Abstract
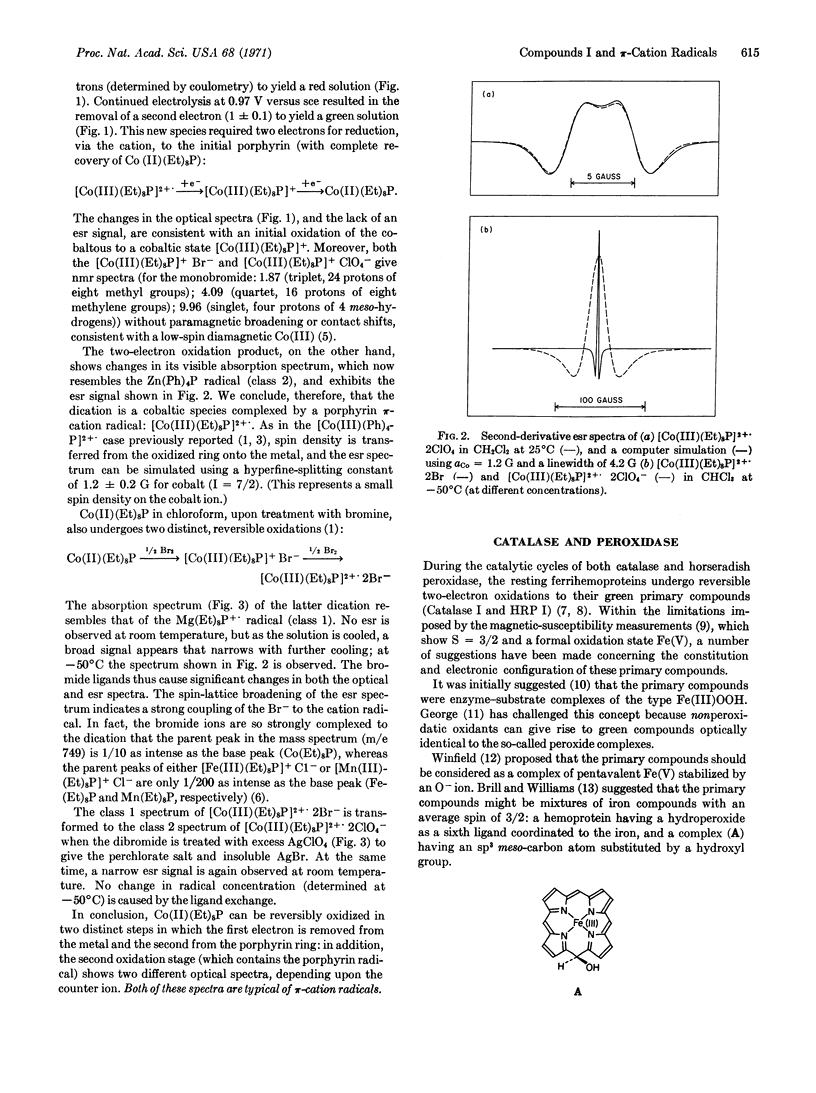
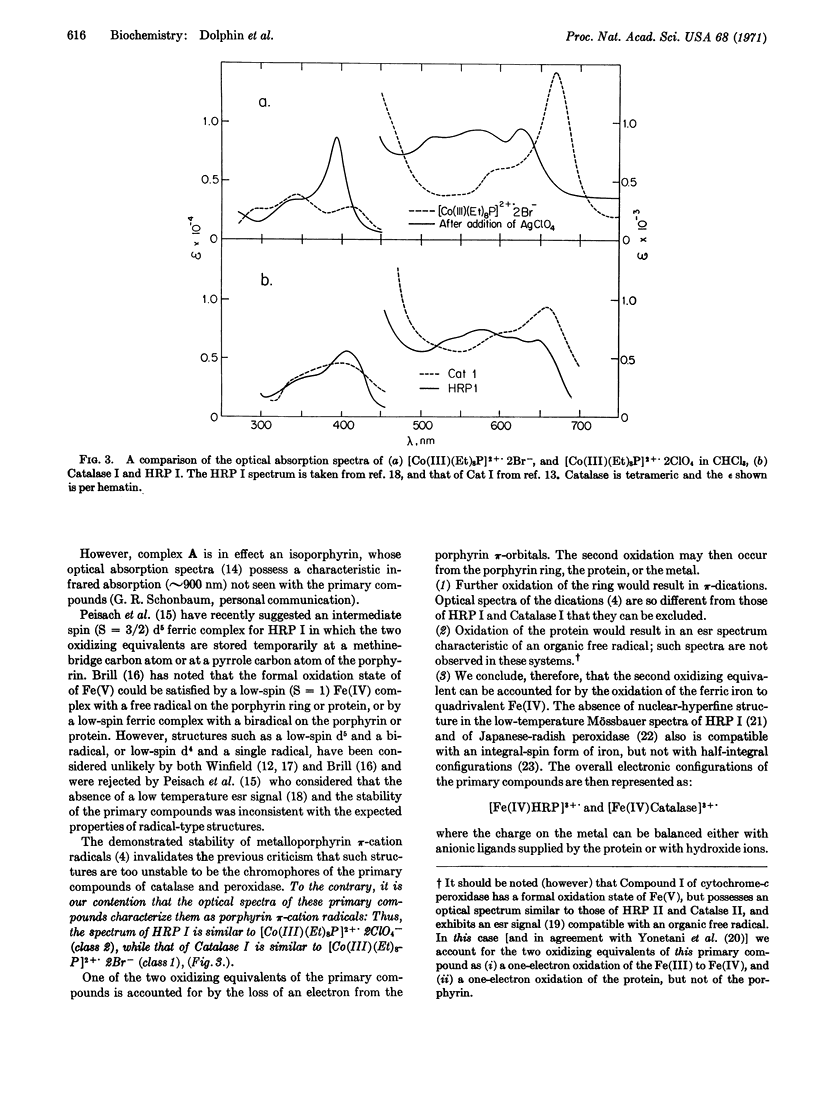
Two-electron oxidation of cobaltous octaethylporphyrin [Co(II)(Et)8P] yields a stable π-cation radical [Co(III)(Et)8P]2+., the optical spectrum of which exhibits spectral changes dependent upon the nature of the counterion. Comparison of these spectra with those of Compounds I of horseradish peroxidase and catalase leads us to propose that these Compounds I contain a π-cation radical of the heme prosthetic group. This proposal explains the oxidation level, optical spectra, and stability of the primary compounds without recourse to properties such as stoichiometric mixtures of special porphyrins, stable Fe(V) porphyrins, or unique conformers of heme porphyrins. Explanations are advanced to account for the missing electron spin resonance signal of Compound I of horseradish peroxidase.
