Abstract
Background
Following a mass distribution of long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) in Benin, we used WHO guidelines to develop an assessment tool which is described in this report. It involved assessment of the three WHO indicators: survivorship, integrity and bio-efficacy.
Methods
To evaluate the assessment tool, we selected four communities, two in the Southern part of the country, and two in the North. One of the two assessment communities in each geographic setting had ready access to water and a higher reported frequency of washing LLINs. It was assumed that nets in communities with greater washing frequencies would show greater loss of durability. If the tool was sensitive enough to detect such differences, the field testing would confirm its suitability for general use in different settings in Benin. While durability indicators of survival and fabric integrity were quantified using standard WHO methodology, bio-efficacy was assessed using a ‘new’ alternative (to the WHO bioassay test), involving gas chromatography. Additionally, data management used current internet technology for ‘real time’ analysis at a central monitoring location.
Results
While no difference in survivorship was observed between sites with ready access to water for washing, both in the North and the South, there was a significant difference in integrity. In the South and in the North, nets from sites near water (Kessounou and Malanville) showed greater damage to integrity than did the nets from Allada and Kandi (sites far from water). As expected, LLIN integrity was significantly lower when a community was near water (p < 0.01). Bio-efficacy measurements, based on GC, were found to be so variable.
Conclusion
A rapid decrease of the LLINs fabric integrity was observed in areas near water for washing following the first 6 months post-distribution. Due to the way that the insecticide is incorporated into the LLIN fiber and its migration to the surface, confounding results were observed with the GC analysis suggesting that the WHO bio-efficacy method may also be similarly affected. The report of other assessments could help to better understand the durability of the LLINs.
Keywords: LLIN, Monitoring, Survivorship, Fabric integrity, Gas chromatography
Background
Malaria remains a major health issue in Sub-Saharan Africa. In addition to taking a toll in terms of health, it consumes up to 40% of public health expenditure in poor countries, an estimated cost of US$ 12 billion in lost Gross Domestic Product (GDP) every year in Africa [1]. In Benin, malaria accounts for 39.7% of health care issues. It is ranked top as one of the major diseases affecting communities [2].
Recently, it has been shown that the use of insecticide-treated materials can reduce malaria morbidity by 50 to 60% and malaria mortality by 20% [3-6]. WHO recommends that countries integrate Long Lasting Insecticide-treated Nets (LLINs) use into national plans against malaria. Among these treated materials, mosquito nets impregnated with pyrethroids are considered to be a powerful prevention tool whose mode of intervention is to break human contact with the vector [7]. LLINs provide both a physical and chemical barrier against malaria vectors [8,9]. Under epidemiological and socio-economic conditions of malaria-endemic countries, LLINs are presently the only usable method for individual and collective protection [10]. In recent years, funds allocated to the fight against malaria have significantly increased allowing considerable progress in the availability of LLINs [11,12]. At the individual level, they protect the user against mosquito bites, and at community level, they kill enough mosquitoes to reduce the number of bites in the community at large. This effect of insecticide treated nets (ITNs) on mosquito vectors may not occur unless the majority (at least 80%) of the targeted community uses them. The lethal effect of the insecticide is then reflected in younger populations of mosquitoes, and a drastic decrease of parasite transmission [13,14]. Therefore, large-scale LLINs have become a good vector control strategy in public health [15-17].
In July 2011, the Government of Benin with the support of the President’s Malaria Initiative (PMI) conducted a mass distribution campaign of Long Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLINs). This mass distribution campaign comes to reinforce the Indoor Residual Spray (IRS) implemented in Benin since 2008. Overall, more than 4 million of LLINs were distributed across all the 77 communes of Benin. This mass distribution can significantly increase the national coverage and the use of LLINs in Benin. To maintain the impact of this vector control strategy, it is important to replace nets that do not meet WHO standards (low durability) [18,19] in a timely way such that ongoing impact is not affected.
To assess LLIN durability, WHO recommends [20] quantifying three indicators: survivorship, fabric integrity and bio-efficacy. This study describes a monitoring (tracking) tool implemented and field tested in Benin to assess the durability of the LLINs distributed. We eventually plan to use the observed rate of change in the indicators to better describe the rate at which the impact of the intervention could change. Results are discussed to inform national malaria control policies but also to show the advantages and the limitations of the new methodological approach used in this study to assess LLINs bio-efficacy.
Methods
Study sites
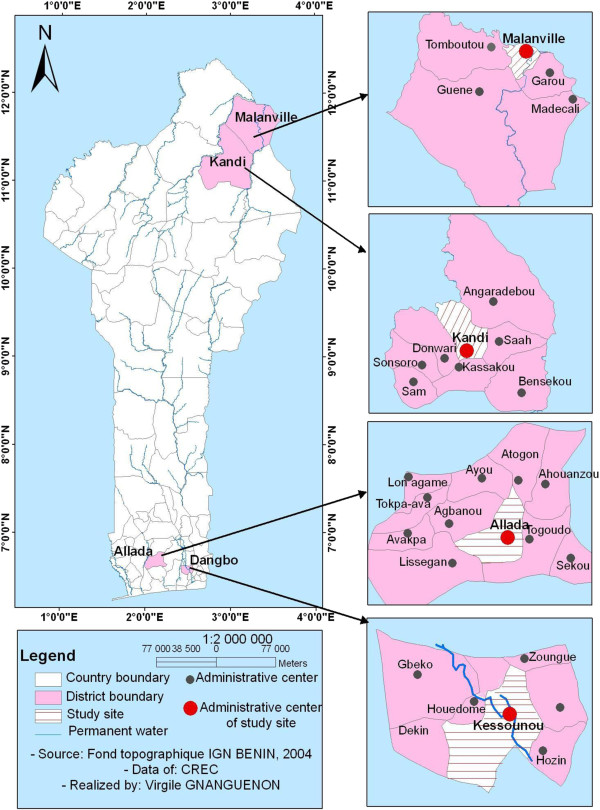
Four arrondissements (sub districts) were selected, two in the South: Kessounou, in Oueme department and Allada, in Atlantic department, and two in the North: Kandi1 and Malanville, both in Alibori department (Figure 1). Residents of Kessounou, located on the Oueme River, have ready access to water for washing nets. In contrast, residents of Allada must carry water for washing to their homes. Similar criteria (easy access to washing site versus more difficult access) were applied to the selection of tracking sites in the North. Malanville is located near the Niger River, where water for washing nets is easily accessible. In contrast, Kandi, like Allada in the south, has a more remote water source.
Figure 1.
A map of Benin showing LLIN tracking sites: Kessounou and Allada in the South and Malanville and Kandi in the North.
