Abstract
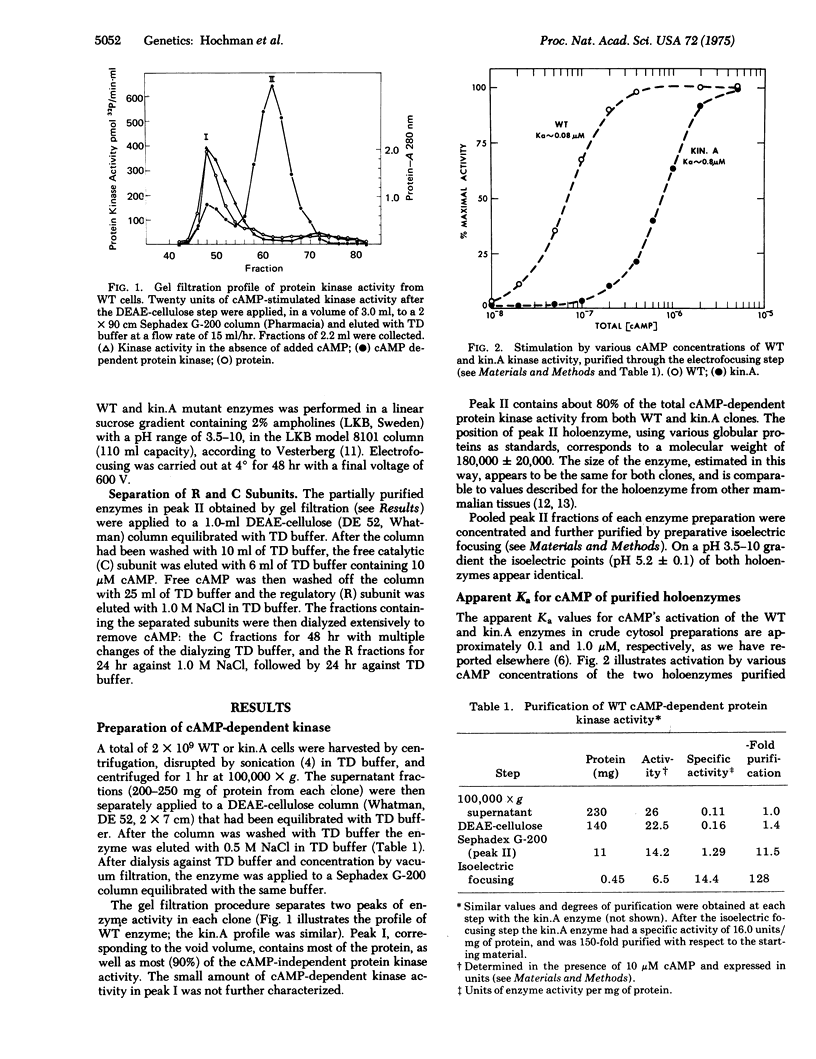
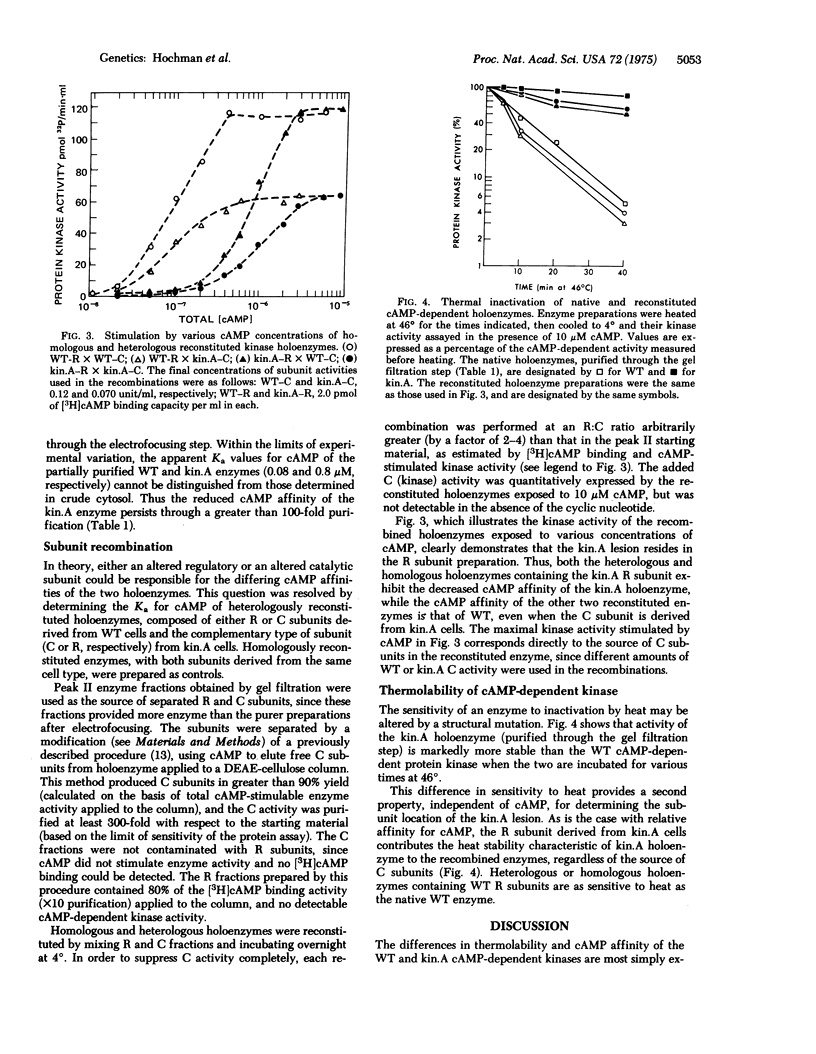
Compared to the wild-type parental line of S49 mouse lymphoma cells, intact cells of a mutant line (kin.A) are 10-fold less sensititive to biologic effects of exogenous cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophophosphate (cAMP), such as induction of cAMP phosphodiesterase, cell cycle-specific growth inhibition, and cytolysis. The cAMP-dependent protein kinase (ATP:protein phosphotransferase; EC 2.7.1.37) activity of kin.A cells exhibits an apparent Ka for activation by cAMP 10-fold greater than that of wild type, and is much more resistant to inactivation by heat. These differences between the wild-type and mutant enzymes persist through a high degree of purification, suggesting a structural alteration in the kin.A holoenzyme. Heterologous reconstitution experiments, using separated R and C subunits of the wild-type and kin.A cAMP-dependent kinases, show that the altered cAMP affinity and thermolability are conferred by the R component of the kin.A enzyme. These results are most consistent with a structural mutation in the kin.A gene coding for the R subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Evidence for a structural mutation helps to define one mechanism of heritable variation in cultured somatic cells. The phenotype produced by the kin.A structural mutation also greatly strengthens the conslusion that cAMP-dependent protein kinase is essential for cAMP regulation of growth and enzyme induction in intact S49 cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaudet A. L., Roufa D. J., Caskey C. T. Mutations affecting the structure of hypoxanthine: guanine phosphoribosyltransferase in cultured Chinese hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):320–324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Mechanisms of control for cAMP-dependent protein kinase from skeletal muscle. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:241–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Melmon K. L., Tomkins G. M., Weinstein Y. Genetic analysis of cyclic AMP in a mammalian cell. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:771–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Tomkins G. M. Somatic genetic analysis of cyclic AMP action: characterization of unresponsive mutants. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Jun;85(3):611–620. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Tomkins G. M., Dion S. Regulation of phosphodiesterase synthesis: requirement for cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1973 Sep 7;181(4103):952–954. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4103.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A. Mutations affecting adenine phosphoribosyl transferase activity in Chinese hamster cells. Cell. 1974 May;2(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Bourne H. R., Tomkins G. M. Somatic genetic analysis of cyclic AMP action: selection of unresponsive mutants. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Jun;85(3):603–610. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Gray J. W., Tomkins G. M. Cyclic AMP, a nonessential regulator of the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):878–882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Bourne H. R., Tomkins G. M. Altered metabolism and endogenous cyclic AMP in cultured cells deficient in cyclic AMP-binding proteins. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 8;244(136):167–169. doi: 10.1038/newbio244167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Litwack G., Tomkins G. M. Induction of cytolysis of cultured lymphoma cells by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and the isolation of resistant variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):76–79. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Kemp R. G., Riley W. D., Cooper R. A., Krebs E. G. Activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by adenosine triphosphate and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2200–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. Mutation rates in cells at different ploidy levels. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Oct;78(2):177–184. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horibata K., Harris A. W. Mouse myelomas and lymphomas in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Apr;60(1):61–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen J. K., Steinberg D. Activation and phosphorylation of purified adipose tissue hormone-sensitive lipase by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 1;239(3):411–427. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen J. K., Steinberg D., Mayer S. E. ATP-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent activation of rat adipose tissue lipase by protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):290–295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie C. W., 3rd, Stellwagen R. H. Differences between liver and hepatoma cells in their complements of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-binding proteins and protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5755–5762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie C. W., 3rd, Stellwagen R. H. Heterogeneity and unusually high affinity in the interactions of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate with specific binding proteins from liver and hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5763–5771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in bacteria. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):339–344. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Erlichman J., Rosen O. M. Molecular forms and subunit composition of a cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase purified from bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):36–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Sachs L. Temperature sensitivity of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-binding proteins and the regulation of growth and differentiation in neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3236–3242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R., Hickenbottom J. P., Reimann E. M., Hunkeler F. L., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Inactivation of glycogen synthetase and activation of phosphorylase kinase by muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 10;245(23):6317–6328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Harkins J. L., Stanners C. P. A mammalian cell mutant with a temperature-sensitive leucyl-transfer RNA synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3094–3098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


