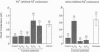Abstract
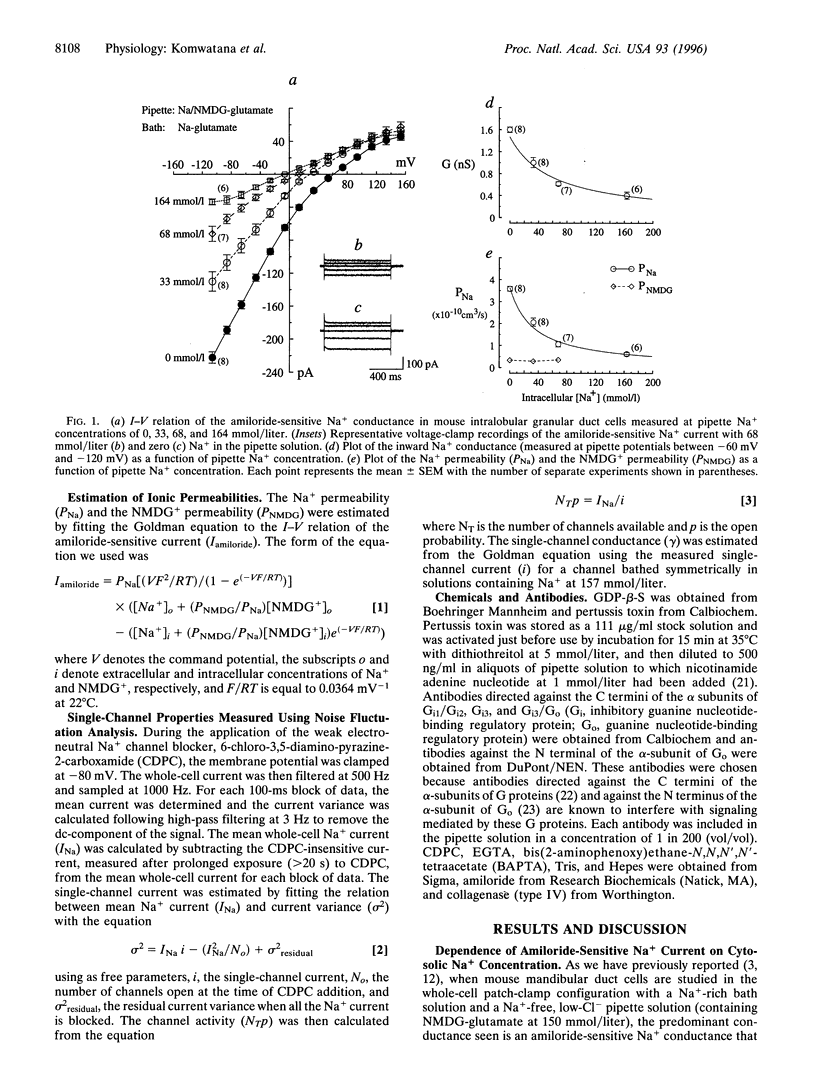
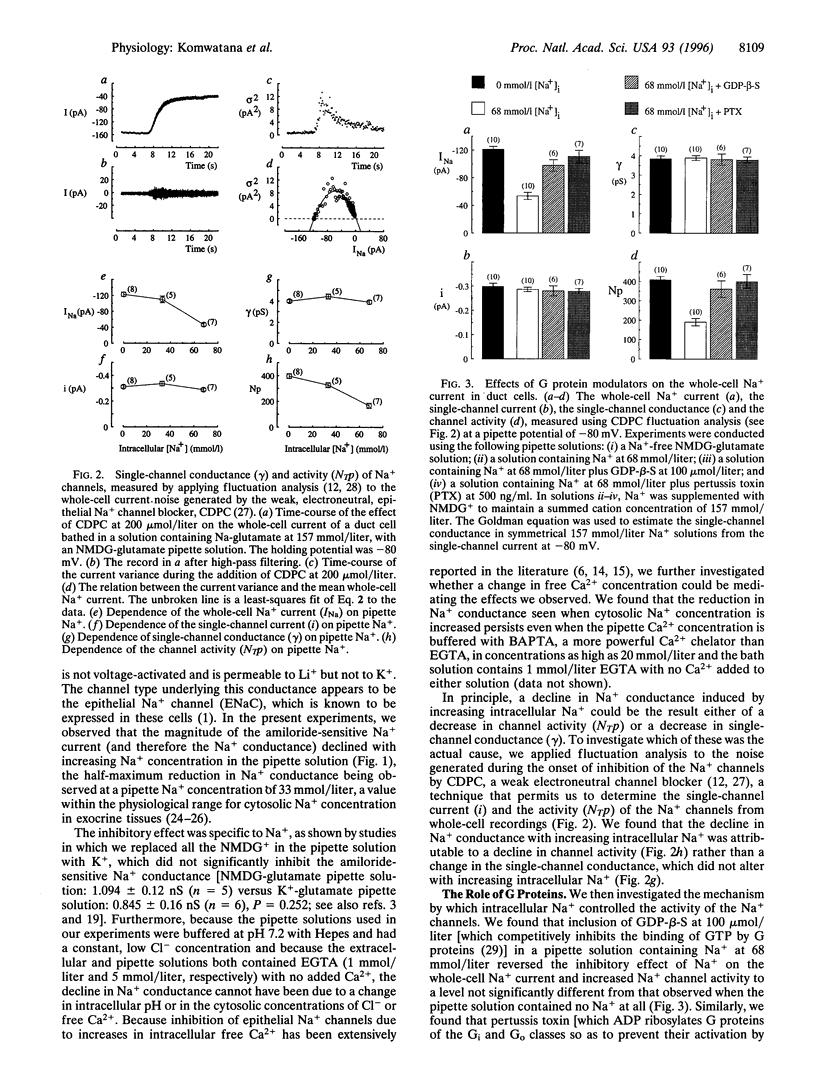
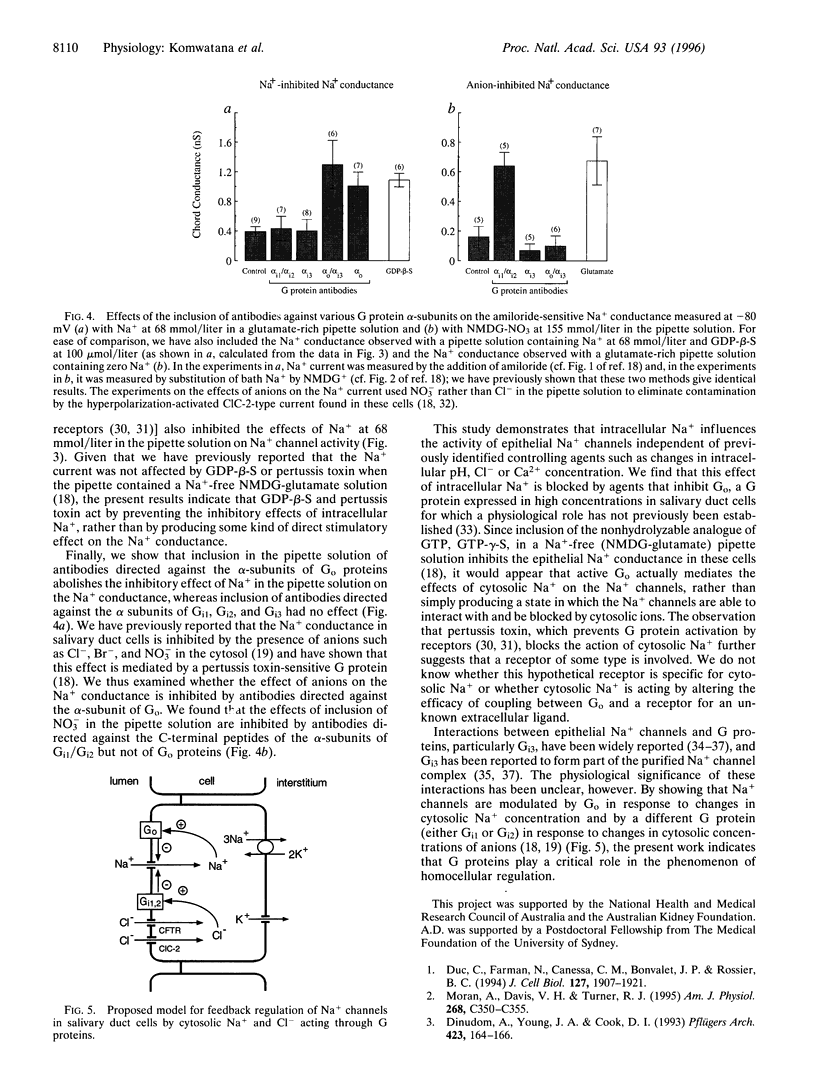
In tight Na+-absorbing epithelial cells, the fate of Na+ entry through amiloride-sensitive apical membrane Na+ channels is matched to basolateral Na+ extrusion so that cell Na+ concentration and volume remain steady. Control of this process by regulation of apical Na+ channels has been attributed to changes in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration or pH, secondary to changes in cytosolic Na+ concentration, although cytosolic Cl- seems also to be involved. Using mouse mandibular gland duct cells, we now demonstrate that increasing cytosolic Na+ concentration inhibits apical Na+ channels independent of changes in cytosolic Ca2+, pH, or Cl-, and the effect is blocked by GDP-beta-S, pertussis toxin, and antibodies against the alpha-subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (Go). In contrast, the inhibitory effect of cytosolic anions is blocked by antibodies to inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (Gi1/Gi2. It thus appears that apical Na+ channels are regulated by Go and Gi proteins, the activities of which are controlled, respectively, by cytosolic Na+ and Cl-.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammälä C., Bokvist K., Larsson O., Berggren P. O., Rorsman P. Demonstration of a novel apamin-insensitive calcium-activated K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B cells. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Feb;422(5):443–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00375069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausiello D. A., Stow J. L., Cantiello H. F., de Almeida J. B., Benos D. J. Purified epithelial Na+ channel complex contains the pertussis toxin-sensitive G alpha i-3 protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4759–4765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinudom A., Komwatana P., Young J. A., Cook D. I. Control of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ current in mouse salivary ducts by intracellular anions is mediated by a G protein. J Physiol. 1995 Sep 15;487(Pt 3):549–555. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinudom A., Poronnik P., Allen D. G., Young J. A., Cook D. I. Control of intracellular Ca2+ by adrenergic and muscarinic agonists in mouse mandibular ducts and end-pieces. Cell Calcium. 1993 Oct;14(9):631–638. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(93)90088-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinudom A., Young J. A., Cook D. I. Amiloride-sensitive Na+ current in the granular duct cells of mouse mandibular glands. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Apr;423(1-2):164–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00374977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinudom A., Young J. A., Cook D. I. Na+ and Cl- conductances are controlled by cytosolic Cl- concentration in the intralobular duct cells of mouse mandibular glands. J Membr Biol. 1993 Sep;135(3):289–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00211100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc C., Farman N., Canessa C. M., Bonvalet J. P., Rossier B. C. Cell-specific expression of epithelial sodium channel alpha, beta, and gamma subunits in aldosterone-responsive epithelia from the rat: localization by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 2):1907–1921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Cassel D., Levkovitz H., Lowe M., Selinger Z. Guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate). An inhibitor of adenylate cyclase stimulation by guanine nucleotides and fluoride ions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9829–9834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Silver R. B., Windhager E. E., Palmer L. G. Feedback regulation of Na channels in rat CCT. II. Effects of inhibition of Na entry. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):F565–F574. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.3.F565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs W., Larsen E. H., Lindemann B. Current-voltage curve of sodium channels and concentration dependence of sodium permeability in frog skin. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(1):137–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H. Molecular properties of epithelial, amiloride-blockable Na+ channels. FASEB J. 1994 May;8(8):522–528. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.8.8181670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey B. J., Thomas S. R., Ehrenfeld J. Intracellular pH controls cell membrane Na+ and K+ conductances and transport in frog skin epithelium. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Dec;92(6):767–791. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.6.