To test the hypothesis that conditions on the ground affect indicators of LLIN useful life, tracking sites were intentionally selected because of ‘differences’ that would, most likely, change loss rates associated with the three indicators: (1) proximity to water for washing LLINs (expected to increase loss associated with durability and bio-efficacy by increasing the frequency of net washing); and (2) mosquito biting density/nuisance level (expected to increase loss associated with durability by increasing the frequency of LLIN use, and in turn LLIN wear and tear). Table 1 summarizes these differences.
Table 1.
LLIN tracking sites: geographic location, climate, water for washing LLIN available/not available in the community; estimated frequency of washing*
|
*Based on questionnaire administered at T
6
| |
| -Water not available; estimated percentage of residents who washed the LLIN > 5 times between T0 and T6*: ≤ 0.5% (n = 43/871) |
Allada
|
| |
South Benin |
| |
Climate: Guinean coastal ‘upland’ away from Oueme River |
| |
Kandi 1
|
| |
North Benin |
| |
Climate: Sudanian ‘upland’ away from Niger River |
| LLINs washed ‘at site’; -estimated percentage of residents who washed the LLIN >5 times between T0 and T6: 16% (n = 157/984) |
Kessounou
|
| South Benin | |
| Climate: Guinean coastal community on Oueme River | |
|
Malanville
| |
| Geography: North Benin | |
| Climate: Sudanian community on Niger River | |
Approximately 500 households at each site (one LLIN/household) were tracked *based on questionnaire administered to households at T 6 .
Ethical consideration
This tracking study was planned under the Ministry of Health and approved by the National Ethics Committee for Health Research of the Ministry of Health of Benin. Community leaders were informed before the study and all gave consent before initiation. Written consent was also obtained from all participating households.
LLINs used in the study
In July 2011, around four millions of Olyset® nets, a polyethylene 150D LLIN (PE-150D) impregnated with permethrin (2%), were distributed throughout the country. The monitoring tool was used at the four sites to monitor the durability of the LLIN product distributed in order to provide information for future procurement according to WHO guidelines [20].
Household census and LLINs distribution
Before the distribution campaign, a census of all households was carried out throughout the country including our study sites. The census and the distribution process was already described by the Ministry of Health [21]. The census recorded the name of the village, the name of the head of household, the household identification number, the number of adults and children living in the house and distributed a coupon, used to obtain the LLINs. The information was recorded in a master list. Net allocation to the household was based on the household size and the ratio one net for two persons (the national policy for universal coverage). This distribution campaign covered an average of 90% of the households in the country.
LLINs distributed have labels sewn into them at factory that helps to distinguish them from those distributed during other campaigns or received from other sources.
Households sampling and bar coding of LLINs (T0)
WHO suggested estimating sample size on the basis of the attrition of the LLIN product. But in Benin, PE-150D product attrition rate is not known. Sample size was then estimated following the WHO guidelines, which reported that a sample of 250 LLINs will allow detection of a 10% point difference if the best-performing product has an attrition rate of 10% and a 12 point difference with an attrition rate of 20% [20]. This sample size was doubled and 500 LLINs were selected by study sites to provide more precision in point difference detection. A subsample of 50 LLINs representing 10% of the total sample was randomly selected to measure insecticidal activity.
One LLIN per household was selected at each study site. Household selection at each of the four sites took into account the number of villages to ensure a representative sampling of the study site. For example, Kessounou is divided in five villages: Kodonou, Kessounou, Glehoue, Hetin-Sota and Glahounsa. Because the assessment was based on information from 500 LLINs, approximately 100 households (LLINs) were selected at random in each of the five villages. Table 2 summarizes the selection process. Households included in each village were randomly selected from the registration list of the distribution.
Table 2.
Distribution of tracking households by location
| District | Sector | Code | Households selected (T 0 ) | Households visited (T 6 ) | % completion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Kessounou |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Kodonou |
KOD |
100 |
98 |
98 |
| |
Kessounou |
KES |
100 |
99 |
99 |
| |
Glehoue |
GLH |
100 |
98 |
98 |
| |
Hetin-Sota |
HS/HSZ |
100 |
99 |
99 |
| |
Glahounsa |
GLA |
100 |
99 |
99 |
| |
Total |
|
500 |
493 |
99 |
|
Allada |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Alomey-Ahito |
ALO/AHI |
100 |
82 |
82 |
| |
Gbowele-Dodomey |
GBO/DOD |
100 |
84 |
84 |
| |
Dogoudo-Gbegamey |
DOG/GBE |
100 |
84 |
84 |
| |
Donou-Togoh |
DON/TOG |
100 |
80 |
80 |
| |
Tokpota-Zebou |
TOK/ZEB |
100 |
90 |
90 |
| |
Total |
|
500 |
420 |
84 |
|
Kandi 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Damadi |
DAM |
100 |
87 |
87 |
| |
Gansosso |
GNS |
100 |
85 |
85 |
| |
Keferi |
KEF |
100 |
95 |
95 |
| |
Pede |
PED |
100 |
86 |
86 |
| |
Gandokossikana |
KSK |
100 |
98 |
98 |
| |
Total |
|
500 |
451 |
90 |
|
Malanville |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Wouro-yesso |
WOY |
100 |
90 |
90 |
| |
Kotchi1 |
KOT |
100 |
95 |
95 |
| |
Kotchi2 |
KCH |
100 |
92 |
92 |
| |
Haro-banda |
GAL |
101 |
90 |
90 |
| |
Galiel |
GLL |
100 |
88 |
88 |
| |
Total |
|
501 |
455 |
91 |
| TOTAL | 2000 | 1819 | 91 |
Two teams composed of two technicians and a local village health worker (VHW) visited each selected household. The head of household or an adult person acting on behalf of the head was interviewed. In certain occasions where no appropriate respondent was found in a particular household, the visit of the next home was scheduled. Approximately 500 households (500–501), where campaign net(s) had been hung (and were in use), were selected at each tracking site. The teams identified the campaign LLIN (on the basis of the label sewn) in each selected household (or randomly chose one net, if multiple nets were present). They marked the LLIN for tracking assessment using a double marking system, an additional label with a unique study code plus an indelible ink mark. The team also recorded the GPS coordinates of each selected household for follow up visits. Google Earth 6.1 was used to map the study households. Written consent, to return at 6-monthly intervals, was obtained from the head of household or an adult living in the household.
Prospective survey and questionnaire
Households included for follow-ups were located by the name of the head of household and by GPS coordinates. Households that were not opened for inspection after two visits at the 6 months assessment visit were visited at the following assessment visits until they are recorded as unresponsive for three assessment visits and replaced.
