Abstract
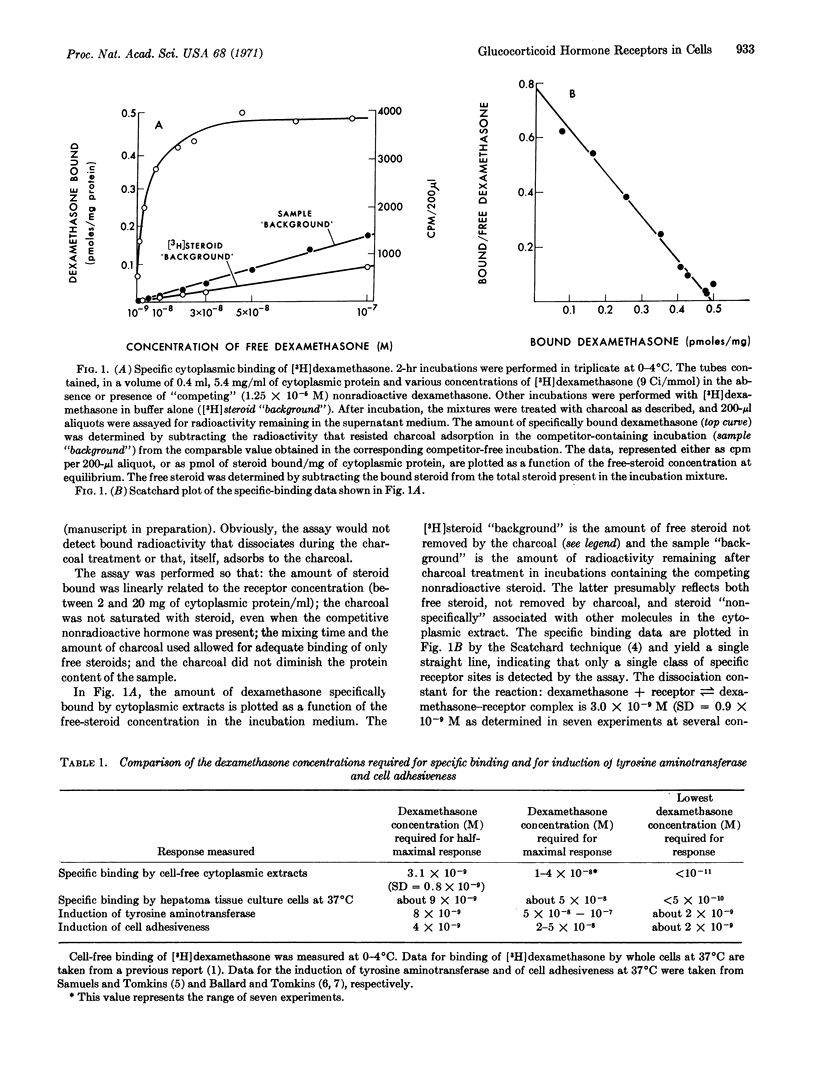
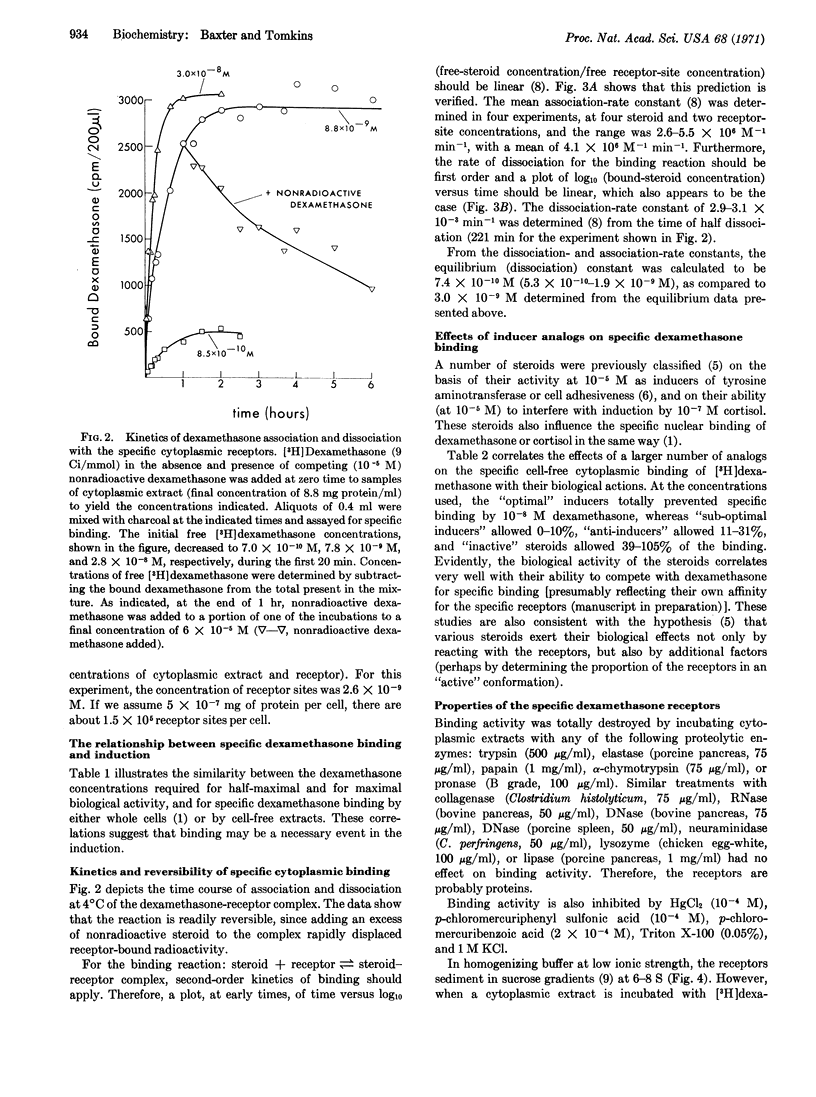
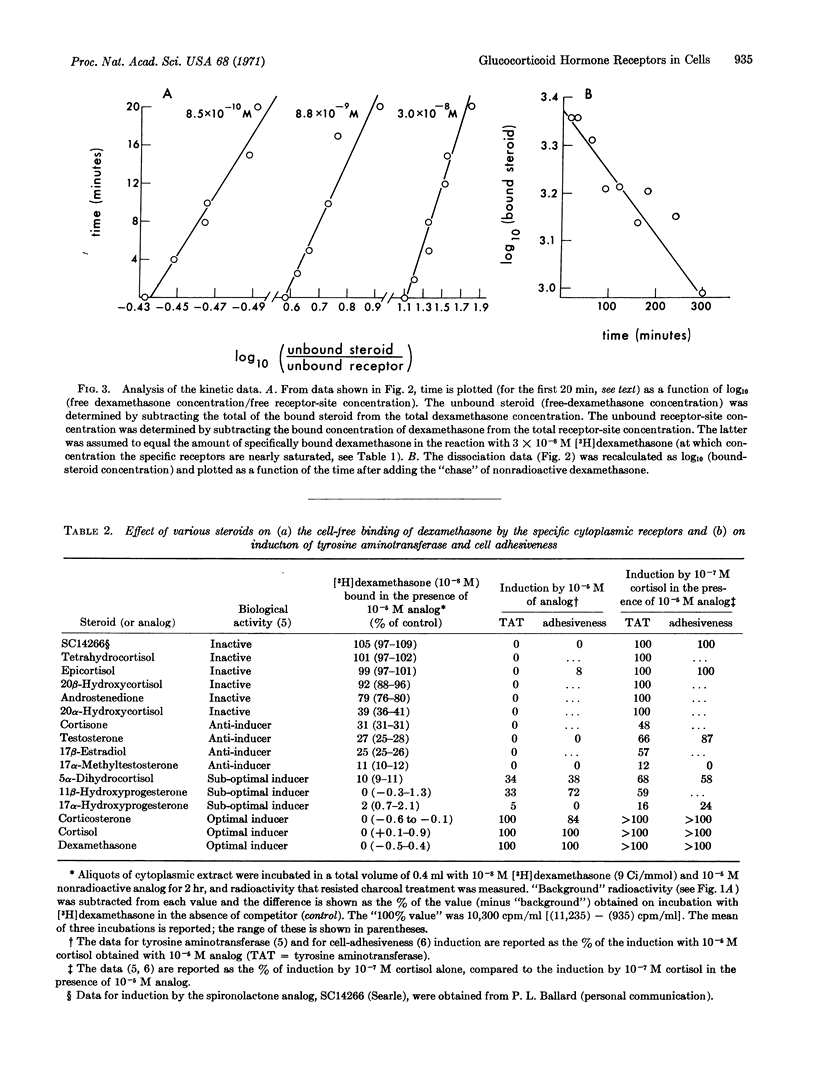
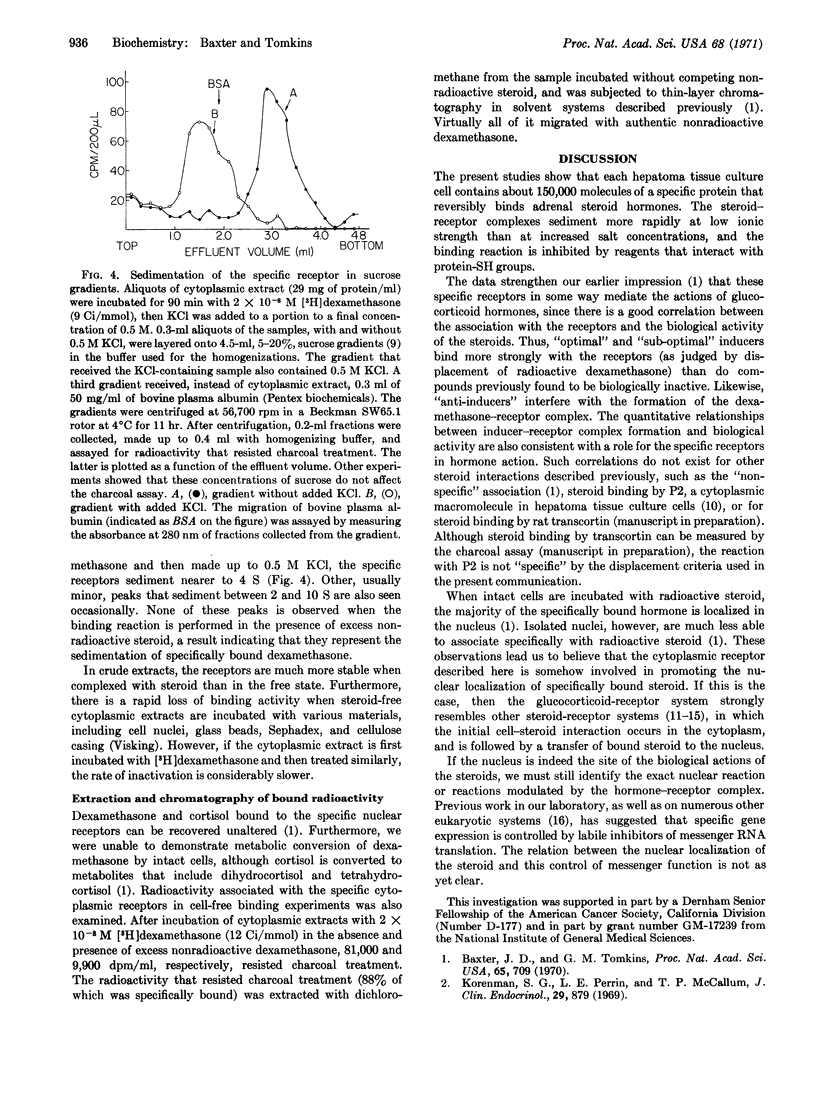
Kinetic and equilibrium studies are presented for the reversible binding of [3H]dexamethasone by “specific” macromolecular receptors in the cytoplasmic fraction of cultured rat hepatoma cells. As in the case of the nuclear receptors in the same cells, the binding affinities of various steroids for the cytoplasmic receptors are closely correlated with the activities of these compounds as inducers of both tyrosine aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.5) and cell adhesiveness. This suggests that the binding reaction is important for the biological effects of the hormones. Steroid-binding activity is inhibited by various proteases, mercurials, and 1 M KCl, but not by DNase or RNase. The receptors sediment in sucrose gradients in 0.5 M KCl near 4S, and at lower ionic strength near 7S; some of their physical properties are altered upon binding steroid. Bound dexamethasone can be recovered from the receptors as the unaltered steroid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard P. L., Tomkins G. M. Glucocorticoid-induced alteration of the surface membrane of cultured hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Oct;47(1):222–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.1.