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., Berdiev B. K., Benos D. J. Regulation by Na+ and Ca2+ of renal epithelial Na+ channels reconstituted into planar lipid bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Sep;106(3):445–466. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismailov I. I., McDuffie J. H., Benos D. J. Protein kinase A phosphorylation and G protein regulation of purified renal Na+ channels in planar bilayer membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10235–10241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. ADP ribosylation of the specific membrane protein of C6 cells by islet-activating protein associated with modification of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7210–7216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komwatana P., Dinudom A., Young J. A., Cook D. I. Characterization of the Cl- conductance in the granular duct cells of mouse mandibular glands. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Oct;428(5-6):641–647. doi: 10.1007/BF00374588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komwatana P., Dinudom A., Young J. A., Cook D. I. Control of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ current in salivary duct cells by extracellular sodium. J Membr Biol. 1996 Mar;150(2):133–141. doi: 10.1007/s002329900038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Specificity and functional applications of antipeptide antisera which identify G-protein alpha subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1994;237:268–283. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(94)37068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moises H. C., Rusin K. I., Macdonald R. L. mu-Opioid receptor-mediated reduction of neuronal calcium current occurs via a G(o)-type GTP-binding protein. J Neurosci. 1994 Jun;14(6):3842–3851. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-06-03842.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran A., Davis V. H., Turner R. J. Na+ channels in membrane vesicles from intralobular salivary ducts. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):C350–C355. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.2.C350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Conductance and gating of epithelial Na channels from rat cortical collecting tubule. Effects of luminal Na and Li. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):121–138. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poronnik P., Schumann S. Y., Cook D. I. HCO3(-)-dependent ACh-activated Na+ influx in sheep parotid secretory endpieces. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Apr;429(6):852–858. doi: 10.1007/BF00374810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. A., Foskett J. K. Na+ transport pathways in secretory acinar cells: membrane cross talk mediated by [Cl-]i. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jul;267(1 Pt 1):C146–C156. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.1.C146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G. Homocellular regulatory mechanisms in sodium-transporting epithelia: avoidance of extinction by "flush-through". Am J Physiol. 1981 Dec;241(6):F579–F590. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.6.F579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. B., Frindt G., Windhager E. E., Palmer L. G. Feedback regulation of Na channels in rat CCT. I. Effects of inhibition of Na pump. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):F557–F564. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.3.F557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnheim K. Intrinsic regulation of apical sodium entry in epithelia. Physiol Rev. 1991 Apr;71(2):429–445. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Driessche W., Lindemann B. Concentration dependence of currents through single sodium-selective pores in frog skin. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):519–520. doi: 10.1038/282519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. L., Oliver C., D'Silva N., Belton C. M. Localization of the G-protein G(o) in exocrine glands. J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Jan;42(1):41–47. doi: 10.1177/42.1.7505300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. M., Foskett J. K. Oscillations of cytosolic sodium during calcium oscillations in exocrine acinar cells. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1014–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.1948071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Zhao H., Diaz J., Muallem S. Regulation of [Na+]i in resting and stimulated submandibular salivary ducts. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 18;270(33):19606–19612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zong X., Lux H. D. Augmentation of calcium channel currents in response to G protein activation by GTP gamma S in chick sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Aug;14(8):4847–4853. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-08-04847.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]