A questionnaire was used to collect data from the head of household or an adult living in the household. The collected information included the status of each LLIN, the pattern of LLIN use and handling, observations on fabric integrity and the condition of the LLIN.
GPS coordinates and net codes were entered into the database. In the field, data were recorded on PDAs (Samsung Galaxy Tablets).
Measurement of indicators of LLINs durability
Survivorship
Survivorship at T0 (enrollment visit) was 100% (attrition was 0%). After six months, each tracking household received a follow-up visit. A visual verification of the presence/absence of the coded LLIN was done and when the coded LLIN was not in the house, the assessment teams determined how it was lost. Households that were not opened for assessment were re-visited and if it was still closed it was targeted for re-visit in the next 6 months assessment visit.
LLINs fabric integrity
At the enrollment visit (T0), none of the LLINs had holes (loss of fabric integrity was 0%). After 6 months, LLIN fabric integrity was assessed by a visual examination, without removal of coded nets from tracking households. LLIN physical integrity was assessed by verifying if the coded LLINs had holes or not and recorded the major holes category found on the LLINs as follow:
smaller than a thumb (0.5–2 cm),
larger than a thumb but smaller than a fist (2–10 cm) and
larger than a fist but smaller than a head (10–25 cm)
Holes less than 0.5 cm were ignored. The 6 months follow up assessment only recorded the major categories (no holes size-4 were counted) of holes found in the LLINs but did not count them. Their natures, locations, evidence of repairs and the type of repair were also not recorded, and represented an important limitation of the 6 months assessment study.
Bio-efficacy assessment method using gas chromatography (GC)
WHO recommends the use of the cone bio-assay method [20] for monitoring bio-efficacy. However, problems related to rearing the large numbers of colonized, pyrethroid-susceptible vector females, needed to support the application of this method to a statistically meaningful number of LLINs, hinder its correct use. An alternative method, the colorimetric test was developed for use with deltamethrin-treated LLINs [22,23]. Colorimetric assessment of LLIN bio-efficacy involves a two-step process. In step one, a magnetic sampling device (MSD) is used to sample the insecticide level on the LLIN surface (without removing or damaging the LLIN). The amount of insecticide on the MSD sample, a filter paper disc, is proportional to the amount of insecticide on the LLIN. Because sampling is standardized, results for different LLINs in the sampling frame are comparable. The second colorimetric assessment step uses colorimetric chemistry to estimate the amount of deltamethrin in the sample. Colorimetric results have been validated, by comparing WHO cone test bio-assay results and colorimetric results for a series of LLINs with different surface levels of deltamethrin. Using the standard curve from this study, it is possible to interpret the colorimetric result in terms of whether or not an LLIN meets the minimum WHO ‘threshold’ for bio-efficacy (nets causing >80% mortality in a cone bio-assay test).
A conceptually similar ‘chemical test’ approach was used for tracking the bio-efficacy of the PE-150D LLINs in this assessment. The approach, based on gas chromatography (GC), was developed in order to circumvent the problems previously described that are associated with the WHO cone bio-assay method for bio-efficacy assessment. With PE-150D technology, the insecticide molecules migrate to the surface continuously replacing lost insecticide at the surface, where vectors are exposed to its effects. Based on this theory, the LLIN surface insecticide level sampling tool was modified to enable sampling of PE-150D LLINs without removal or replacement; samples were collected on position B (Figure 2). This was done as a precautionary measure since the owners may put blankets on top of position D of the net which may rub some of the insecticide off. Also, placement on Position A under the mattress may result in the removal of the insecticide. Therefore, the best position to collect the sample is position B in the middle of the net.
Figure 2.
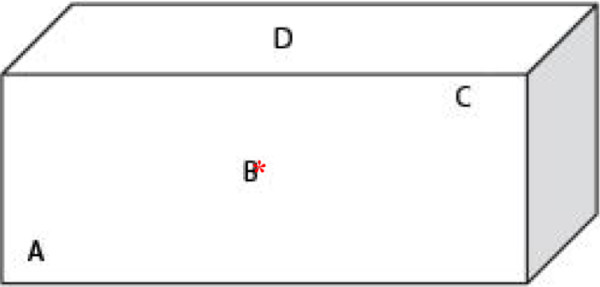
Identification of sampling positions.
The net to be tested is hung and position B is identified and fixed on an embroidery hoop (4 inches diameter). A portion of lens paper is applied to the surface of a cap attached to a 50-mL plastic tube. The lens paper is rubbed along the inside diameter of the hoop for 10 rotations. The lens paper (25 mm diameter) is removed and inserted into a 1-mL syringe and compressed with the plunger. The reverse side of the net is repeated in the same manner (Figure 3). 100 μL of acetone containing 0.05 mg/mL of triphenyl phosphate as an internal standard is added to the syringe containing the 2 compressed portions of the lens paper. The syringe outlet is plugged to allow the paper to soak for 5 minutes. After removal of the plug, the acetone is eluted via the syringe plunger into a small tube followed by another 100 μL of acetone. 1 μL of the eluant is injected into the GC (SRI 8610C GAS CHROMATOGRAPH) and the permethrin and internal standard is detected using flame ionization detection with hydrogen as the carrier gas. Sample response is compared with the response from a calibration standard and the amount of permethrin adhering to the lens paper is determined.
Figure 3.
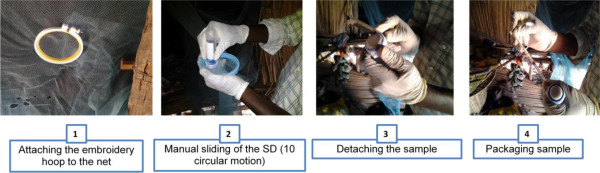
Sampling a mosquito net at Kessounou.
To estimate a bio-efficacy threshold for the GC method, 37 PED-150 LLINs (11 new nets and 26 nets that were in use in field for 3 to 4 months) were submitted to Cone test bioassay following WHO guidelines [24]. Interpretation of results (how GC test data are used to predict whether or not an LLIN would meet the minimum WHO bio-efficacy threshold) was done based on the comparison approach, outlined for the colorimetric method. A cut off value, established by comparing GC results with WHO cone test bio-assay results for the same LLINs, some of which met or exceeded the WHO minimum threshold for bio-efficacy and some which did not, was used to interpret the GC results. Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis, applied to the two data sets, GC and WHO cone bio-assay, was used to define the cut off value for nets that would be expected to meet the WHO cone test threshold. A minimum GC permethrin concentration was identified and used as a cut off value to estimate the percentage of nets at T0 and T6 that would not meet WHO minimum standards for bio-efficacy.
