Abstract
To evaluate the effect of chlorogenic acid supplementation in patients with retinitis pigmentosa, we evaluated objective change in visual function with multifocal electroretinography, along with visual acuity, visual field, standard electroretinography, and contrast sensitivity. Eighteen patients diagnosed with retinitis pigmentosa were enrolled in this prospective, non-comparative, single-arm study. Multifocal electroretinography, best-corrected visual acuity in Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study letters, total point score on visual field examination with Humphrey Field Analyzer II, electroretinography, and contrast sensitivity were measured and repeated after 3 months supplementation with chlorogenic acid. The amplitude of ring 5 was significantly higher on multifocal electroretinography after 3 months of chlorogenic acid supplementation (7.2 ± 9.5 vs 8.3 ± 10.8 nV/deg2, mean ± standard deviation, P = 0.022). There were no significant changes in the best-corrected visual acuity, total point score on Humphrey Field Analyzer, 30 Hz flicker amplitude on standard electroretinography, or contrast sensitivity. Chlorogenic acid may have a beneficial effect on the peripheral area at the margins of retinal degeneration, and should be considered as an anti-oxidant for the management of retinitis pigmentosa.
Keywords: Retinitis Pigmentosa, Chlorogenic Acid, Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants, Retinal Degeneration
INTRODUCTION
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is known to be caused by various genetic changes in the components of the phototransduction pathway. Some genetic changes may alter rod cells to be more susceptible to oxidative damage in the retina, which is exposed directly to the effects of light, leading to progressive retinal degeneration (1, 2). In other genetic mutations, rod cells may die from other primary processes; and then when the rod cells die, the oxygen content in the retina rises, causing oxidative stress and secondary degeneration of the remaining cone cells. The retina is highly metabolically active, and is therefore prone to oxidative damage. Various anti-oxidants have been considered as possible candidates that might delay this progression. There have been numerous reports on the effects of antioxidants in delaying the degeneration of photoreceptors in animal models of RP (3). Anti-oxidant supplementation has been found to be effective in the intervention of atrophic age-related macular degeneration (4). Human clinical trials for antioxidants such as vitamins A and E, lutein, and docosahexaenoic acid have been conducted for RP with some beneficial effects noted (5-8). Additionally, continuous modifications of anti-oxidant dosages and regimens have been tried as possible candidates for nutritional supplementation in RP. Recently, patients consuming a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and receiving 15,000 IU vitamin A daily were found to have a slower progression in decline of visual acuity over 4 to 6 yr (9), raising hope for a possible delay of progression in RP patients.
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is a polyphenol found in various agricultural products such as coffee, beans, potatoes, and apples, and is formed by the esterification of caffeic and quinic acids. The antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and anti-carcinogenic activities of CGA have been demonstrated in many studies (10-13). CGA showed an anti-oxidant effect in vitro (14), in cultured human endothelial cells (15), and in rat models of ischemia/reperfusion injury to the liver (16). The beneficial effect of CGA in coffee has been suggested in a human study monitoring the oxidation of proteins, DNA membrane lipids, and other redox biomarkers (17). Several studies have also demonstrated its neuroprotective effect (18, 19).
Multifocal electroretinography (mERG) has recently been evaluated as an objective electrophysiological method to evaluate changes in retinal function in RP patients (20). The response amplitude has been found to follow a similar exponential decay as the visual field and may provide reproducible responses, even if standard electroretinography (ERG) is nearly extinguished.
