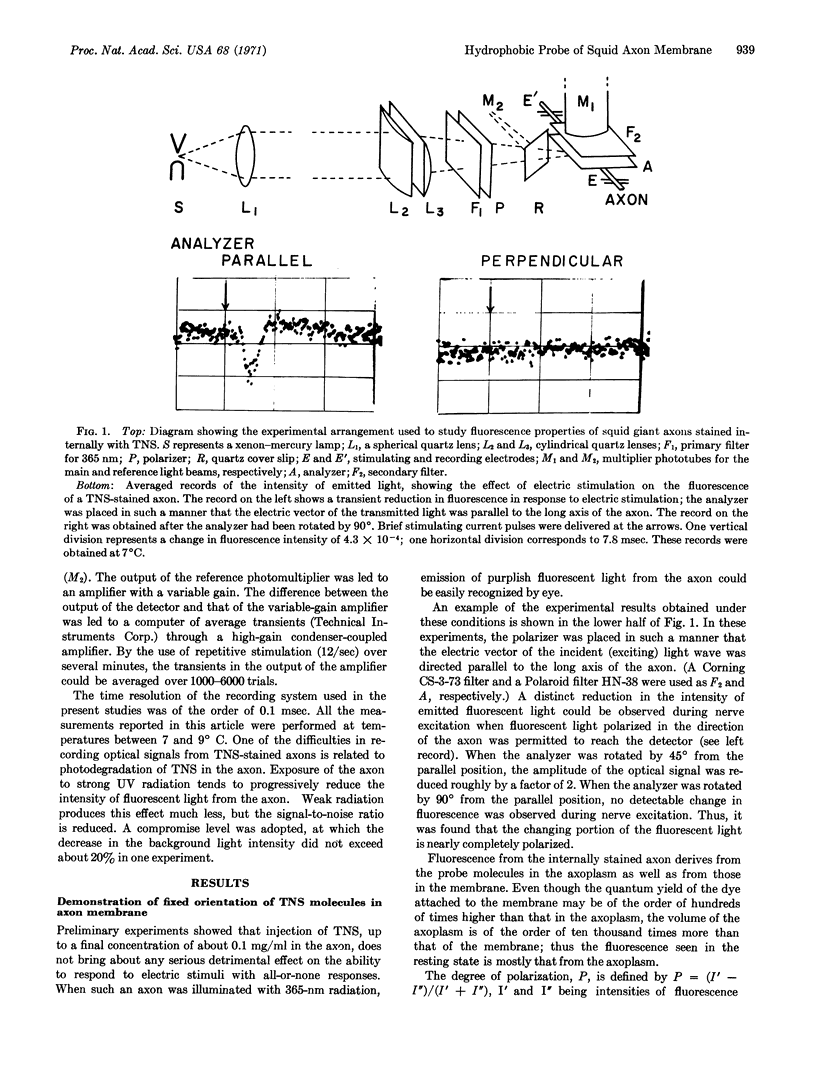
Abstract
A hydrophobic probe, 2-p-toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate (TNS), was introduced into the interior of a squid giant axon and fluorescene properties of the TNS-stained axon were examined under illumination with polarized ultraviolet light. A transient reduction in fluorescence was observed when the axon was stimulated electrically. The light waves contributing to this fluorescence change were found to be nearly completely polarized, indicating that the probe molecules in the membrane are highly oriented. The emission spectra of these TNS-stained axons were examined at rest and during nerve excitation. The results obtained are considered to support the view that the process of nerve excitation is accompanied by a transition of the axon membrane from a hydrophobic to a hydrophilic state.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duke J. A., McKay R., Botts J. Conformational change accompanying modification of myosin ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Nov 8;126(3):600–603. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. O., Edelman G. M. Fluorescent probes for conformational states of proteins. I. Mechanism of fluorescence of 2-p-toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate, a hydrophobic probe. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):1908–1919. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metuzals J., Izzard C. S. Spatial patterns of threadlike elements in the axoplasm of the giant nerve fiber of the squid (Loligo pealii L.) as disclosed by differential interference microscopy and by electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):456–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki I. I., Carnay L., Watanabe A. Transient changes in extrinsic fluorescence of nerve produced by electric stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1362–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki I., Lerman L., Watanabe A. Analysis of excitation process in squid giant axons under bi-ionic conditions. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jan;216(1):130–138. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.1.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki I., Watanabe A., Sandlin R., Carnay L. Changes in fluorescence, turbidity, and birefringence associated with nerve excitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):883–888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