Quality of the data
The questionnaire form used in the study was created with ODK Collect 1.2.2 which allows easy data collection on Samsung Galaxy Tab 10.1 used as data terminals. At the end of each assessment visit day, data collected were directly uploaded to a cloud server, and retrieved at the end of the assessment for analysis.
Approximately 10% of the households were revisited independently to make sure that the survey was not biased.
Data analysis
Survivorship and attrition
The number of coded LLINs in the location, the proportion of the indicator and 95% confidence interval was reported.
The indicators were estimated as follow:
Survivorship:
Attrition rate-1 for nets that have been destroyed or disposed of (Physical damage):
Attrition rate-2 for nets not available for sleeping under (Removal):
Attrition rate-3 for nets re-purposed (Re-purposed):
The survivorship rate plus attrition rate-1, attrition rate-2 and attrition rate-3 was added up to 100%.
Two locations were reported to show significantly different survivorship at the 6 months assessment visit if the 95% confidence limits for survivorship do not overlap.
Fabric integrity
Physical integrity was analyzed for all the coded LLINs found and assessed in the households (and used for sleeping under). One WHO indicator was calculated at the 6 months assessment visit: the proportion of LLINs with holes.
Proportion of LLINs with any holes (with 95% confidence interval):
Holes index of the LLINs was not calculated due to the limit of 6 months questionnaire that did not count each category of holes.
Bio-efficacy
For assessment of bio-efficacy, a sub-sample (n = 50/site) of LLINs was randomly selected and tested to determine the amount of insecticide on the surface of the net. The percentage of nets in the sample falling below a cut-off value for LLINs that cause > 80% mortality in a WHO cone bio-assay test [24] was used to quantify net loss associated with bio-efficacy at T6.
Factors associated with durability of the LLIN
Other factors that contributed to the LLINs durability, as measured by fabric integrity and insecticidal activity, were assessed by multivariate regression analysis. The contributing factors included the house environment and behaviour related to net use, handling and washing, was derived from answers to the questionnaire used for the sub-sample of 50 LLINs selected for bio- efficacy in each location (around 200 LLINs in total).
Results
Survivorship and attrition
Table 3 summarizes T6 results for survivorship and attrition. One hundred forty seven out of 2002 coded LLINs were no longer present in the households where they were located at T0. That is, after 6 months, survivorship had dropped from 100% to between 90 and 96%, giving attrition of 10%, 9%, 4% and 6% percent respectively in Kessounou, Allada, Kandi and Malanville. Attrition rate-2 (LLINs removal) was the principal reason for LLINs lost; ranging from 4-8%. Attrition rate-1 was the second cause of LLINs lost; ranging from 0-2%. Attrition rate-3 was very low and only observed at Kessounou (Table 3). We did not assess factors associated with higher and lower survivorship loss rates, however, differences in survival between locations in the South and the North were significant (p < 0.05).
Table 3.
LLIN tracking T 6 results by study sites: survivorship and attrition
| Kessounou | Allada | Kandi | Malanville | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Survivorship | |||||
| Total coded LLINs (T0) |
N |
501 |
500 |
500 |
501 |
| Visited households (T6) |
N |
493 |
420 |
451 |
455 |
| People covered |
N |
1518 |
971 |
1201 |
1243 |
| Average people per LLINs |
N |
3.08 |
2.31 |
2.66 |
2.73 |
| LLINs missing |
N |
49 |
46 |
21 |
31 |
|
Survivorship |
% |
90 |
91 |
96 |
94 |
|
CI 95% |
|
87.30-92.52 |
87.95-93.03 |
93.66-97.24 |
91.35-95.61 |
|
Attrition | |||||
| (LLINs missing) |
N |
(49) |
(46) |
(21) |
(31) |
| ‘Physical damage’ responses |
N |
10 |
5 |
1 |
3 |
| ‘Removal’ responses |
N |
35 |
41 |
20 |
28 |
| ‘Re-purposed’ responses |
N |
4 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Attrition rate-1
|
(%) |
2 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
CI 95%
|
|
01.09-03.63 |
00.43-02.32 |
00.04-01.12 |
00.20-01.75 |
|
Attrition rate-2
|
(%) |
7 |
08 |
4 |
5 |
|
CI 95%
|
|
05.07-09.56 |
06.10-10.94 |
02.60-06.10 |
03.89-07.96 |
|
Attrition rate-3
|
(%) |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
CI 95%
|
|
00.31-02.03 |
|
|
|
|
Total attrition |
(%) |
10 |
9 |
4 |
6 |
| CI 95% | 07.48-12.70 | 06.97-12.05 | 02.76-06.34 | 04.39-08.65 | |
LLINs fabric integrity
At the 6 months assessment visit, LLINs found with holes (Table 4) was 36% at locations with less access to water for washing and 52-64% at locations with ready access to water (p < 0.01). The number of LLINs with size 1 holes was relatively low at all sites (when compared with the number of LLINs observed with size 2 and 3 holes).
Table 4.
LLIN found with holes
| Kessounou | Allada | Kandi | Malanville | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLINs found and assessed |
N |
444 |
374 |
430 |
424 |
| LLINs with any hole(s) (T6) |
N |
230 |
134 |
153 |
271 |
| |
% |
52* |
36 |
36 |
64** |
| |
IC95 |
[45.04-56.54] |
[28.96-40.92] |
[31.05-40.31] |
[59.14-68.49] |
| LLINs with size 1 holes |
N |
12 |
12 |
24 |
34 |
| |
% |
5 |
9 |
16 |
13 |
| |
IC95 |
[2.72-8.94] |
[4.71-15.12] |
[10.32-22.44] |
[08.85-17.09] |
| LLINs with size 2 holes |
N |
103 |
52 |
55 |
120 |
| |
% |
45 |
39 |
36 |
44 |
| |
IC95 |
[38.24-51.46] |
[30.51-47.6] |
[28.36-44.09] |
[38.27-50.42] |
| LLINs with size 3 holes |
N |
115 |
70 |
74 |
117 |
| |
% |
50 |
52 |
48 |
43 |
| IC95 | [43.36-56.65] | [43.44-60.94] | [40.22-56.58] | [37.19-49.30] |
*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Assessment of bio-efficacy
Determining a GC threshold for LLINs that meet minimum WHO bio-efficacy criteria
Figure 4 showed the mortalities observed with WHO cone test bioassay. On the 37 LLINs, 23 have mortality >80%. The mean mortality observed was 83% for the new nets and 79% for the nets collected from field. The minimum mortality was 18% mortality and the maximum was 100%. The median mortality was 89% for the new nets and 83% for the net selected from the field. Comparing the results with the GC method, we identified a GC value of 2.73 μg/sample or greater, for identification of LLINs that would be expected to cause >80% mortality in a WHO cone bio-assay. That is LLINs with permethrin levels high enough to meet the WHO minimum threshold for adequate LLIN bio- efficacy. LLINs giving GC results less than the 2.73 μg cut off were counted as not meeting the minimum WHO threshold for bio-efficacy. Statistical evaluation of the test, using Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis showed that the GC method can predict the WHO result within reasonable margins (specificity = 75.9%, sensitivity = 87.0%, AUC = 0.83 (0.7-0.92)) (Figure 5). The sampling frame for bio-efficacy testing was determined to be 172 assessment LLINs, selected at random (n.b analysis of this many nets by means of the WHO cone bio-assay would be logistically very difficult). Despite the need for additional development work, the GC approach was used in the tracking study.