In order to evaluate the effect of CGA supplementation in patients with RP, we utilized mERG to objectively evaluate changes in visual function, along with visual acuity, visual field, standard electroretinography (ERG) results, and contrast sensitivity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
Eighteen patients diagnosed with RP were enrolled in this prospective, non-comparative, single-arm study from October 2010 to January 2011. Patients received supplementation with CGA 60 mg once per day. Patients that were already taking other anti-oxidants, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, were kept on their regimens. The best corrected visual acuity (measured using Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study [ETDRS] letters), mERG (RETIscan System; Roland Consult, Brandenbrug, Germany), visual field (measured using Humphrey Field Analyzer [HFA] II [Carl Zeiss Meditech, Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA]), ERG, and contrast sensitivity (Vistech 6500 chart, Vistech Consultants, Inc., Dayton, OH, USA) were measured at baseline and then measured again after 3 months of CGA supplementation. RP patients with a residual visual field of less than 10 degrees in any direction on the visual field examination, a best corrected visual acuity of less than 50 ETDRS letters, a history of CGA supplementation within the prior 3 months, or abnormal liver enzyme (aspartate and alanine aminotrasferase > 40 IU/L, alkaline phosphatase > 130 IU/L), creatinine (> 1.4 mg/dL), or blood urea nitrogen levels (> 26 mg/dL) suggestive of liver or kidney dysfunction were excluded from the study.
The amplitude of each ring on mERG was evaluated as the primary outcome measure. The eye with the larger amplitude on ring 1 of mERG was selected for analysis. Additionally, the total point score on HFA with target size III was used for the visual field evaluation. Full-field ERG followed the guidelines of the International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision (ISCEV) (21); rod-specific and standard bright flash ERG were both recorded after a minimum of 20 min of dark adaptation, and the photopic 30 Hz flicker and single flash cone response was recorded following 10 min of light adaptation. The full-field rod, cone and combined response amplitude was also studied as a secondary outcome measure. The log10 (contrast sensitivity) at each spatial frequency (1.5, 3, 6, 12, and 18 cycles/degree) was also used as a secondary outcome measure. Any systemic adverse effects and subjective improvement of vision were also evaluated.
Statistical analyses
IBM SPSS Statistics 21 for Windows (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for statistical analyses. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for analysis of parameters before and after CGA supplementation. A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Ethics statement
The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB No. 1008-131-329), and the study conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was confirmed by the board.
RESULTS
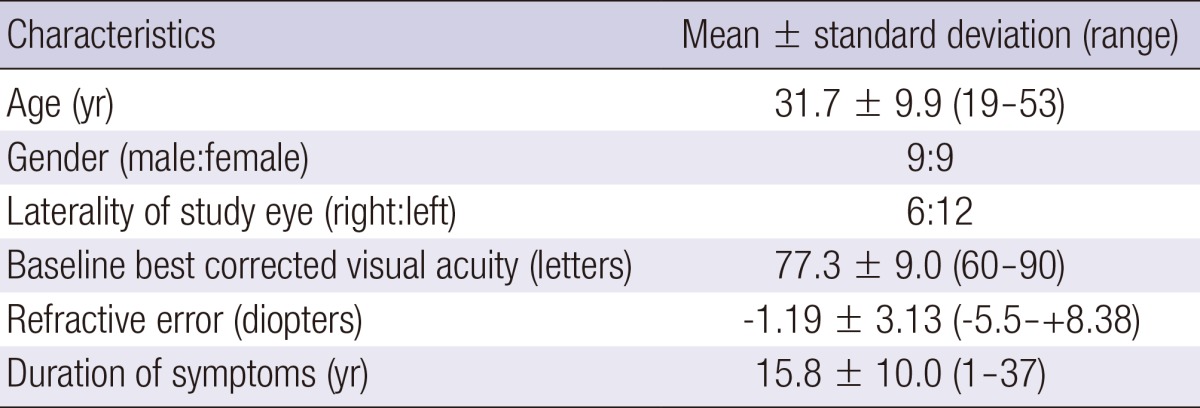
The demographic characteristics of the study patients are listed in Table 1. The mean age of the patients included in the study was 31.7 ± 9.9 yr. The mean visual acuity was 77.3 ± 9.0 letters.
