Abstract
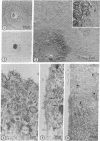
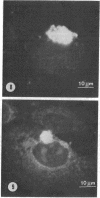
The relationship between microtubules and concanavalin A surface receptors during concanavalin A capping in primary cultures of rabbit ovarian granulosa cells was examined by electron microscopic and fluorescence labeling techniques. Cells treated with concanavalin A and hemocyanin at 4 degree or 37 degree and then incubated at 37 degree for 1 hr formed large juxtanuclear caps that were observed with shadow cast replicas of the cell surface. Thin section analysis of capped cells revealed an abundance of microtubules immediately beneath the cap which were arranged approximately perpendicular to the plane of the membrane. The capping process was unaffected by the antimicrotubule agents colchicine or vinblastine. Further, vinblastine treatment of capped calls resulted in the formation of numerous paracrystals that were confined to the cytoplasm underlying the capped region of the membrane; uncapped cells displayed paracrystals that were randomly dispersed in the cytoplasm. Exposure of fixed cells to fluorescein thiocarbamyl colchicine, which localizes colchicine binding proteins, revealed an intensely fluorescent region that corresponded to the cap; this staining pattern was absent in uncapped cells. These findings indicate that concanavalin A mediated capping modifies the cytoplasmic disposition of microtubules and colchicine binding proteins. Further, it is suggested that the capped region of the plasma membrane is a preferred site of microtubule polymerization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker J. S., Oliver J. M., Berlin R. D. Fluorescence techniques for following interactions of microtubule subunits and membranes. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):152–154. doi: 10.1038/254152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K. G., Malawista S. E. Microtubular crystals in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):95–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D., Oliver J. M., Ukena T. E., Yin H. H. Control of cell surface topography. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):45–46. doi: 10.1038/247045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge M. B. Fine structure of nerve fibers and growth cones of isolated sympathetic neurons in culture. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):713–735. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I., Wang J. L. Receptor mobility and receptor-cytoplasmic interactions in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson G. F., Challis J. R., Ryan K. J. A developmental study on the capacity of rabbit granulosa cells to respond to trophic hormones and secrete progesterone in vitro. Dev Biol. 1974 Oct;40(2):208–224. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskin F., Cantor C. R., Shelanski M. L. Turbidimetric studies of the in vitro assembly and disassembly of porcine neurotubules. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):737–755. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoué S., Borisy G. G., Kiehart D. P. Growth and lability of Chaetopterus oocyte mitotic spindles isolated in the presence of porcine brain tubulin. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):175–184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Ukena T. E., Berlin R. D. Effects of phagocytosis and colchicine on the distribution of lectin-binding sites on cell surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):394–398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Zurier R. B., Berlin R. D. Concanavalin a cap formation on polymorphonuclear leukocytes of normal and beige (chediak-higashi) mice. Nature. 1975 Feb 6;253(5491):471–473. doi: 10.1038/253471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. R., Todaro G. J., Fonte V. A scanning electron microscope study of surface features of viral and spontaneous transformants of mouse Balb-3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):633–642. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Axline S. G. Subplasmalemmal microfilaments and microtubules in resting and phagocytizing cultivated macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):12–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. L., Child F. M. Flagellar regeneration in protozoan flagellates. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):345–364. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. B., Borysenko J. Z., Karnovsky M. J. Factors affecting the redistribution of surface-bound concanavalin A on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):351–365. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L. Chemistry of the filaments and tubules of brain. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jun;21(6):529–539. doi: 10.1177/21.6.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P. P., Martínez-Palomo A., Gonzalez-Robles A. Membrane structure and surface coat of Entamoeba histolytica. Topochemistry and dynamics of the cell surface: cap formation and microexudate. J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):538–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Revel J. P. Mapping of concanavalin A binding sites on the surface of several cell types. Dev Biol. 1972 Mar;27(3):434–441. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Franke W. W. Characterization of the colchicine binding of membrane fractions from rat and mouse liver. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):297–303. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Sanger L., Stein Y. Colchicine-induced inhibition of lipoprotein and protein secretion into the serum and lack of interference with secretion of biliary phospholipids and cholesterol by rat liver in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):90–103. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukena T. E., Berlin R. D. Effect of colchicine and vinblastine on the topographical separation of membrane functions. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):1–7. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukena T. E., Borysenko J. Z., Karnovsky M. J., Berlin R. D. Effects of colchicine, cytochalasin B, and 2-deoxyglucose on the topographical organization of surface-bound concanavalin A in normal and transformed fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):70–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev J. M., Gelfand I. M., Domnina L. V., Ivanova O. Y., Komm S. G., Olshevskaja L. V. Effect of colcemid on the locomotory behaviour of fibroblasts. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1970 Nov;24(3):625–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Bamburg J. R., Mizel S. B., Grisham L. M., Creswell K. M. Interaction of drugs with microtubule proteins. Fed Proc. 1974 Feb;33(2):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. Modulation of lymphocyte receptor redistribution by concanavalin A, anti-mitotic agents and alterations of pH. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):152–155. doi: 10.1038/246152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. The effects of concanavalin A on the mobility of lymphocyte surface receptors. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Sep;81(1):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Spooner B. S., Wessells N. K. Axon growth: roles of microfilaments and microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1206–1212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Petris S. Concanavalin A receptors, immunoglobulins, and theta antigen of the lymphocyte surface. Interactions with concanavalin A and with Cytoplasmic structures. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):123–146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]