Figure 4.
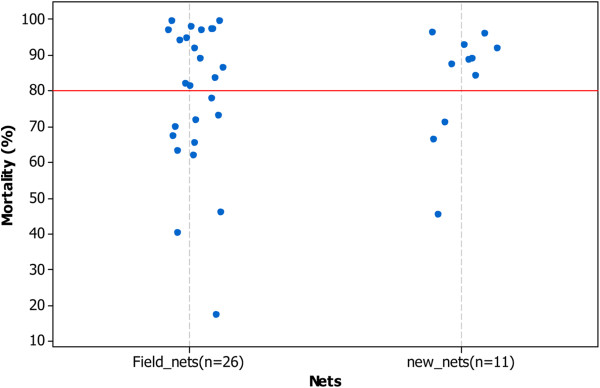
Mortality observed with WHO cone test and used to determine GC threshold.
Figure 5.
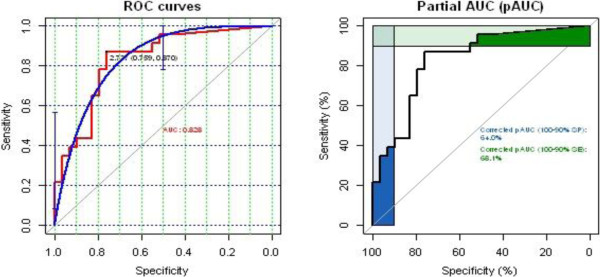
ROC curves showing prediction of WHO cone bio-essay results by GC method.
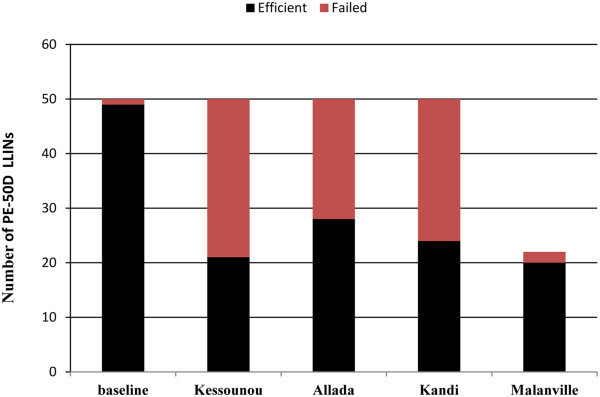
Bio-efficacy of LLINs 6 months post-distribution
A total of 222 nets were subjected to GC analysis to assess bio-efficacy. Results are summarized in Figures 6 and 7. There was significant loss associated with bio-efficacy at all four sites during the assessment period (T0-T6) (p = 0.0001). However, there was no significant difference between locations with more versus less access to water for washing. Measurements were based on gas chromatographic analysis of LLIN surface samples collected at randomly selected households in each study at T6. Results are compared with baseline (T0) measurements on recently distributed nets using the same approach. The red dotted line shows the GC cut-off equivalent to a surface insecticide level high enough to give >80% mortality in the WHO cone bio-assay, a minimum threshold for adequate LLIN bio-efficacy set by WHO.
Figure 6.
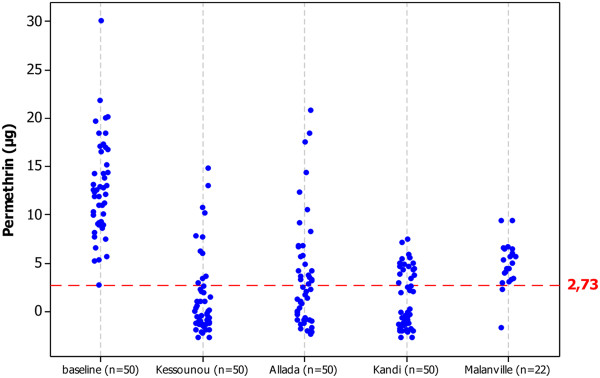
Scatter plot of LLIN surface insecticide (permethrin) levels for 212 LLINs.
Figure 7.
Net loss associated with bio-efficacy. Number of nets with insecticide levels below and above WHO threshold T0 versus T6.
Bio-efficacy at baseline (T0) was high. The results showed that 98% (49/50) had surface insecticide levels that were above the minimum WHO threshold for bio-efficacy (loss associated with bio-efficacy at T0 was set at 2%). After six months of use, net loss associated with bio-efficacy was 58% in Kessounou, 52% in Kandi, 44% in Allada and 9% in Malanville. At T6 there were 42% LLINs below the GC cut off for WHO minimum bio-efficacy.
Factors associated with LLINs durability
Table 5 indicated responses from a questionnaire used to assess the house environment and behaviour related to net use, handling and washing of the sub-sample selected. At Kessounou and Malanville, most residents indicated that they washed their nets between 2–5 times in the preceding 6 months, whereas most residents at Allada and Kandi, stated that washing occurred less frequently <2 times in the preceding 6 months. Modalities with very few responses were aggregated for the multivariate analysis.
Table 5.
