Abstract
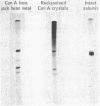
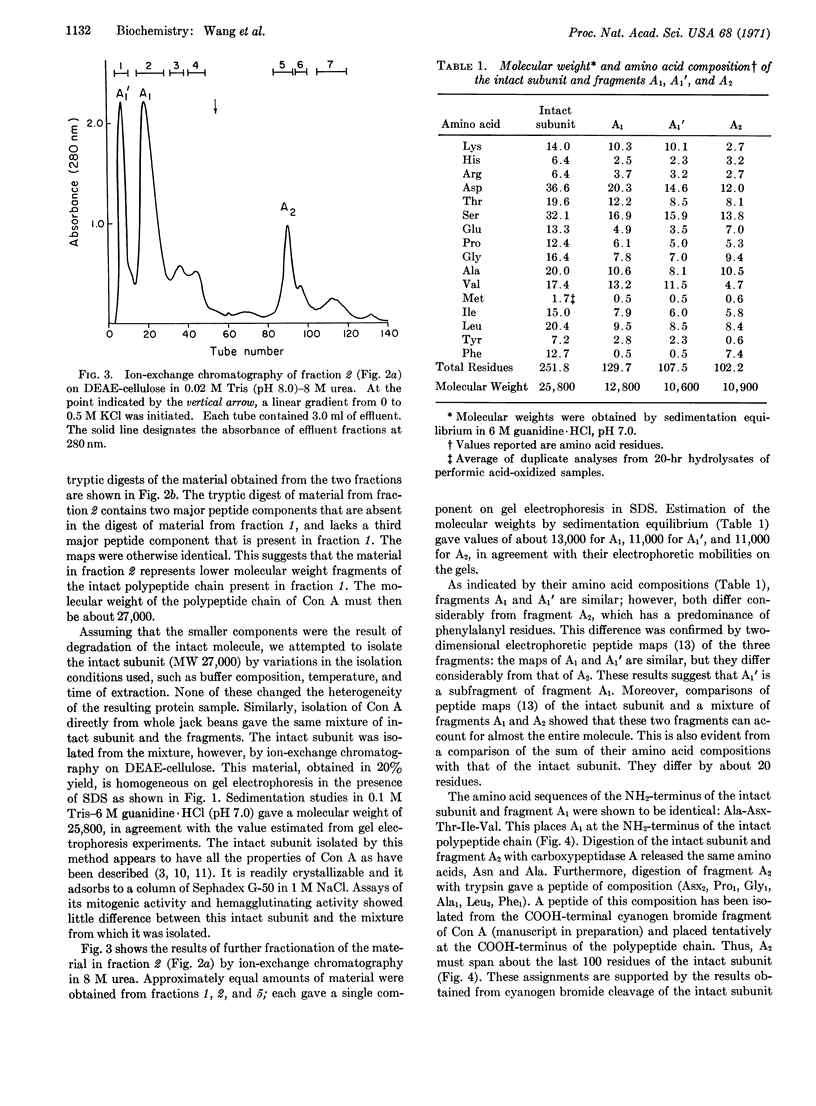
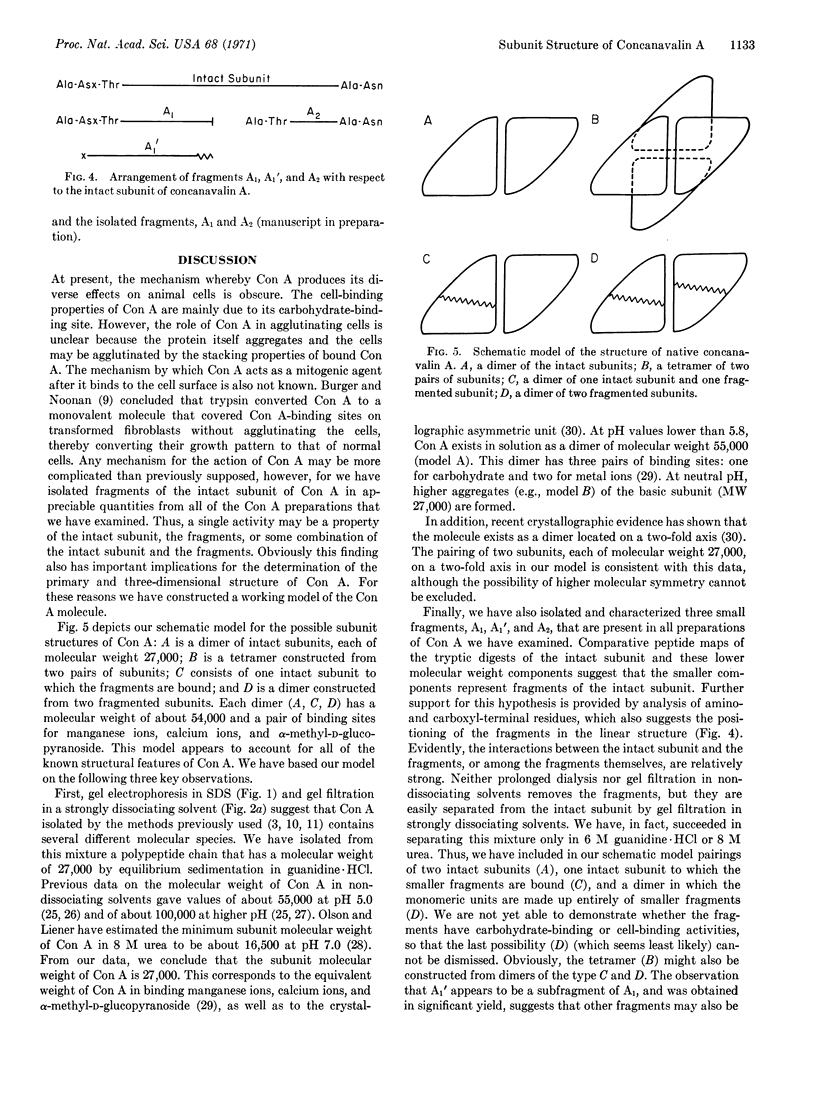
Gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and gel filtration in guanidine. HCl indicate that native concanavalin A contains several molecular species. An intact subunit of molecular weight 27,000 has been purified from this mixture. In addition, three fragments of the intact subunit have been isolated and characterized. A working model of the concanavalin A molecule has been constructed based on pairings of the intact subunit and of subunits consisting of fragments.
Keywords: gel electrophoresis, molecular weights
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler W. H., Takiguchi T., Marsh B., Smith R. T. Cellular recognition by mouse lymphocytes in vitro. I. Definition of a new technique and results of stimulation by phytohemagglutinin and specific antigens. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1049–1078. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal B. B., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. VI. Isolation of concanavalin A by specific adsorption on cross-linked dextran gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 23;147(2):262–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal B. B., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. VII. Physical and chemical studies on concanavalin A, the hemagglutinin of the jack bean. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):218–229. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckert W. H., Sharkey M. M. Mitogenic activity of the jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis) with rabbit peripheral blood lymphocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(4):337–341. doi: 10.1159/000230361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M., Noonan K. D. Restoration of normal growth by covering of agglutinin sites on tumour cell surface. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):512–515. doi: 10.1038/228512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummingham B. A., Gottlieb P. D., Konigsberg W. H., Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. V. Partial amino acid sequence of the light chain. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1983–1994. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W., Dulbecco R., Burger M. M. Temperature-dependent surface changes in cells infected or transformed by a thermosensitive mutant of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):283–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gall W. E., Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. I. Isolation and characterization of the whole molecule, the polypeptide chains, and the tryptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1950–1958. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gottlieb P. D. A genetic marker in the variable region of light chains of mouse immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1192–1199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb P. D., Cunningham B. A., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. VI. Amino acid sequence of the light chain. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 4;9(16):3155–3161. doi: 10.1021/bi00818a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J., Kaufman H. W., Kalb A. J. An x-ray crystallographic study of concanavalin A. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar 14;48(2):365–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Sachs L. Interaction of the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A with normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1418–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Lustig A. The molecular weight of concanavalin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Liener I. E. Some physical and chemical properties of concanavalin A, the phytohemagglutinin of the jack bean. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):105–111. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Liener I. E. The association and dissociation of concanavalin A, the phytohemagglutinin of the jack bean. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3801–3808. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell A. E., Leon M. A. Reversible interaction of human lymphocytes with the mitogen concanavalin A. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Oct;62(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90560-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J. H., EDELMAN G. M. Comparisons of Bence-Jones proteins and L polypeptide chains of myeloma globulins after hydrolysis with trypsin. J Exp Med. 1963 Jul;118:41–53. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B., Howell S. F. Identification of Hemagglutinin of Jack Bean with Concanavalin A. J Bacteriol. 1936 Aug;32(2):227–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.2.227-237.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]