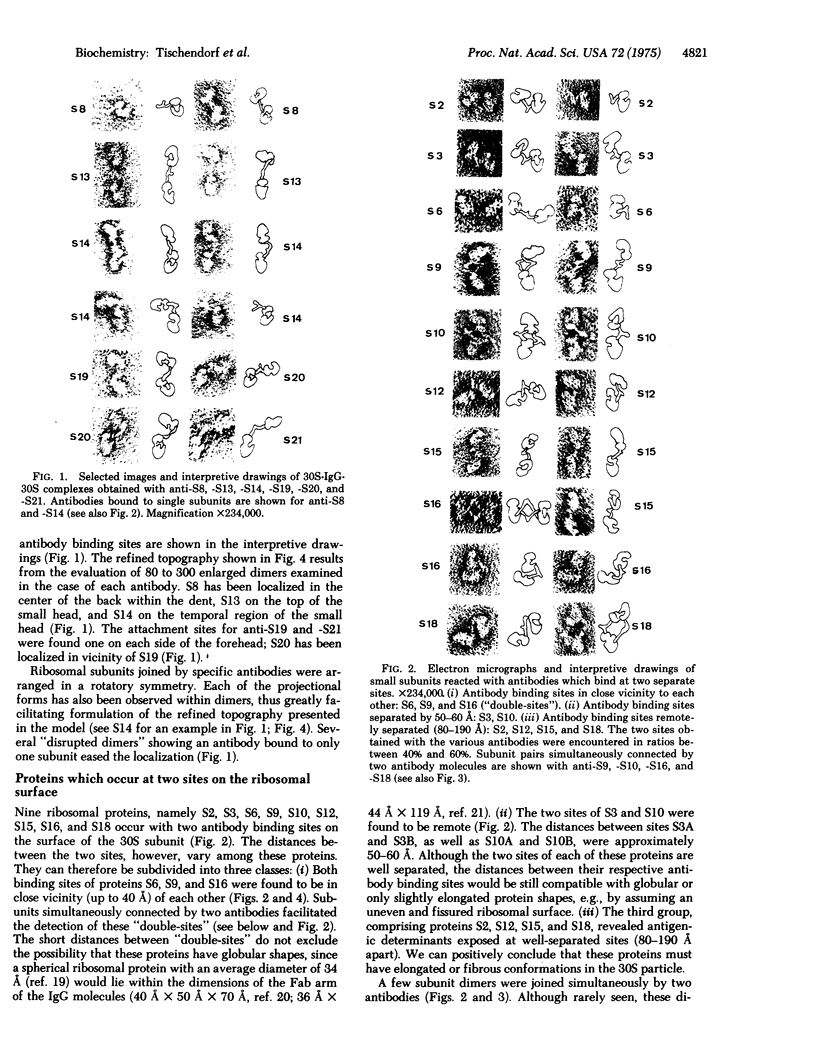
Binding sites for antibodies specific to nineteen of the twenty-one ribosomal proteins from the 30S subunit of E. coli ribosomes have been localized on the surface of the 30S ribosomal subunit by immune electron microscopy. The locations of 13 ribosomal proteins from the 50S subunit were similarily assessed. The arrangement of these proteins is illustrated in three-dimensional models of the 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits and of 70S ribosomes. With specific antibodies to six proteins of the 30S subunit we found only one attachment point for each protein. Antibodies against each of nine of the proteins attached at two separate sites that were separated by various distances. Four further proteins were exposed at three or four sites for antibody binding. Altogether eight to ten of the 19 proteins of the 30S subunit have shown antibody attachment sites at remote points on the surface of the ribosome, at distances which are incompatible with globular shapes; these proteins must therefore have elongated or fibrous structures within the ribosome. On the other hand, only two proteins of the 50S subunit, namely L11 and L18, have so far revealed two separated antibody binding sites; proteins L7/L12 occurred, however, at multiple sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruskov V. I., Kiselev N. A. Electron microscope study of the structure of Escherichia coli riboomes and CM-like particles. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):367–377. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART R. G. Electron microscopy of the 50-S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 16;60:629–637. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A., Pendergast M., Kahan L., Nomura M. Localization of Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins S4 and S14 by electron microscopy of antibody-labeled subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4688–4692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin M. Observations on the shape of the 50S ribosomal subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1454–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonomura Y., Blobel G., Sabatini D. Structure of liver ribosomes studied by negative staining. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):303–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz I., Kratky O., Licht A., Sela M. Shape and volume of anti-poly(D-alanyl) antibodies in the presence and absence of tetra-D-alanine as followed by small-angle x-ray scattering. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4998–5005. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron E. Z., Kohler R. E., Davis B. D. Polysomes extracted from Escherichia coli by freeze-thaw-lysozyme lysis. Science. 1966 Sep 2;153(3740):1119–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3740.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma V. R., Silverton E. W., Davies D. R., Terry W. D. The three-dimensional structure at 6 A resolution of a human gamma Gl immunoglobulin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3753–3759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Hasenbank R., Lütgehaus M., Maschler R., Morrison C. A., Zeichhardt H., Garrett R. A. The accessibility of proteins of the Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit to antibody binding. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 20;127(2):89–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00333659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischendorf G. W., Zeichhardt H., Stöffler G. Determination of the location of proteins L14, L17, L18, L19, L22, L23 on the surface of the 5oS ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli by immune electron microscopy. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;134(3):187–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00267715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischendorf G. W., Zeichhardt H., Stöffler G. Location of proteins S5, S13 and S14 on the surface of the 3oS ribosomal subunit from Escherichia coli as determined by immune electron microscopy. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;134(3):209–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00267716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev V. D. Electron microscopy study of 70 S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 10;14(4):203–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80617-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wabl M. R. Electron microscopic localization of two proteins on the surface of the 50 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli using specific antibody markers. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 5;84(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90582-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir A., Miskin R., Elson D. Inactivation and reactivation of ribosomal subunits: amino acyl-transfer RNA binding activity of the 30 s subunit of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):347–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]