Responses from the questionnaire administered to the sub-sample selected in each site
| Predictors | Modalities | KESSOUNOU | ALLADA | KANDI | MALANVILLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Washing frequency |
None |
7 |
21 |
21 |
10 |
| |
1 time |
8 |
21 |
18 |
7 |
| |
2-5 time |
25 |
7 |
11 |
26 |
| |
6-10 time |
2 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
| |
10+ |
7 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
|
Maintenance |
Good |
18 |
19 |
19 |
17 |
| |
Low |
31 |
31 |
31 |
33 |
|
LLINs use |
Don’t know |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
| |
Not use |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
| |
Often |
5 |
10 |
7 |
4 |
| |
Every night |
44 |
37 |
43 |
45 |
|
Roof of the house |
Pave stone |
2 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
| |
Straw |
15 |
0 |
1 |
9 |
| |
Sheet-metal |
31 |
50 |
48 |
38 |
| |
Tile |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
LLINs position |
Hanged |
44 |
37 |
41 |
35 |
| |
Stiked |
1 |
7 |
9 |
14 |
| |
Tidy |
4 |
6 |
0 |
1 |
|
Location of the kitchen of the house |
Outside |
35 |
48 |
35 |
46 |
| |
Inside |
14 |
2 |
14 |
4 |
|
Fabric integrity of the LLINs |
With holes |
14 |
35 |
30 |
13 |
| |
Without holes |
35 |
15 |
20 |
37 |
|
Distance to water for washing |
>5 km |
0 |
50 |
50 |
0 |
| < 0.5 km | 49 | 0 | 0 | 50 |
In summary (Table 6), the 6 months data showed that frequency of LLINs use, sleeping material, washing frequency and the distance to water for washing were significantly associated with loss of fabric integrity (p < 0.05).
Table 6.
Factor associated with loss of fabric integrity
| Factors | Modalities | LLINs with any holes (N) | Total LLINs | % of LLINs with any holes | OR | OR (95%CI) | P (Wald test) | P (LR-test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Frequency of LLIN use |
Often |
7 |
30 |
23.33 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.004 |
| |
Every night |
100 |
169 |
59.17 |
4.76 |
[1.94-11.71] |
0.006 |
|
|
Sleeping material |
Bed |
34 |
86 |
39.53 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.016 |
| |
Mat |
72 |
111 |
64.86 |
2.82 |
[1.58-5.05] |
0.018 |
|
|
Washing frequency |
None |
20 |
59 |
33.90 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.001 |
| |
1 |
21 |
54 |
38.89 |
1.24 |
[0.58-2.67] |
0.860 |
|
| |
2-5 |
66 |
86 |
76.74 |
6.43 |
[3.08-13.43] |
0.003 |
|
|
Location of the Kitchen |
Outside |
93 |
176 |
52.84 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.369 |
| |
Inside |
14 |
23 |
60.87 |
1.39 |
[0.57-3.37] |
0.366 |
|
|
LLINs maintenance |
Good |
37 |
73 |
50.68 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.976 |
| |
Low |
70 |
126 |
55.56 |
1.22 |
[0.68-2.17] |
0.976 |
|
|
Distance to water for washing |
>5 km |
35 |
100 |
35.00 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.020 |
| < 0.5 km | 72 | 99 | 72.73 | 4.95 | [2.71-9.06] | 0.020 |
Table 7 showed that only factors like frequency of LLIN use and sleeping material were significantly associated with insecticide decay (p < 0.05). Factors like washing frequency, LLINs maintenance, location of the kitchen and distance to water for washing did not seem to play a key role in the insecticide decay observed.
Table 7.
Factors associated with loss of insecticide bio-efficacy
| Factors | Modalities | N ineffective | Total | % ineffective | OR | OR (95%CI) | P (Wald test) | P (LR-test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Frequency of LLIN use |
Often |
11 |
28 |
39.29 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.028 |
| |
Every night |
89 |
144 |
61.81 |
2.50 |
[1.09-5.73] |
0.031 |
|
|
Sleeping material |
Bed |
65 |
104 |
62.50 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.0117 |
| |
Mat |
35 |
68 |
51.47 |
0.64 |
[0.34-1.17] |
0.12 |
|
|
Washing frequency |
None |
31 |
53 |
58.49 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.728 |
| |
1 |
28 |
50 |
56.00 |
0.90 |
[0.41-1.97] |
0.431 |
|
| |
2-5 |
41 |
69 |
59.42 |
1.04 |
[0.50-2.15] |
0.751 |
|
|
Location of the Kitchen |
Outside |
86 |
151 |
56.95 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.451 |
| |
Inside |
14 |
021 |
66.67 |
1.51 |
[0.58-3.96] |
0.455 |
|
|
LLINs maintenance |
Good |
33 |
064 |
51.56 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.489 |
| |
Low |
67 |
108 |
62.04 |
1.54 |
[0.82-2.87] |
0.489 |
|
|
Distance to water for washing |
>5 km |
59 |
100 |
59.00 |
1.00 |
- |
- |
0.17 |
| <0.5 km | 41 | 072 | 56.94 | 0.92 | [0.5-1.7] | 0.174 |
Discussion
The National Malaria Control Program of Benin conducted a country-wide distribution of permethrin-treated Olyset® LLINs in July 2011. As early as 6 months into the assessment, we observed that measures of fabric integrity and bio-efficacy had decreased rapidly bringing into question the assumption that LLIN condition remains “relatively uniform for at least three years”. The report of other assessments will help us to more understand the effective life of the intervention. However, loss associated with bio-efficacy and fabric integrity during the first six months, was great enough to suggest that the impact of the LLIN intervention on malaria transmission could be affected.
After the first 6 months, survivorship has decreased to 93%. The main cause of net loss or missing nets was due to the removal of nets. Net missing due to poor physical condition was low. These findings suggest that LLIN survivorship would drop significantly during years two and three post distribution if the attrition rate observed continue at the same rate and could affect the impact of the LLIN intervention on malaria transmission.
A high-coverage and compliance with nightly use of LLINs, provides a ‘community protection’ benefit. Considering the observed attrition rate, over six months, it may well be that, at best; any ‘community’ protection associated with the intervention would be higher in some areas and could disappear in other areas within two years or less if the LLINs were removed and used in areas different to their initial locations and net loss associated with poor physical condition increased. Additionally, there was anecdotal evidence that homeowner re-purpose LLINs in ways that increase the attrition rate. In Kessounou, for example, a striking cause of the loss included LLINs that had been converted into fishing nets, as well as covers for protecting crops and animals. Strengthening information and communication activities around future distribution campaigns should be evaluated and incorporated into distribution campaign strategy to increase the value that community members place of correct use of nets [25].
While there were differences in survivorship, associated with geo-climatic variation (South versus North), the differences in fabric integrity, seen at geo-climatically similar sites where access to water was different, were more pronounced. LLINs found with any holes were greater in areas where water (for washing nets) was easily obtained. Proximity to a LLIN washing site seems to encourage more frequent washing of nets, thereby accelerating loss of fabric integrity. The effect of local differences on LLIN physical integrity loss, such as proximity to water, as well as regional differences, e.g. seasonal rainfall patterns, point out the importance of conducting tracking net interventions in different geographic areas [26]. Frequent washing of nets, >5 times in 6 months, was 3–4 times more common in river sites of Kessounou and Malanville, than in upland sites of Allada and Kandi, where water for washing was transported by community members. This factor as well as the sleeping material and the frequency of LLIN use played a significant role in loss associated with LLIN integrity.
