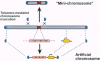
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton N. R., Goldstein L. S. Going mobile: microtubule motors and chromosome segregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 5;93(5):1735–1742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Willard H. F. The human X-inactivation centre is not required for maintenance of X-chromosome inactivation. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):154–156. doi: 10.1038/368154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. E., Barnett M. A., Burgtorf C., Shaw P., Buckle V. J., Brown W. R. Dissecting the centromere of the human Y chromosome with cloned telomeric DNA. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1227–1237. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R. Mammalian artificial chromosomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Jun;2(3):479–486. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth B., Sniegowski P., Stephan W. The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):215–220. doi: 10.1038/371215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L. Centromeres of budding and fission yeasts. Trends Genet. 1990 May;6(5):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90149-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr C. J., Bayne R. A., Kipling D., Mills W., Critcher R., Cooke H. J. Generation of a human X-derived minichromosome using telomere-associated chromosome fragmentation. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 1;14(21):5444–5454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr C. J., Stevanovic M., Thomson E. J., Goodfellow P. N., Cooke H. J. Telomere-associated chromosome fragmentation: applications in genome manipulation and analysis. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):275–282. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr C., Fantes J., Goodfellow P., Cooke H. Functional reintroduction of human telomeres into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7006–7010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Warburton P. E., Willard H. F. Integration of human alpha-satellite DNA into simian chromosomes: centromere protein binding and disruption of normal chromosome segregation. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):681–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90436-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlaczky G., Praznovszky T., Cserpán I., Keresö J., Péterfy M., Kelemen I., Atalay E., Szeles A., Szelei J., Tubak V. Centromere formation in mouse cells cotransformed with human DNA and a dominant marker gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8106–8110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnenberger K. M., Baum M. P., Polizzi C. M., Carbon J., Clarke L. Construction of functional artificial minichromosomes in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):577–581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanish J. P., Yanowitz J. L., de Lange T. Stringent sequence requirements for the formation of human telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8861–8865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller R., Brown K. E., Burgtorf C., Brown W. R. Mini-chromosomes derived from the human Y chromosome by telomere directed chromosome breakage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 9;93(14):7125–7130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.7125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley C. Mammalian artificial chromosomes: a new tool for gene therapy. Gene Ther. 1994 Jan;1(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itzhaki J. E., Barnett M. A., MacCarthy A. B., Buckle V. J., Brown W. R., Porter A. C. Targeted breakage of a human chromosome mediated by cloned human telomeric DNA. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):283–287. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin Z., Fricker M. D., Tyler-Smith C. De novo formation of several features of a centromere following introduction of a Y alphoid YAC into mammalian cells. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 May;3(5):689–695. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.5.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. D., Karpen G. H. Interactions between the nod+ kinesin-like gene and extracentromeric sequences are required for transmission of a Drosophila minichromosome. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90378-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. D., Karpen G. H. Localization of centromere function in a Drosophila minichromosome. Cell. 1995 Aug 25;82(4):599–609. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90032-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Schultes N. P., Szostak J. W. Chromosome length controls mitotic chromosome segregation in yeast. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi H., Wakui K., Ogawa K., Okano T., Niikawa N., Fukushima Y. A stable acentric marker chromosome: possible existence of an intercalary ancient centromere at distal 8p. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Dec;55(6):1202–1208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Mackay A. M., Ainsztein A. M., Goldberg I. G., Earnshaw W. C. The centromere: hub of chromosomal activities. Science. 1995 Dec 8;270(5242):1591–1594. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5242.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan B. A., Schwartz S. Identification of centromeric antigens in dicentric Robertsonian translocations: CENP-C and CENP-E are necessary components of functional centromeres. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Dec;4(12):2189–2197. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.12.2189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler-Smith C., Willard H. F. Mammalian chromosome structure. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Jun;3(3):390–397. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90110-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voullaire L. E., Slater H. R., Petrovic V., Choo K. H. A functional marker centromere with no detectable alpha-satellite, satellite III, or CENP-B protein: activation of a latent centromere? Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1153–1163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]