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L., Tomkins G. M. Hormone induced modification of the cell surface. Nature. 1969 Oct 25;224(5217):344–345. doi: 10.1038/224344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. The relationship between glucocorticoid binding and tyrosine aminotransferase induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):709–715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M., Brändle W., Biesewig D., Sekeris C. E. On the mechanism of hormone action. XVI. Transfer of (1,2-3H2)cortisol from the cytoplasm to the nucleus of rat-liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 14;208(1):125–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang S., Anderson K. M., Liao S. Receptor proteins for androgens. On the role of specific proteins in selective retention of 17-beta-hydroxy-5-alpha-androstan-3-one by rat ventral prostate in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 25;244(24):6584–6595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. S., Tomkins G. M. Steroid hormone binding to a macromolecule from hepatoma tissue culture cells. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 10;244(17):4761–4767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Suzuki T., Kawashima T., Stumpf W. E., Jungblut P. W., DeSombre E. R. A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):632–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenman S. G., Perrin L. E., McCallum T. P. A radio-ligand binding assay system for estradiol measurement in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Jul;29(7):879–883. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-7-879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., Sherman M. R., Toft D. O. Progesterone "receptors" in the cytoplasm and nucleus of chick oviduct target tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):501–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tomkins G. M. Relation of steroid structure to enzyme induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug 28;52(1):57–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaneck G. E., Chu L. L., Edelman I. S. Stereospecific binding of aldosterone to renal chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5382–5389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins G. M., Gelehrter T. D., Granner D., Martin D., Jr, Samuels H. H., Thompson E. B. Control of specific gene expression in higher organisms. Expression of mammalian genes may be controlled by repressors acting on the translation of messenger RNA. Science. 1969 Dec 19;166(3912):1474–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3912.1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