Full text
PDF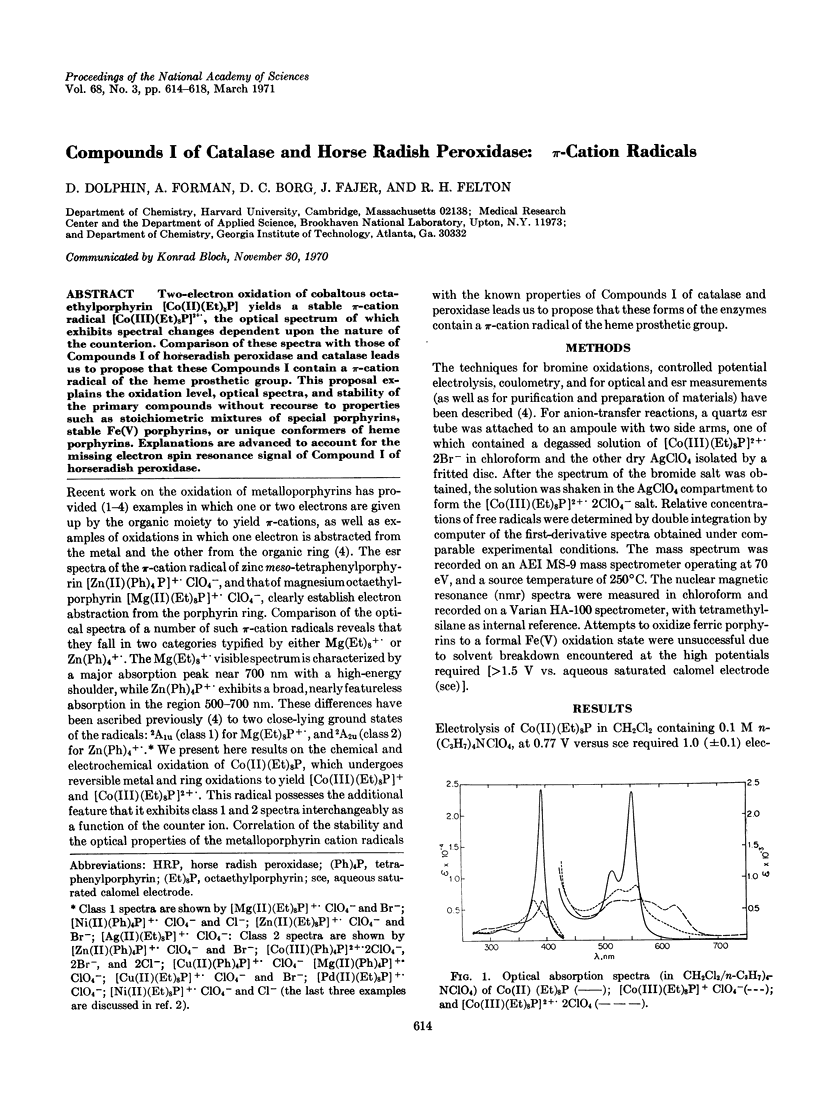


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg W. E., Peisach J., Wittenberg B. A., Wittenberg J. B. The electronic structure of protoheme proteins. I. An electron paramagnetic resonance and optical study of horseradish peroxidase and its derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1854–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill A. S., Williams R. J. Primary compounds of catalase and peroxidase. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78(2):253–262. doi: 10.1042/bj0780253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer J., Borg D. C., Forman A., Dolphin D., Felton R. H. pi-Cation radicals and dications of metalloporphyrins. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Jun 3;92(11):3451–3459. doi: 10.1021/ja00714a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrhop J. H., Mauzerall D. The one-electron oxidation of metalloporphyrins. J Am Chem Soc. 1969 Jul 16;91(15):4174–4181. doi: 10.1021/ja01043a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGE P. Intermediate compound formation with peroxidase and strong oxidizing agents. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):413–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka T., Kotani M., Yonetani T. A thermal equilibrium between high- and low-spin states in ferric cytochrome c peroxidase and some discussion on the enzyme-substrate complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 8;167(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORITA Y., MASON H. S. AN ELECTRON SPIN RESONANCE STUDY OF SOME HEMOPROTEINS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2654–2659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. H., Ehrenberg A., Bearden A. J. Mössbauer spectroscopic evidence for the electronic configuration of iron in horseradish peroxidase and its peroxide derivatives. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4159–4162. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J., Blumberg W. E., Wittenberg B. A., Wittenberg J. B. The electronic structure of protoheme proteins. 3. Configuration of the heme and its ligands. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1871–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg B. A., Kampa L., Wittenberg J. B., Blumberg W. E., Peisach J. The electronic structure of protoheme proteins. II. An electron paramagnetic resonance and optical study of cytochrome c peroxidase and its derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1863–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg A., Manassen J. Electrochemical and electron paramagnetic resonance studies of metalloporphyrins and their electrochemical oxidation products. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 May 20;92(10):2982–2991. doi: 10.1021/ja00713a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