Loss associated with fabric integrity increase the probability of man-mosquito contact and transmission of malaria [27-29]. On the down side, at two assessment sites, Kessounou and Malanville, the fabric integrity of more than half of the LLINs was compromised using the six months following distribution. The problem of physical damage could be addressed through better education [30] for correct hanging, care and repair of nets [31]. Solving the problem may require emphasis on less frequent washing of nets and more care when hanging and using the LLINs to increase the effective life of LLINs under field conditions, a critical modification, since national replacement of LLINs on any schedule less than every three years is, programmatically, highly unlikely.
LLINs are supposed to be effective even if torn [32,33], because of “repellency” associated with the insecticide. In this assessment, we applied a new method, which is faster than the WHO cone, does not require mosquitoes, is not destructive and easier to test statistically meaningful sample size, to capture and quantify insecticide residue on the LLINs surface. The GC method, used to estimate the proportion of nets with a surface insecticide level above the WHO threshold, uses a standardized sampling technique to sample the surface concentration of permethrin, and to compare the results to a GC threshold concentration of 2.73 μg permethrin/GC sample. The threshold concentration was estimated through testing LLINs that were previously evaluated by means of the WHO cone bio-assay test. Nets that exceeded the WHO test threshold value (a surface insecticide levels adequate to cause >80% mortality) as well as nets that were not (≤ 80% mortality) were identified and used to establish a GC cut off value that distinguishes the two groups. ROC analysis was used to compare bioassay and GC results. While potentially offering several advantages, the GC method as described here, was observed to have several limitations. The PE-150D LLINs technology incorporates molecules of permethrin in the nets fibers [34]. In theory the insecticide molecules migrate to the surface continuously replacing insecticide loss at the surface [35]. However, this regeneration process is not necessarily rapid and time (after washing) until completion of regeneration may be up to three weeks, during which the surface insecticide concentration, measured by the GC method, can be low [36]. This implies that the GC method may well have underestimated bio-efficacy. The multivariate analysis performed on the bio-efficacy data confirmed this observation because washing frequency and distance to water for washing were not associated with insecticide decay and suggested that other factor(s) was responsible of the low insecticide quantity observed in the ineffective LLINs. These results suggested that the GC method needs to be improved to assess the real bio-efficacy of these LLINs.
Our results support a conclusion that LLINs intervention, under field conditions [37], need to be strengthen by communication with community using LLIN to reduce removal practice and assure an effective impact of the distribution strategy. The results raise the question of whether or not greater emphasis on care and repair of nets at the household level could slow this process down. Additionally, LLIN manufacturers are working on the durability characteristics of the mesh used for manufacturing LLINs. A combination of cultural and net-related changes should be implemented and evaluated to improve LLIN effective life.
Conclusion
LLINs were widely distributed by Benin NMCP in July 2011. We developed and tested a tool for monitoring the durability of the nets. After six months of use under field conditions, measures of integrity and bio-efficacy had dropped more quickly than anticipated. At present the WHO cone test appears to be the only reliable measure of net bio-efficacy for polyethylene-permethrin impregnated LLINs. The way in which the insecticide is incorporated into the LLIN fiber, and its migration to the surface during regeneration, may be responsible for confounding the GC results. If so, then the WHO cone test method may also be similarly affected. The results of other assessments could help us to better understand the effective operational life of this intervention.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
RA: co-designed the study, designed experiments, coordinated field activities, collected and analyzed data, wrote and revised the paper; VG: mapping, participated in data collection, field activities and revised the paper; SH: participated in field activities and data collection; FO: assisted with the statistical analysis and participated in field activities and data collection; MG: technical assistance of the study and participated in design of the study; AM: designed the study, supervised field activities and revised the paper. All authors have read and approved the content of the submitted manuscript.
Contributor Information
Roseric Azondekon, Email: roseric_2000@yahoo.fr.
Virgile Gnanguenon, Email: amerusangel@yahoo.fr.
Frederic Oke-Agbo, Email: fredook15@yahoo.fr.
Speraud Houevoessa, Email: speraudhouevoessa@yahoo.fr.
Michael Green, Email: mdg4@cdc.gov.
Martin Akogbeto, Email: akogbetom@yahoo.fr.
Acknowledgements
Our thanks are addressed to the Village Health Workers, Benin NMCP, CDC and USAID. This investigation received financial support from the US President’s Malaria Initiative.
References
- Kitua AY, Ogundahunsi OAT, Lines J, Mgone CS. Conquering malaria: Enhancing the impact of effective interventions towards elimination in the diverse and changing epidemiology. J Glob Infect Dis. 2011;3:161. doi: 10.4103/0974-777X.81694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NMCP. Benin’s strategic plan against malaria from 2006 to 2010. Cotonou: Ministry of health; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso PL, Lindsay SW, Schellenberg JRMA, Keita K, Gomez P, Shenton FC, Hill AG, David PH, Fegan G, Cham K, Greenwood BM. A malaria control trial using insecticide-treated bed nets and targeted chemoprophylaxis in a rural area of The Gambia, West Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1993;87:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(93)90174-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso PL, Lindsay SW, Armstrong JRM, de Francisco A, Shenton FC, Greenwood BM, Conteh M, Cham K, Hill AG, David PH, Fegan G, Hall AJ. The effect of insecticide-treated bed nets on mortality of Gambian children. The Lancet. 1991;337:1499–1502. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93194-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro U, Olaleye BO, McGuire W, Thomson MC, Langerock P, Bennett S, Greenwood BM. A comparison of the efficacy of insecticide-treated and untreated bed nets in preventing malaria in Gambian children. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1995;89:596–598. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(95)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binka FN, Kubaje A, Adjuik M, Williams LA, Lengeler C, Maude GH, Armah GE, Kajihara B, Adiamah JH, Smith PG. Impact of permethrin impregnated bednets on child mortality in Kassena-Nankana district, Ghana: a randomized controlled trial. Trop Med Int Health. 2007;1:147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.1996.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaim M, Aitio A, Nakashima N. Safety of pyrethroid-treated mosquito nets. Med Vet Entomol. 2000;14:1–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2915.2000.00211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis CF, Jana-Kara B, Maxwell CA. Insecticide treated nets: impact on vector populations and relevance of initial intensity of transmission and pyrethroid resistance. J Vector Borne Dis. 2003;40:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonio-Nkondjio C, Demanou M, Etang J, Bouchite B. Impact of cyfluthrin (Solfac EW050) impregnated bed nets on malaria transmission in the city of Mbandjock: lessons for the nationwide distribution of long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) in Cameroon. Parasites & Vectors. 2013;6:10. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengeler C. International Development Research Centre (IDRC), World Health Organization (WHO) Ottawa: IDRC; 1996. (Net Gain: A New Method for Preventing Malaria Deaths). [Google Scholar]