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of the patients included in this study
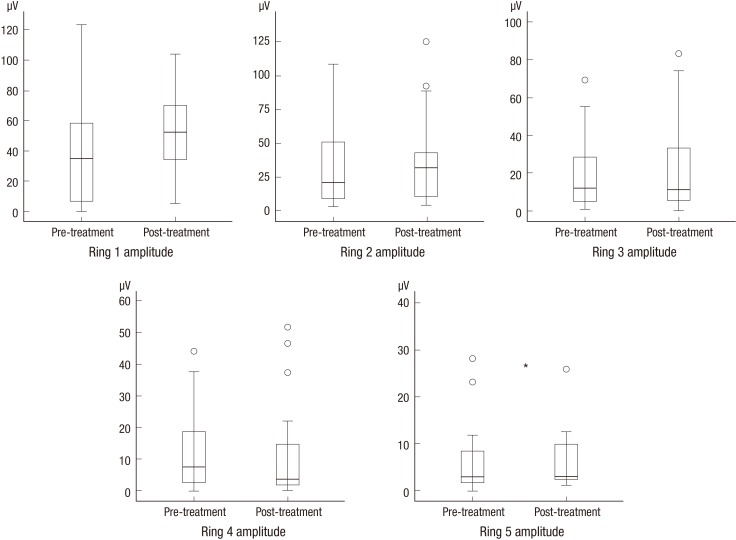
The pre- and post-treatment measurements are compared in Table 2. There was no significant change in best corrected visual acuity, total point score on HFA, rod, cone and combined response amplitude on standard ERG, or contrast sensitivity; however, the amplitude of ring 5 on mERG was significantly higher after 3 months of CGA supplementation (7.2 ± 9.5 vs 8.3 ± 10.8 nV/deg2, mean ± standard deviation, P = 0.022, Wilcoxon signed-rank test) (Fig. 1).
Table 2.
A comparison of visual function parameters before and after CGA supplementation
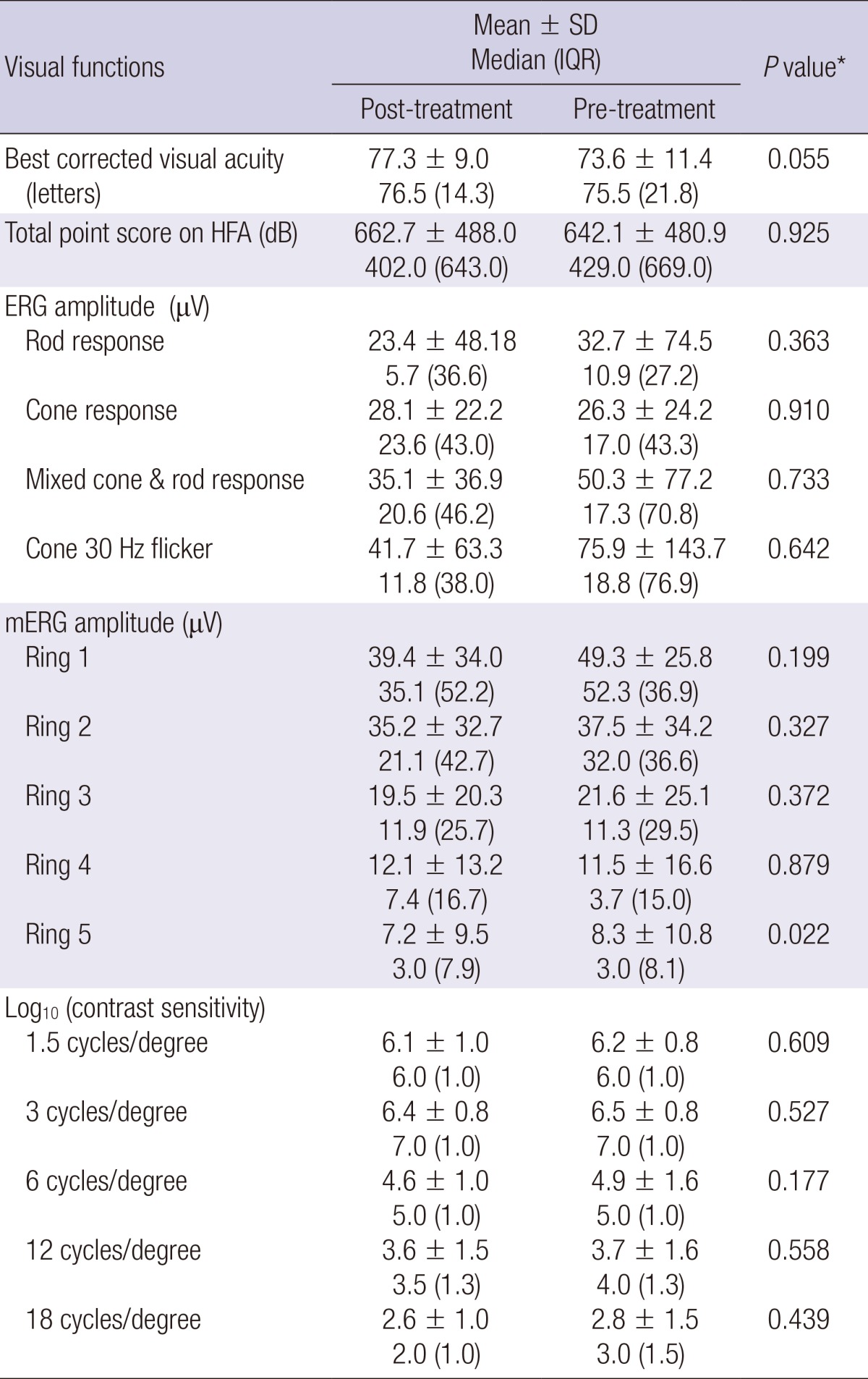
*Wilcoxon signed-rank test. SD, standard deviation; IQR, interquartile range; CGA, chlorogenic acid; HFA, Humphrey Field Analysis; ERG, electroretinography; mERG, multifocal electroretinography.
Fig. 1.
A comparison of amplitude on multifocal electroretinography before and after CGA supplementation. *P < 0.05. CGA, chlorogenic acid.
No systemic adverse events were noted with 3 months' supplementation of CGA. Five patients expressed a subjective improvement of visual function, while 12 patients said they experienced no change. No patients noticed deterioration of visual function during the study period.
DISCUSSION
This study demonstrated that CGA significantly increased the amplitude of mERG, raising the possibility of a beneficial effect on the peripheral area at the margins of the retinal degeneration. However, this study failed to show a significant improvement in visual outcome measurements after CGA supplementation.
