Abstract
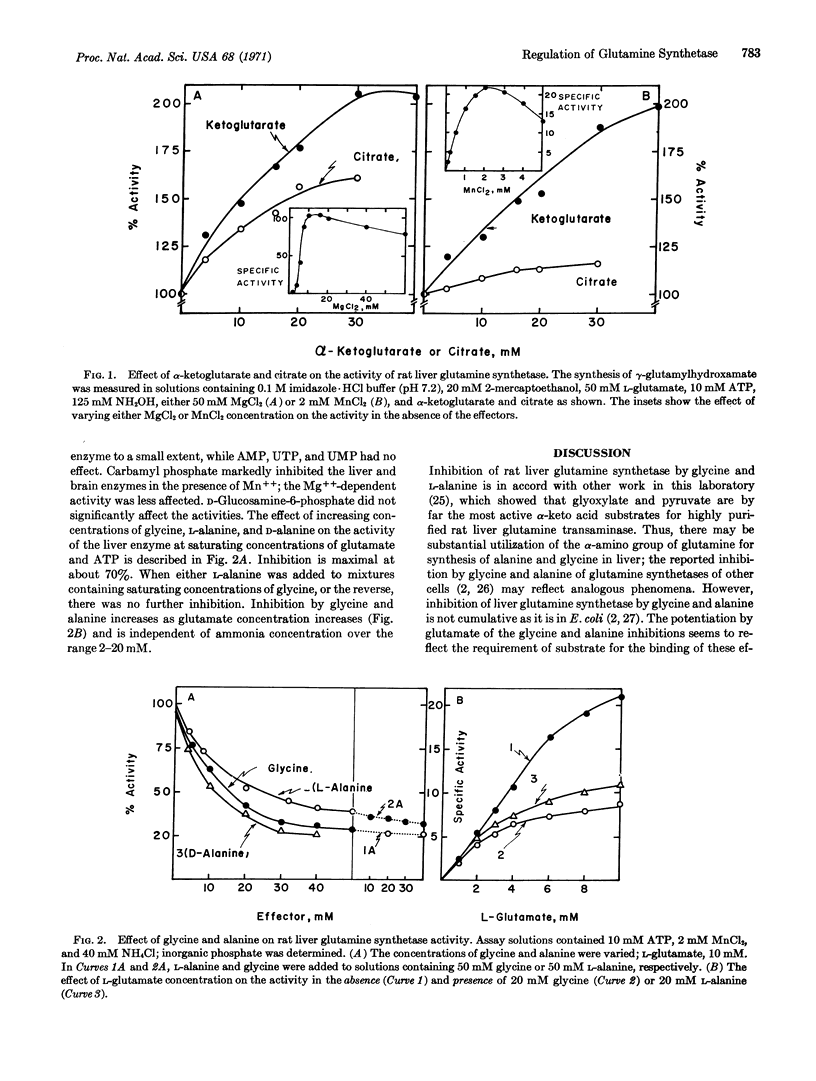
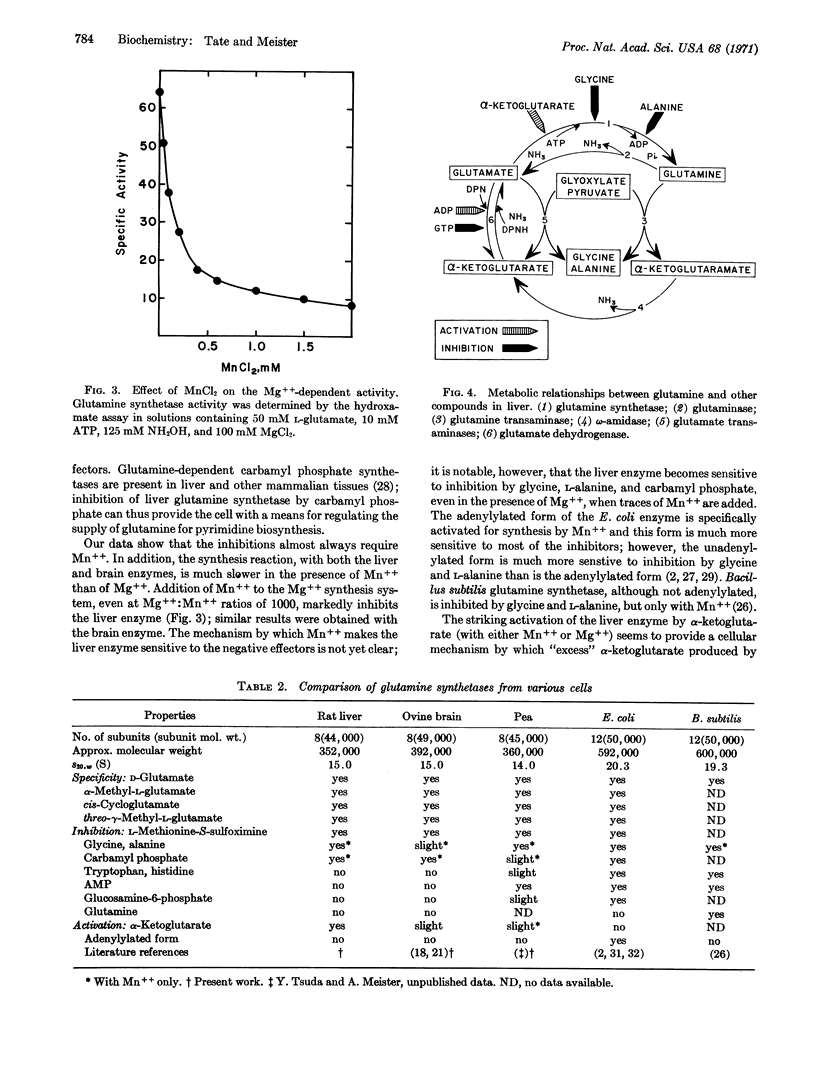
Rat liver glutamine synthetase (s20,w 15.0 S; MW about 352,000) resembles ovine brain glutamine synthetase in that it (a) has 8 subunits, (b) acts on both L- and D-glutamate and certain glutamate analogs (e.g., β-glutamate, cis-cycloglutamate, and α-methyl-L-glutamate), and (c) is irreversibly inhibited by L-methionine-S-sulfoximine. The liver enzyme (but not the brain enzyme) is (a) markedly activated by α-ketoglutarate and less so by citrate, and (b) inhibited noncumulatively by glycine and alanine, in the presence of Mn++ but not Mg++; inhibition increases with increasing concentrations of glutamate. These regulatory phenomena seem to be correlated with metabolically related enzymes, e.g., glutamine transaminase. Both liver and brain glutamine synthetases are inhibited by carbamyl phosphate (with Mn++ but not with Mg++), which provides a means for controlling glutamine for pyrimidine biosynthesis. Addition of Mn++ to the Mg++-synthetase system, even at Mg++: Mn++ ratios of 1000, markedly inhibits synthesis by both brain and liver enzymes. This finding, and the fact that Mn++ promotes sensitivity to the negative effectors, indicates that Mn++ plays a central role in the regulation of glutamine synthetase. Properties of the glutamine synthetases that have been isolated from mammalian, plant, and bacterial cells are compared. They are similar with respect to subunit size, substrate specificity, inhibition by methionine sulfoximine, and Mn++-sensitive inhibition by glycine, alanine, and carbamyl phosphate, but differ in certain other regulatory phenomena and in subunit structure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowers W. F., Czubaroff V. B., Haschemeyer R. H. Subunit structure of L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase from Alcaligenes faecalis. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 23;9(13):2620–2625. doi: 10.1021/bi00815a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Ginsburg A., Yeh J., Shelton E., Stadtman E. R. Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase. Purification and physical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5195–5205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Stadtman E. R. Some kinetic properties of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5206–5213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG J., LICHTENSTEIN N. Effect of manganous and magnesium ions concentration on glutamine synthetase and glutamotransferase of sheep brain. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2337–2339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager S. E., Jones M. E. A glutamine-dependent enzyme for the synthesis of carbamyl phosphate for pyrimidine biosynthesis in fetal rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 25;242(24):5674–5680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haschemeyer R. H. Electron microscopy of enzymes. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Apr;30(6):875–891. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1968.tb02531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haschemeyer R. H. Electron microscopy of enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1970;33:71–118. doi: 10.1002/9780470122785.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer H. Regulation of enzymes by enzyme-catalyzed chemical modification. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:297–326. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. On the synthesis and utilization of glutamine. Harvey Lect. 1969;63:139–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. Stereochemical mapping of the active site of glutamine synthetase. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):100–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monder C. Metal ion interactions and glutamine synthetase activity. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2677–2686. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Meister A. Phosphorylation of methionine sulfoximine by glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):164–170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of glutamine synthetase by methionine sulfoximine. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):1066–1075. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Wilk S., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Preparation and studies on the characterization of sheep brain glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2670–2674. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Wilk S., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Preparation and studies on the characterization of sheep brain glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2670–2674. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Wilk S., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Preparation and studies on the characterization of sheep brain glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2670–2674. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. B., Meister A. Identification of L-methionine-S-sulfoximine as the convulsant isomer of methionine sulfoximine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):500–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Ginsburg A. Effects of specific divalent cations on some physical and chemical properties of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Taut and relaxed enzyme forms. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2153–2167. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Kingdon H. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. VII. Adenylyl glutamine synthetase: a new form of the enzyme with altered regulatory and kinetic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):642–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Glutamine synthetase deadenylylating enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jan 11;30(1):32–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90708-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Shapiro B. M., Ginsburg A., Kingdon H. S., Denton M. D. Regulation of glutamine synthetase activity in Escherichia coli. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1968 Jun;21(2):378–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Shapiro B. M., Kingdon H. S., Woolfolk C. A., Hubbard J. S. Cellular regulation of glutamine synthetase activity in Escherichia coli. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1968;6:257–289. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(68)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatibana M., Ito K. Control of pyrimidine biosynthesis in mammalian tissues. I. Partial purification and characterization of glutamine-utilizing carbamyl phosphate synthetase of mouse spleen and its tissue distribution. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5403–5413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2143–2152. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellner V. P., Meister A. Binding of adenosine triphosphate and adenosine diphosphate by glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1966 Mar;5(3):872–879. doi: 10.1021/bi00867a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


