Abstract
Highly purified cAMP-dependent protein phosphokinase from adrenal-cortical tissue contains cAMP-receptor activity. In activating the kinase, cAMP binds to the receptor and causes it to dissociate from its complex with the kinase. The kinase, freed of receptor, is fully activated and no longer stimulable by cAMP. Kinase can be similarly activated by differentially denaturing the receptor with heat. Addition of receptor suppresses kinase activity; this suppression can be overcome by cAMP. After dissociation of receptor, two molecular forms of the activated kinase exist. The cAMP receptor thus functions as a repressor of the protein kinase; binding of cAMP to receptor causes it to dissociate from the kinase, which is then fully activated.
Full text
PDF
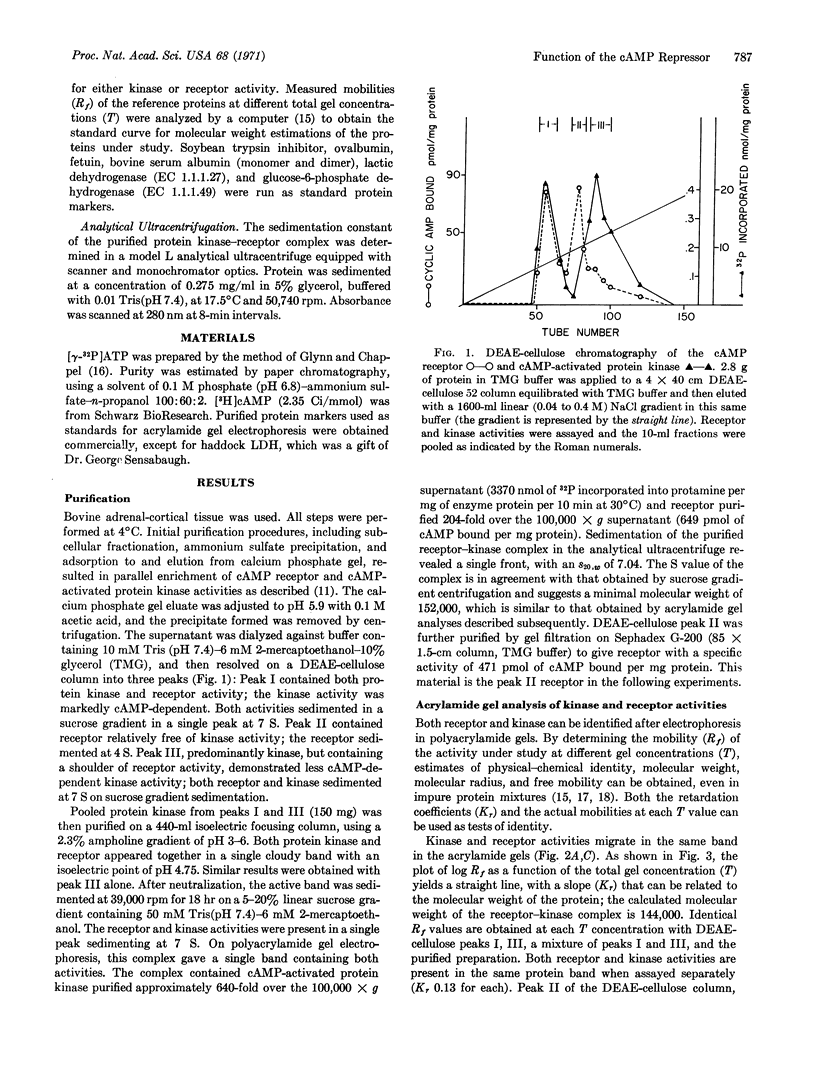
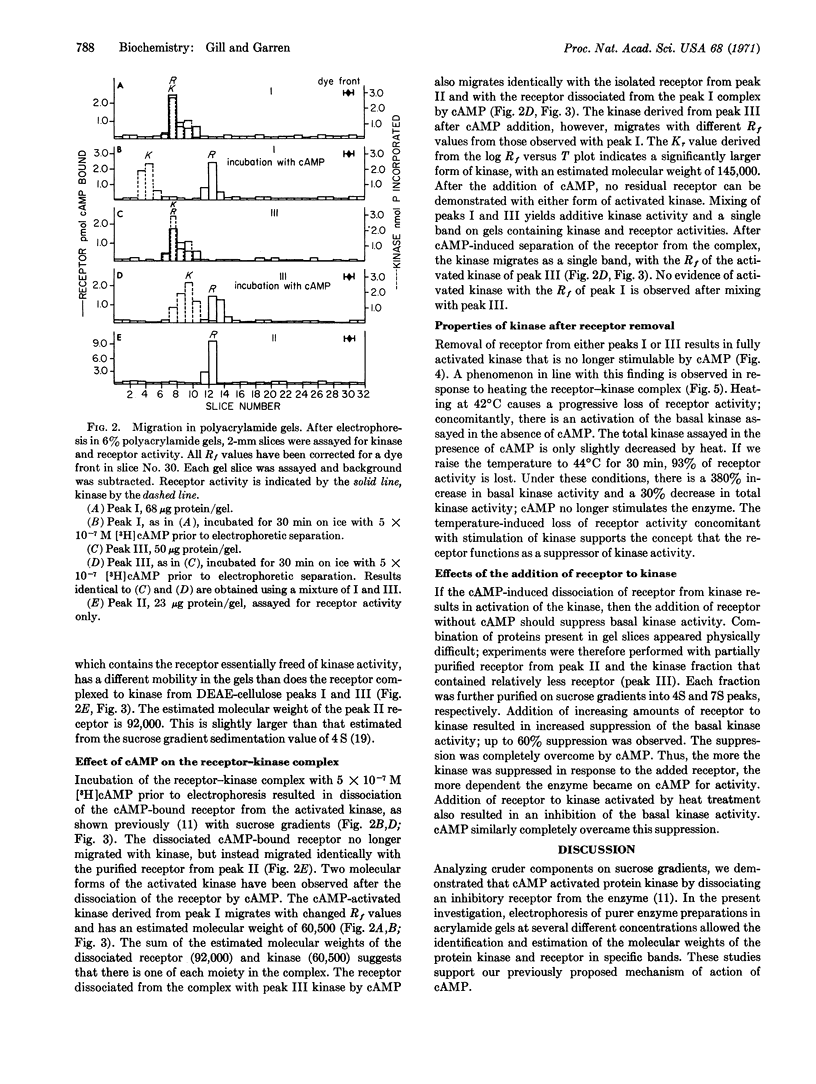
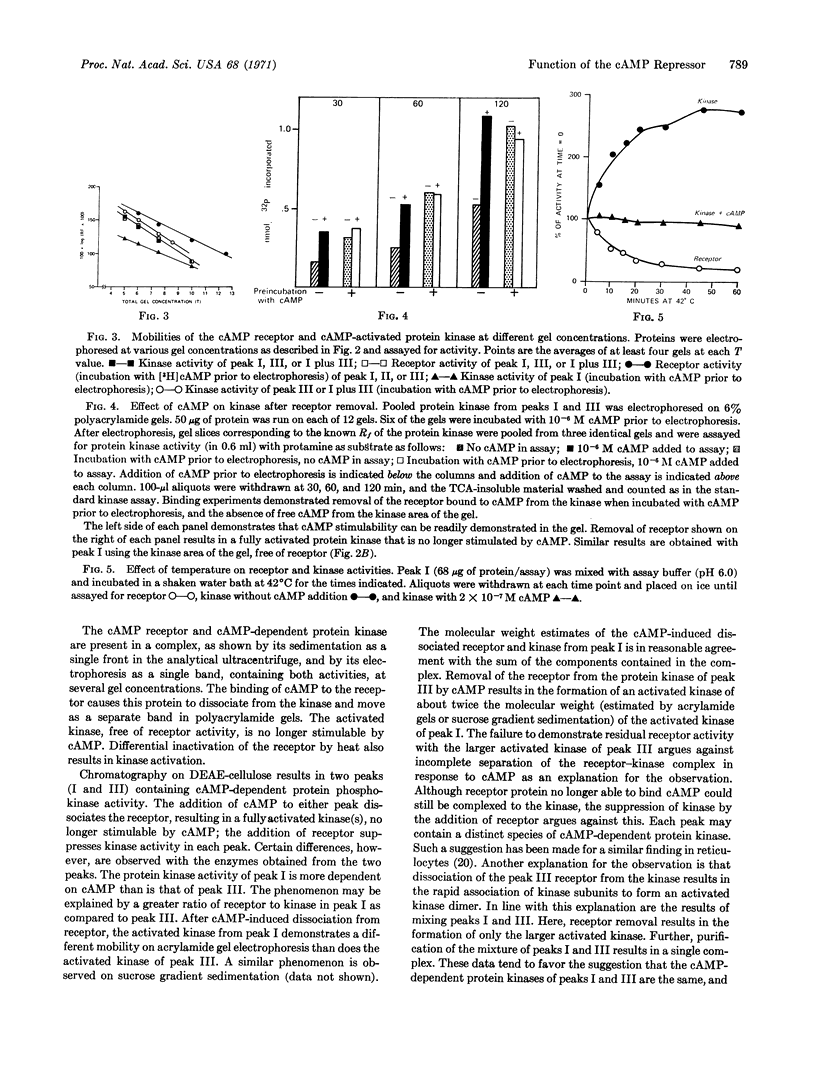

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Emmer M., deCrombrugghe B., Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic AMP receptor protein of E. coli: its role in the synthesis of inducible enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):480–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON K. A. STARCH-GEL ELECTROPHORESIS--APPLICATION TO THE CLASSIFICATION OF PITUITARY PROTEINS AND POLYPEPTIDES. Metabolism. 1964 Oct;13:SUPPL–SUPPL1002. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Distinct subunits for the regulation and catalytic activity of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1054–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Garren L. D. A cyclic-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate dependent protein kinase from the adrenal cortex: comparison with a cyclic AMP binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 11;39(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90581-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Garren L. D. On the mechanism of action of adrenocorticotropic hormone: the binding of cyclic-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate to an adrenal cortical protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):512–519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen J. K., Steinberg D., Mayer S. E. ATP-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent activation of rat adipose tissue lipase by protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):290–295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jergil B., Dixon G. H. Protamine kinase from rainbow trout testis. Partial purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):425–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumon A., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. Mode of action of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate on protein kinase from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 9;41(5):1290–1297. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A. Histone phosphorylation: stimulation by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Science. 1968 Nov 1;162(3853):579–580. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3853.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Brostrom C. O., Corbin J. D., King C. A., Krebs E. G. Separation of regulatory and catalytic subunits of the cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase(s) of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWARTZ M. N., KAPLAN N. O., FRECH M. E. Significance of heat-activated enzymes. Science. 1956 Jan 13;123(3185):50–53. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3185.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R., Hickenbottom J. P., Reimann E. M., Hunkeler F. L., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Inactivation of glycogen synthetase and activation of phosphorylase kinase by muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 10;245(23):6317–6328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M., Salas M. L., Lipmann F. Mechanism of activation by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate of a protein phosphokinase from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):408–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton G. M., Garren L. D. An assay for adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate based on the association of the nucleotide with a partially purified binding protein. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 13;9(21):4223–4229. doi: 10.1021/bi00823a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland O., Siess E. Interconversion of phospho- and dephospho- forms of pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):947–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Schwartz D., Beckwith J. Mechanism of activation of catabolite-sensitive genes: a positive control system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):104–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