Considering the pathophysiology of photoreceptor cell damage in hereditary retinal degeneration such as RP, various anti-oxidants have been recommended to delay progression in these patients. However, there are difficulties in evaluating the effect on the degree of progression for slowly progressing diseases like RP, as conducting clinical trials for extended periods of time and controlling dietary intake is challenging. Therefore, the effect of anti-oxidants in RP patients is generally based on theoretical background, while the evidence from clinical trials is sparse. Vitamin A has been found to decrease the rate of decline in ERG amplitude and marginally affect the rate of decline in the visual field area (22). Docosahexaenoic acid, an omega-3 fatty acid, was found to have an additional benefit in patients naive to vitamin A supplementation in the initial 2 yr (8). Lutein supplementation slowed the loss of the mid-peripheral visual field in nonsmoking adults with RP taking vitamin A (5).
Peripheral ring 5 amplitude on mERG increased with CGA intake in our study. In a previous study (20), mERG was suggested as an effective tool for the long-term follow-up of disease progression and as an objective outcome measure in studies evaluating treatment outcome in RP patients. Ring 5 amplitude was found to be strongly correlated with the scotopic ERG mixed cone-rod response amplitude, but only mildly correlated with the visual field area. Other previous studies evaluating the effect of antioxidants in RP have not utilized mERG as a visual function evaluation tool (5-9). This increase in amplitude with CGA intake may indicate the possibility of a peripheral scotopic functional improvement effect, and raises the necessity of a long-term study verifying this effect of CGA using other more gross measurement tools, such as visual field measurement. Changes in mERG could be detected in Korean RP patients, who had been reported to have more advanced peripheral visual field defects, while central vision was more preserved (23); these patients may be possible candidates to benefit most from CGA supplementation to improve peripheral visual function.
