Abstract
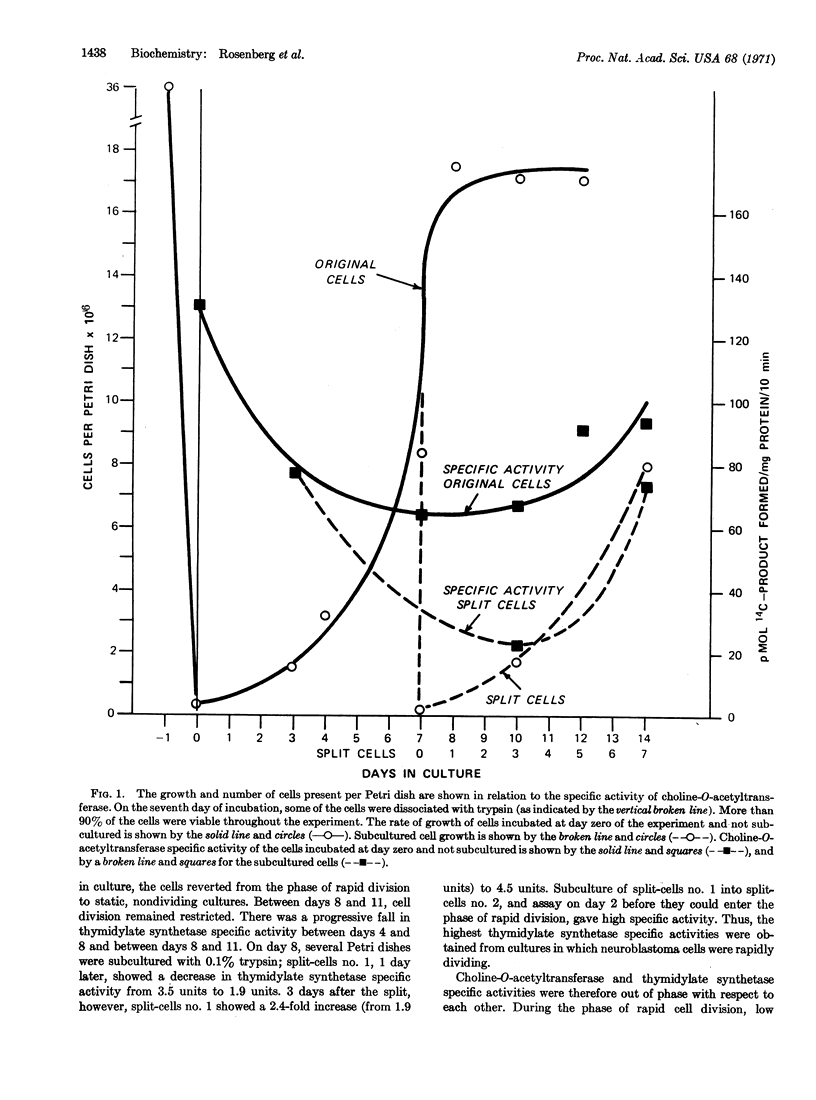
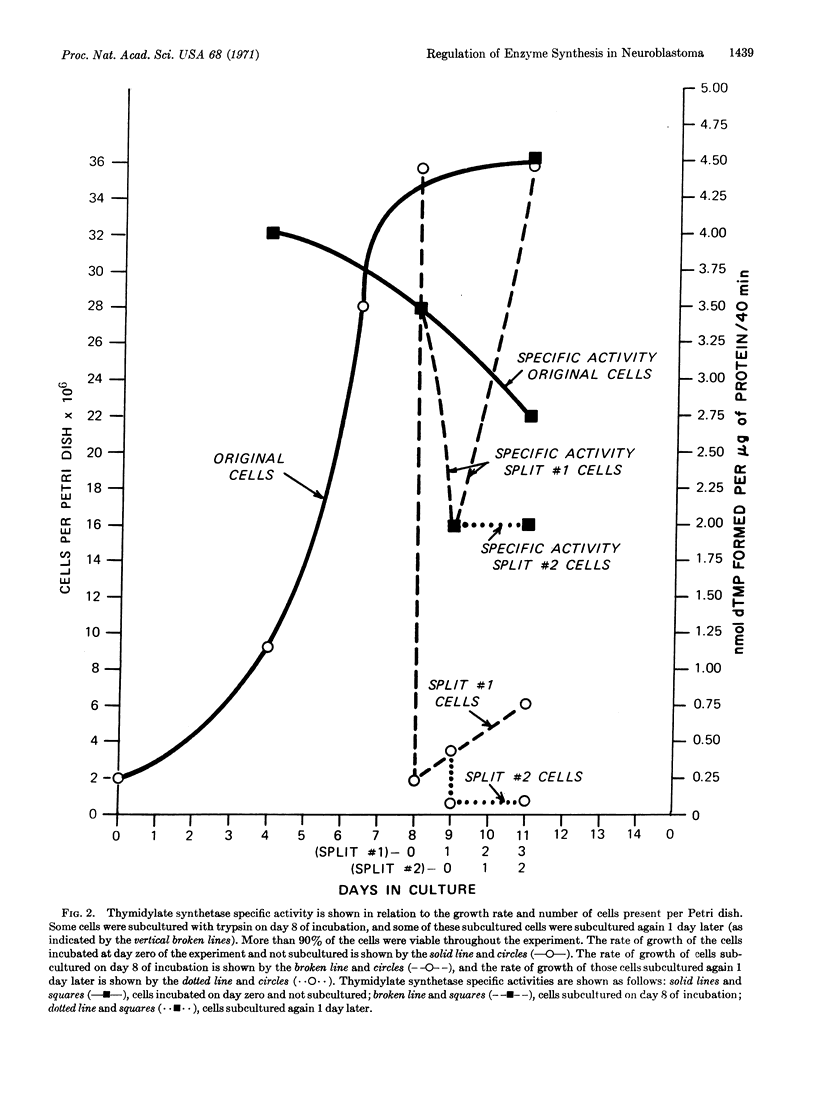
The specific activity of mouse neuroblastoma choline-O-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.6.) increased 5.7-fold when the rate of cell division was restricted (as compared to cells kept rapidly dividing for 9 days); the specific activity of mouse neuroblastoma thymidylate synthetase increased 2.4-fold when nondividing cells again entered the logarithmic phase of cell growth. The highest specific activities for choline-O-acetyltransferase and lowest specific activities for thymidylate synthetase were obtained from cultures where cell division was restricted; the opposite result was observed when the cells were growing rapidly. Thus, the regulation of these two enzymes is out of phase with respect to each other and is dependent on the rate of cell division. The inverse relationship for the regulation of these two enzymes is discussed in relation to the needs of mitotic versus differentiated neuroblastoma cells.
Keywords: confluent cells, rapidly-dividing cells, specific activity
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augusti-Tocco G., Sato G. Establishment of functional clonal lines of neurons from mouse neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):311–315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A., Gilbert F., Wilson S., Farber J., Rosenberg R., Nirenberg M. Regulation of acetylcholinesterase in neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):786–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. J., Dennis M. J. Acetylcholine sensitivity and distribution on mouse neuroblastoma cells. Science. 1970 Feb 27;167(3922):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3922.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P., Ruffner W., Nirenberg M. Neuronal tumor cells with excitable membranes grown in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS H. J., TERRYBERRY J. E. Counting actively metabolizing tissue cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Oct;13(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P., Sidman R. L. Supravital DNA synthesis in the developing human and mouse brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Apr;27(2):246–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. An isotopic assay for thymidylate synthetase. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3546–3548. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier B. K., Shuster L. A simplified radiochemical assay for choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1967 Oct;14(10):977–985. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeds N. W., Gilman A. G., Amano T., Nirenberg M. W. Regulation of axon formation by clonal lines of a neural tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