- Thwing J, Perry R, Townes D, Diouf M, Ndiaye S, Thior M. Success of Senegal’s first nationwide distribution of long-lasting insecticide-treated nets to children under five-contribution toward universal coverage. Malar J. 2011;10:86. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shargie E, Gebre T, Ngondi J, Graves P, Mosher A, Emerson P, Ejigsemahu Y, Endeshaw T, Olana D, WeldeMeskel A. others. Malaria prevalence and mosquito net coverage in Oromia and SNNPR regions of Ethiopia. BMC Public Health. 2008;8:321. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-8-321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougard J-M. Insecticide-treated Nets. Pour Sci. 2008;368:48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Okumu F, Kiware S, Moore S, Killeen G. Mathematical evaluation of community level impact of combining bed nets and indoor residual spraying upon malaria transmission in areas where the main vectors are Anopheles arabiensis mosquitoes. Parasites & Vectors. 2013;6:17. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnevale P, Robert V, Boudin C, Halna JM, Pazart L, Gazin P, Richard A, Mouchet J. Control of malaria using mosquito nets impregnated with pyrethroids in Burkina Faso. Bull Société Pathol Exot Ses Fil. 1988;81:832–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouchet J, Robert V, Carnevale P, Ravaonjanahary C, Coosemans M, Fontenille D, Lochouarn L. Le défi de la lutte contre le paludisme en Afrique tropicale: place et limite de la lutte antivectorielle. Cah Détudes Rech Francoph Santé. 1991;1:277–288. [Google Scholar]
- Bermejo A, Veeken H. Insecticide-impregnated bed nets for malaria control: a review of the field trials. Bull World Health Organ. 1992;70:293–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Report of the Thirteenth WHOPES Working Group Meeting-Review of Olyset® LN, DawaPlus®2.0 LN, Tianjin Yorkool® LN. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yukich J, Bennett A, Keating J, Yukich R, Lynch M, Eisele T, Kolaczinski K. Planning long lasting insecticide treated net campaigns: should households’ existing nets be taken into account? Parasites & Vectors. 2013;6:174. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO/HTM/NTD/WHOPES. Guidelines for Monitoring the Durability of Long-Lasting Insecticidal Mosquito Nets under Operational Conditions. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- NMCP. Free mass-distribution campaign of Long Lasting insecticide-treated Nets in Benin - General Report. Cotonou: Ministry of Health; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Green MD, Mayxay M, Beach R, Pongvongsa T, Phompida S, Hongvanthong B, Vanisaveth V, Newton PN, Vizcaino L, Swamidoss I. Evaluation of a rapid colorimetric field test to assess the effective life of long-lasting insecticide-treated mosquito nets in the Lao PDR. Malar J. 2013;12:57. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green MD, Atieli F, Akogbeto M. Rapid colorimetric field test to determine levels of deltamethrin on PermaNet® surfaces: association with mosquito bioactivity. Trop Med Int Health. 2009;14:381–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2009.02247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for laboratory and field testing of long-lasting insecticidal mosquito nets. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Minakawa N, Dida GO, Sonye GO, Futami K, Kaneko S. Unforeseen misuses of bed nets in fishing villages along Lake Victoria. Malar J. 2008;7:165. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-7-165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atieli FK, Munga SO, Ofulla AV, Vulule JM. The effect of repeated washing of long-lasting insecticide-treated nets (LLINs) on the feeding success and survival rates of Anopheles gambiae. Malar J. 2010;9:304. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnanguenon V, Azondekon R, Oke-Agbo F, Sovi A, Ossè R, Padonou G, Aïkpon R, Akogbeto MC. Evidence of man-vector contact in torn long-lasting insecticide-treated nets. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:751. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochomo EO, Bayoh NM, Walker ED, Abongo BO, Ombok MO, Ouma C, Githeko AK, Vulule J, Yan G, Gimnig JE. The efficacy of long-lasting nets with declining physical integrity may be compromised in areas with high levels of pyrethroid resistance. Malar J. 2013;12:368. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haji K, Khatib B, Smith S, Ali A, Devine G, Coetzee M, Majambere S. Challenges for malaria elimination in Zanzibar: pyrethroid resistance in malaria vectors and poor performance of long-lasting insecticide nets. Parasites & Vectors. 2013;6:82. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ndjinga J, Minakawa N. The importance of education to increase the use of bed nets in villages outside of Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Malar J. 2010;9:279. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toé L, Skovmand O, Dabiré K, Diabaté A, Diallo Y, Guiguemdé T, Doannio J, Akogbeto M, Baldet T, Gruénais M-E. Decreased motivation in the use of insecticide-treated nets in a malaria endemic area in Burkina Faso. Malar J. 2009;8:175. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-8-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Port GR, Boreham PFL. The effect of bed nets on feeding by Anopheles gambiae Giles (Diptera: Culicidae) Bull Entomol Res. 2009;72:483. [Google Scholar]
- Kweka E, Himeidan Y, Mahande A, Mwang’onde B, Msangi S, Mahande M, Mazigo H, Nyindo M. Durability associated efficacy of long-lasting insecticidal nets after five years of household use. Parasites & Vectors. 2011;4:156. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-4-156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- N’Guessan R, Darriet F, Doannio JMC, Chandre F, Carnevale P. Olyset NetR efficacy against pyrethroid-resistant Anopheles gambiae and Culex quinquefasciatus after 3 years’ field use in Cote d’Ivoire. Med Vet Entomol. 2001;15:97–104. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2915.2001.00284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T, Okuno T. Development of Olyset (R) net’ as a Tool for Malaria Control. Sumitomo Kagaku Tokushugo (Sumitomo Chemical Review) 2006. pp. 4–11. http://www.sumitomo-chem.co.jp/english/rd/report/theses/docs/20060200_lni.pdf.
- Gimnig JE, Lindblade KA, Mount DL, Atieli FK, Crawford S, Wolkon A, Hawley WA, Dotson EM. Laboratory wash resistance of long-lasting insecticidal nets. Trop Med Int Health. 2005;10:1022–1029. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2005.01481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trape JF. Contre: Les limites des moustiquaires imprégnées dans la lutte contre le paludisme en Afrique tropicale. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2001;94:174–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]