Previous studies that have noted the beneficial effect of anti-oxidants on the progression of RP have also identified improved visual function at the periphery of the retina, which is the site where degeneration occurs. Berson et al. (5) identified that lutein supplementation of 12 mg/d slowed the loss of the mid-peripheral visual field in nonsmoking adults with RP taking vitamin A. Our finding of improvement in the most-peripheral ring 5 amplitude on mERG is consistent with this hypothesis. There has only been 1 study to date that has reported a benefit in the preservation of central visual function, which was a long-term study of 4 to 6 yr of omega-3 supplementation in RP patients taking vitamin A (9). Parameters associated with central visual function such as total point score on the central visual field examination on HFA, contrast sensitivity, and photopic 30-Hz flicker amplitude on ERG need a longer follow-up time, and as expected, showed no significant change with short-term CGA supplementation. In order to evaluate the possible benefits to central visual function, a long-term study with a supplementation period of several years should be conducted.
There are some shortcomings in this study. The follow-up period was short to evaluate the effects of nutrition supplementation, and the long-term benefit effect remains to be clarified. In addition, this study enrolled a small number of subjects with no control group, raising the possibility of bias. This study included a heterogeneous study population with various degrees of RP progression, various genetic types, altered proteins, and mutations. Another possible factor is that the diseases of patients included in this study were not very advanced, and the patients had considerably larger residual visual function. A randomized, placebo-controlled, long-term clinical trial in a large scale must be conducted to confirm the possible benefit of CGA supplementation in RP patients. Additionally, comparative studies among anti-oxidative agents may be necessary, and CGA should be considered as an anti-oxidant that can be used in the management of RP.
In conclusion, this study confirmed the objective effectiveness of CGA in RP patients, and a clinical benefit of anti-oxidant supplementation in RP. The increased activity in the peripheral retina may raise the possibility of delaying the progressive decline in visual function in hereditary retinal degeneration.
Footnotes
This study was supported by a research grant from the company THEye Korea, Seoul, Korea (2010).
The authors report no conflicts of interest to disclose. The company THEye Korea had no role in the design or conduction of this clinical study.
References
- 1.Sancho-Pelluz J, Arango-Gonzalez B, Kustermann S, Romero FJ, van Veen T, Zrenner E, Ekström P, Paquet-Durand F. Photoreceptor cell death mechanisms in inherited retinal degeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 2008;38:253–269. doi: 10.1007/s12035-008-8045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sanz MM, Johnson LE, Ahuja S, Ekström PA, Romero J, van Veen T. Significant photoreceptor rescue by treatment with a combination of antioxidants in an animal model for retinal degeneration. Neuroscience. 2007;145:1120–1129. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.12.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Komeima K, Rogers BS, Campochiaro PA. Antioxidants slow photoreceptor cell death in mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:809–815. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Richer S, Stiles W, Statkute L, Pulido J, Frankowski J, Rudy D, Pei K, Tsipursky M, Nyland J. Double-masked, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of lutein and antioxidant supplementation in the intervention of atrophic age-related macular degeneration: the Veterans LAST study (Lutein Antioxidant Supplementation Trial) Optometry. 2004;75:216–230. doi: 10.1016/s1529-1839(04)70049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Berson EL, Rosner B, Sandberg MA, Weigel-DiFranco C, Brockhurst RJ, Hayes KC, Johnson EJ, Anderson EJ, Johnson CA, Gaudio AR, et al. Clinical trial of lutein in patients with retinitis pigmentosa receiving vitamin A. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:403–411. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Aleman TS, Duncan JL, Bieber ML, de Castro E, Marks DA, Gardner LM, Steinberg JD, Cideciyan AV, Maguire MG, Jacobson SG. Macular pigment and lutein supplementation in retinitis pigmentosa and Usher syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:1873–1881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bahrami H, Melia M, Dagnelie G. Lutein supplementation in retinitis pigmentosa: PC-based vision assessment in a randomized double-masked placebo-controlled clinical trial [ NCT00029289] BMC Ophthalmol. 