Abstract
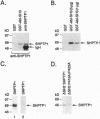
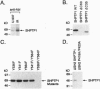
c-Abl is a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase that is activated by certain DNA-damaging agents. The present studies demonstrate that nuclear c-Abl binds constitutively to the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHPTP1. Treatment with ionizing radiation is associated with c-Abl-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of SHPTP1. The results demonstrate that the SH3 domain of c-Abl interacts with a WPDHGVPSEP motif (residues 417-426) in the catalytic domain of SHPTP1 and that c-Abl phosphorylates C terminal Y536 and Y564 sites. The functional significance of the c-Abl-SHPTP1 interaction is supported by the demonstration that, like c-Abl, SHPTP1 regulates the induction of Jun kinase activity following DNA damage. These findings indicate that SHPTP1 is involved in the response to genotoxic stress through a c-Abl-dependent mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brach M. A., Hass R., Sherman M. L., Gunji H., Weichselbaum R., Kufe D. Ionizing radiation induces expression and binding activity of the nuclear factor kappa B. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):691–695. doi: 10.1172/JCI115354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. R., Meyer C. F., Tan T. H. Persistent activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in gamma radiation-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):631–634. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai Z., Pendergast A. M. Abi-2, a novel SH3-containing protein interacts with the c-Abl tyrosine kinase and modulates c-Abl transforming activity. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 1;9(21):2569–2582. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta R., Rubin E., Sukhatme V., Qureshi S., Hallahan D., Weichselbaum R. R., Kufe D. W. Ionizing radiation activates transcription of the EGR1 gene via CArG elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10149–10153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyster J., Baskaran R., Wang J. Y. Src homology 2 domain as a specificity determinant in the c-Abl-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal repeated domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1555–1559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller S. M., Knudsen B., Hanafusa H. c-Abl kinase regulates the protein binding activity of c-Crk. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2341–2351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goga A., Liu X., Hambuch T. M., Senechal K., Major E., Berk A. J., Witte O. N., Sawyers C. L. p53 dependent growth suppression by the c-Abl nuclear tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 1995 Aug 17;11(4):791–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallahan D. E., Sukhatme V. P., Sherman M. L., Virudachalam S., Kufe D., Weichselbaum R. R. Protein kinase C mediates x-ray inducibility of nuclear signal transducers EGR1 and JUN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2156–2160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharbanda S., Pandey P., Ren R., Mayer B., Zon L., Kufe D. c-Abl activation regulates induction of the SEK1/stress-activated protein kinase pathway in the cellular response to 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30278–30281. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharbanda S., Ren R., Pandey P., Shafman T. D., Feller S. M., Weichselbaum R. R., Kufe D. W. Activation of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the stress response to DNA-damaging agents. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):785–788. doi: 10.1038/376785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharbanda S., Saleem A., Shafman T., Emoto Y., Taneja N., Rubin E., Weichselbaum R., Woodgett J., Avruch J., Kyriakis J. Ionizing radiation stimulates a Grb2-mediated association of the stress-activated protein kinase with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18871–18874. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharbanda S., Saleem A., Shafman T., Emoto Y., Weichselbaum R., Kufe D. Activation of the pp90rsk and mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinases by ionizing radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5416–5420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limoli C. L., Ward J. F. A new method for introducing double-strand breaks into cellular DNA. Radiat Res. 1993 May;134(2):160–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz U., Ravichandran K. S., Pei D., Walsh C. T., Burakoff S. J., Neel B. G. Lck-dependent tyrosyl phosphorylation of the phosphotyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP1 in murine T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1824–1834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioni T., Jackson P. K., Bchini-Hooft van Huijsduijnen O., Picard D. Cell cycle arrest by tyrosine kinase Abl involves altered early mitogenic response. Oncogene. 1995 Apr 6;10(7):1325–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D., Lorenz U., Klingmüller U., Neel B. G., Walsh C. T. Intramolecular regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP1: a new function for Src homology 2 domains. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 27;33(51):15483–15493. doi: 10.1021/bi00255a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D., Neel B. G., Walsh C. T. Overexpression, purification, and characterization of SHPTP1, a Src homology 2-containing protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1092–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raitano A. B., Halpern J. R., Hambuch T. M., Sawyers C. L. The Bcr-Abl leukemia oncogene activates Jun kinase and requires Jun for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 5;92(25):11746–11750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Ye Z. S., Baltimore D. Abl protein-tyrosine kinase selects the Crk adapter as a substrate using SH3-binding sites. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):783–795. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renshaw M. W., Lea-Chou E., Wang J. Y. Rac is required for v-Abl tyrosine kinase to activate mitogenesis. Curr Biol. 1996 Jan 1;6(1):76–83. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00424-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers C. L., McLaughlin J., Goga A., Havlik M., Witte O. The nuclear tyrosine kinase c-Abl negatively regulates cell growth. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. L., Datta R., Hallahan D. E., Weichselbaum R. R., Kufe D. W. Ionizing radiation regulates expression of the c-jun protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5663–5666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Alin K., Goff S. P. Abl-interactor-1, a novel SH3 protein binding to the carboxy-terminal portion of the Abl protein, suppresses v-abl transforming activity. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 1;9(21):2583–2597. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez I., Hughes R. T., Mayer B. J., Yee K., Woodgett J. R., Avruch J., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I. Role of SAPK/ERK kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription factor c-Jun. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):794–798. doi: 10.1038/372794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tybulewicz V. L., Crawford C. E., Jackson P. K., Bronson R. T., Mulligan R. C. Neonatal lethality and lymphopenia in mice with a homozygous disruption of the c-abl proto-oncogene. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90011-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij M., Bose R., Lin X. H., Yao B., Jarvis W. D., Grant S., Birrer M. J., Szabo E., Zon L. I., Kyriakis J. M. Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signalling in stress-induced apoptosis. Nature. 1996 Mar 7;380(6569):75–79. doi: 10.1038/380075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch P. J., Wang J. Y. A C-terminal protein-binding domain in the retinoblastoma protein regulates nuclear c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the cell cycle. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90497-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmarsh A. J., Shore P., Sharrocks A. D., Davis R. J. Integration of MAP kinase signal transduction pathways at the serum response element. Science. 1995 Jul 21;269(5222):403–407. doi: 10.1126/science.7618106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan M., Dai T., Deak J. C., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I., Woodgett J. R., Templeton D. J. Activation of stress-activated protein kinase by MEKK1 phosphorylation of its activator SEK1. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):798–800. doi: 10.1038/372798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]