Abstract
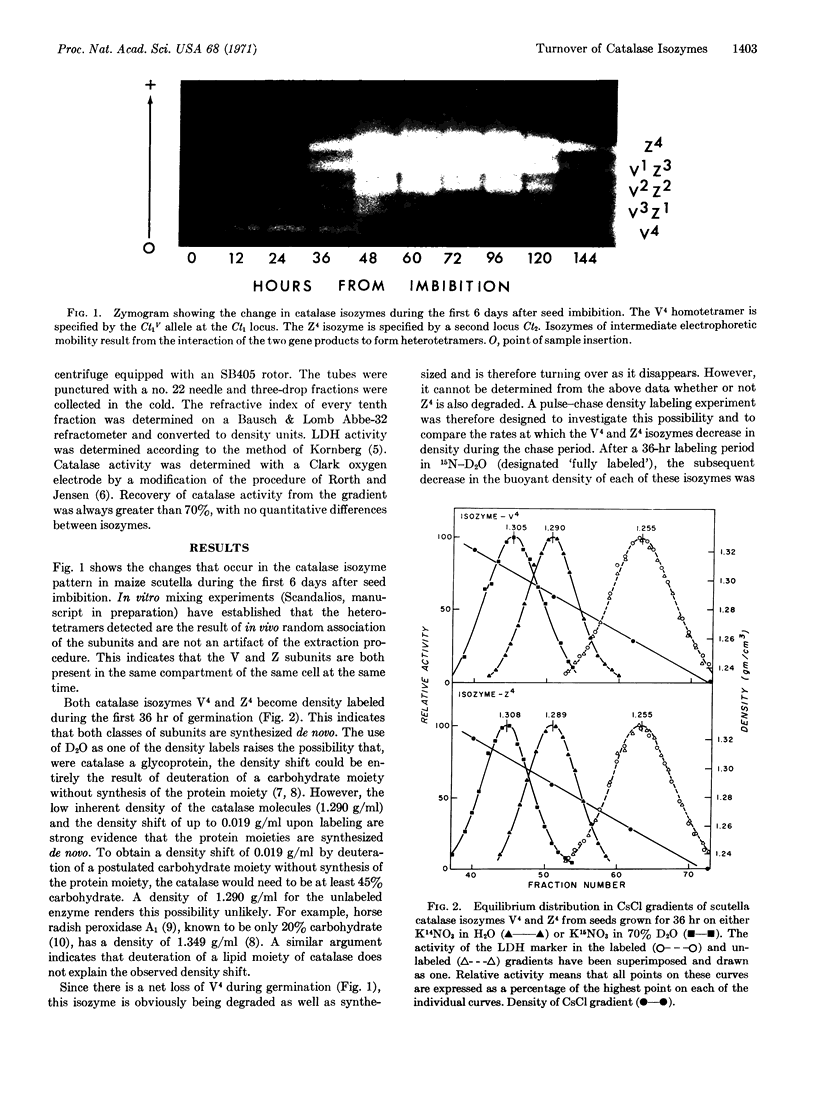
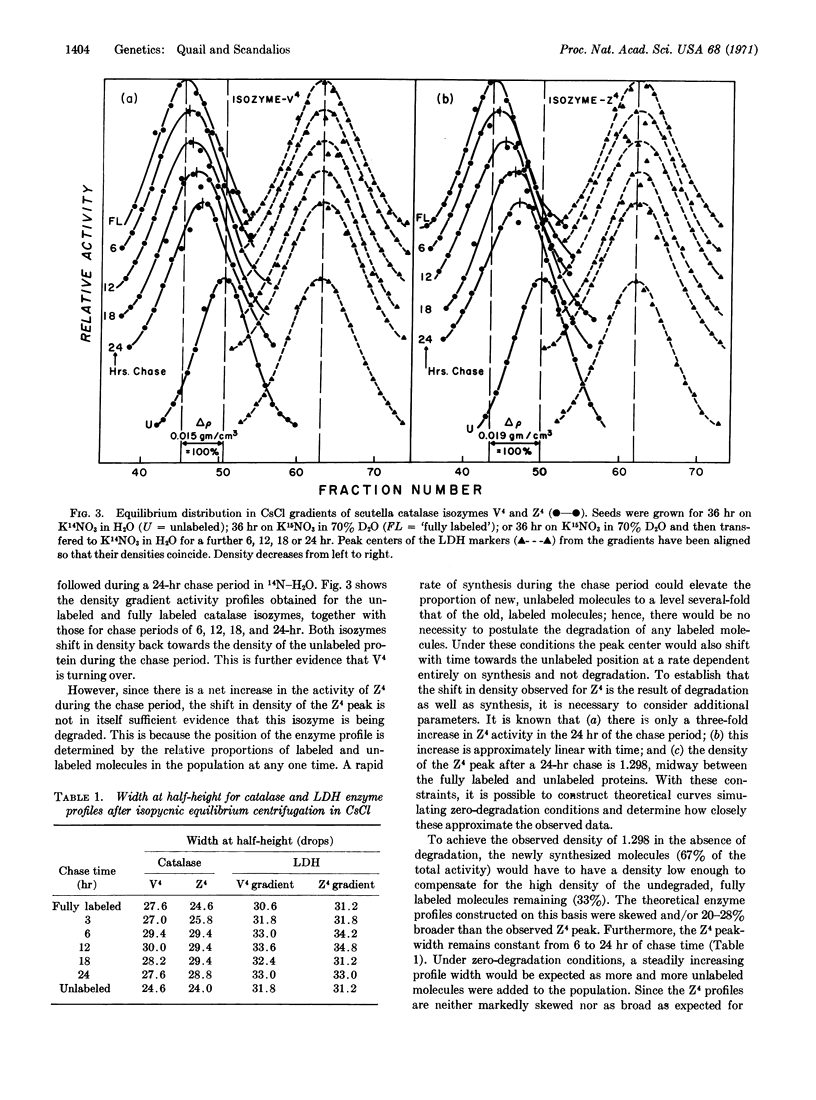
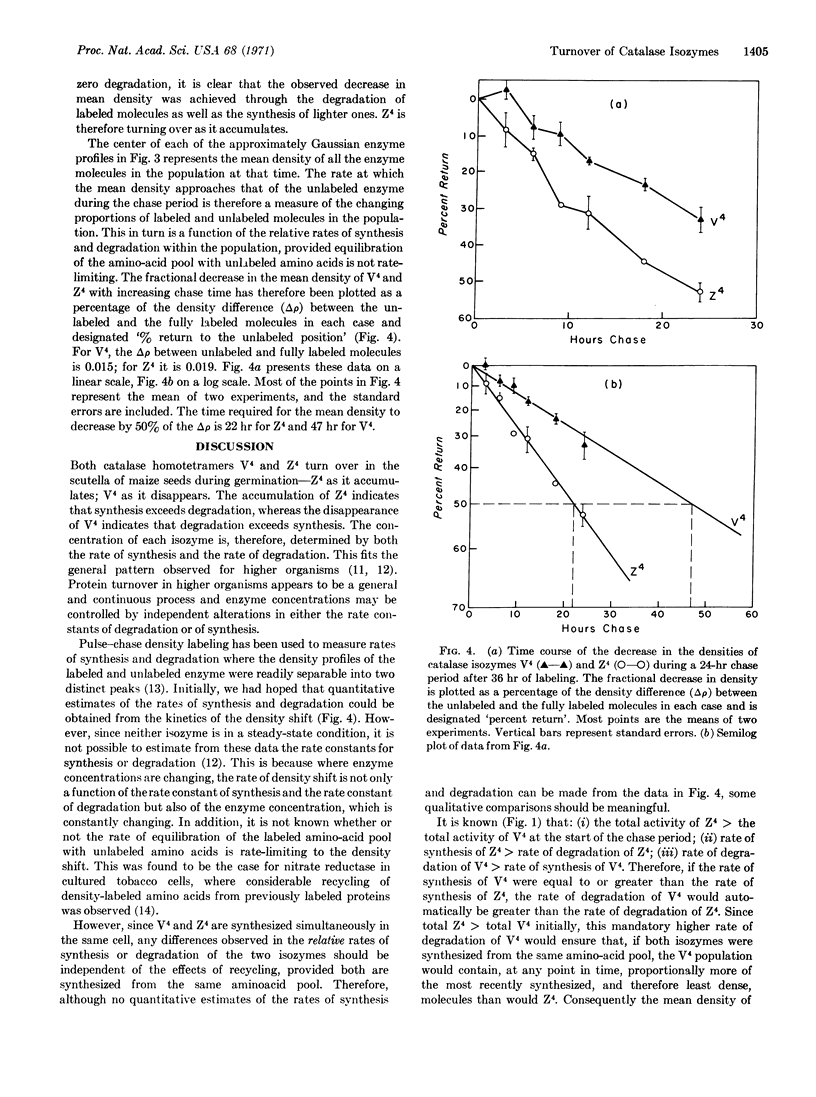
The turnover of two homotetramers of catalase, V4 and Z4, specified by genes at two separate loci, has been studied during germination of maize seed by the techniques of density labeling and starch-gel electrophoresis. Both isozymes were shown to be turning over during this time. However, Z4 accumulates because the rate of synthesis exceeds the rate of degradation, whereas V4 slowly disappears because the rate of degradation exceeds the rate of synthesis. Evidence is also presented that the rate of synthesis of Z4 exceeds that of V4, which suggests that this may be a major factor in the differential expression of the two catalase genes.
Keywords: density labeling, synthesis, degradation, starch-gel electrophoresis
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anstine W., Jacobsen J. V., Scandalios J. G., Varner J. E. Deuterium oxide as a density label of peroxidases in germinating barley embryos. Plant Physiol. 1970 Feb;45(2):148–152. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filner P., Varner J. E. A test for de novo synthesis of enzymes: density labeling with H2O18 of barley alpha-amylase induced by gibberellic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1520–1526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filner P., Varner J. E., Wray J. L. Environmental or developmental changes cause many enzyme activities of higher plants to rise or fall. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):358–367. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HU A. S., BOCK R. M., HALVORSON H. O. Separation of labeled from unlabeled proteins by equilibrium density gradient sedimentation. Anal Biochem. 1962 Dec;4:489–504. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quail P. H., Varner J. E. Combined gradient-gel electropooresis procedures for determining buoyant densities or sedimentation coefficients of all multiple forms of an enzyme simultaneously. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):344–355. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90425-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorth M., Jensen P. K. Determination of catalase activity by means of the Clark oxygen electrode. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):171–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandalios J. G. Subunit dissociation and recombination of catalase isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1035–1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Doyle D. Control of enzyme levels in animal tissues. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:929–976. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.004433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon L. M., Kay E., Lew J. Y. Peroxidase isozymes from horseradish roots. I. Isolation and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 10;241(9):2166–2172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. S., Neidhardt F. C. Synthesis and inactivation of aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetases during growth of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 14;43(3):529–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielke H. R., Filner P. Synthesis and turnover of nitrate reductase induced by nitrate in cultured tobacco cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1772–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