2006;6:23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-6-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Berson EL, Rosner B, Sandberg MA, Weigel-DiFranco C, Moser A, Brockhurst RJ, Hayes KC, Johnson CA, Anderson EJ, Gaudio AR, et al. Further evaluation of docosahexaenoic acid in patients with retinitis pigmentosa receiving vitamin A treatment: subgroup analyses. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:1306–1314. doi: 10.1001/archopht.122.9.1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Berson EL, Rosner B, Sandberg MA, Weigel-Difranco C, Willett WC. ω-3 intake and visual acuity in patients with retinitis pigmentosa receiving vitamin A. Arch Ophthalmol. 2012;130:707–711. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2011.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dos Santos MD, Almeida MC, Lopes NP, de Souza GE. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activities of the natural polyphenol chlorogenic acid. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006;29:2236–2240. doi: 10.1248/bpb.29.2236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cho AS, Jeon SM, Kim MJ, Yeo J, Seo KI, Choi MS, Lee MK. Chlorogenic acid exhibits anti-obesity property and improves lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced-obese mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48:937–943. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kim C, Yu HG, Sohn J. The anti-angiogenic effect of chlorogenic acid on choroidal neovascularization. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2010;24:163–168. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2010.24.3.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shin JY, Sohn J, Park KH. Chlorogenic acid decreases retinal vascular hyperpermeability in diabetic rat model. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28:608–613. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.4.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xu JG, Hu QP, Liu Y. Antioxidant and DNA-protective activities of chlorogenic acid isomers. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:11625–11630. doi: 10.1021/jf303771s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Giordo R, Cossu A, Pasciu V, Hoa PT, Posadino AM, Pintus G. Different redox response elicited by naturally occurring antioxidants in human endothelial cells. Open Biochem J. 2013;7:44–53. doi: 10.2174/1874091X01307010044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yun N, Kang JW, Lee SM. Protective effects of chlorogenic acid against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat liver: molecular evidence of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J Nutr Biochem. 2012;23:1249–1255. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hoelzl C, Knasmüller S, Wagner KH, Elbling L, Huber W, Kager N, Ferk F, Ehrlich V, Nersesyan A, Neubauer O, et al. Instant coffee with high chlorogenic acid levels protects humans against oxidative damage of macromolecules. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010;54:1722–1733. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201000048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chu YF, Brown PH, Lyle BJ, Chen Y, Black RM, Williams CE, Lin YC, Hsu CW, Cheng IH. Roasted coffees high in lipophilic antioxidants and chlorogenic acid lactones are more neuroprotective than green coffees. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:9801–9808. doi: 10.1021/jf902095z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ito H, Sun XL, Watanabe M, Okamoto M, Hatano T. Chlorogenic acid and its metabolite m-coumaric acid evoke neurite outgrowth in hippocampal neuronal cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008;72:885–888. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nagy D, Schönfisch B, Zrenner E, Jägle H. Long-term follow-up of retinitis pigmentosa patients with multifocal electroretinography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008;49:4664–4671. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marmor MF, Fulton AB, Holder GE, Miyake Y, Brigell M, Bach M International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision. ISCEV Standard for full-field clinical electroretinography (2008 update) Doc Ophthalmol. 2009;118:69–77. doi: 10.1007/s10633-008-9155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Berson EL, Rosner B, Sandberg MA, Hayes KC, Nicholson BW, Weigel-DiFranco C, Willett W. A randomized trial of vitamin A and vitamin E supplementation for retinitis pigmentosa. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993;111:761–772. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1993.01090060049022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hwang JS, Yu HG. Visual field defect of patients with retinitis pigmentosa in Koreans. Korean J Optom Vis Sci. 2012;11:42–47. [Google Scholar]