Abstract
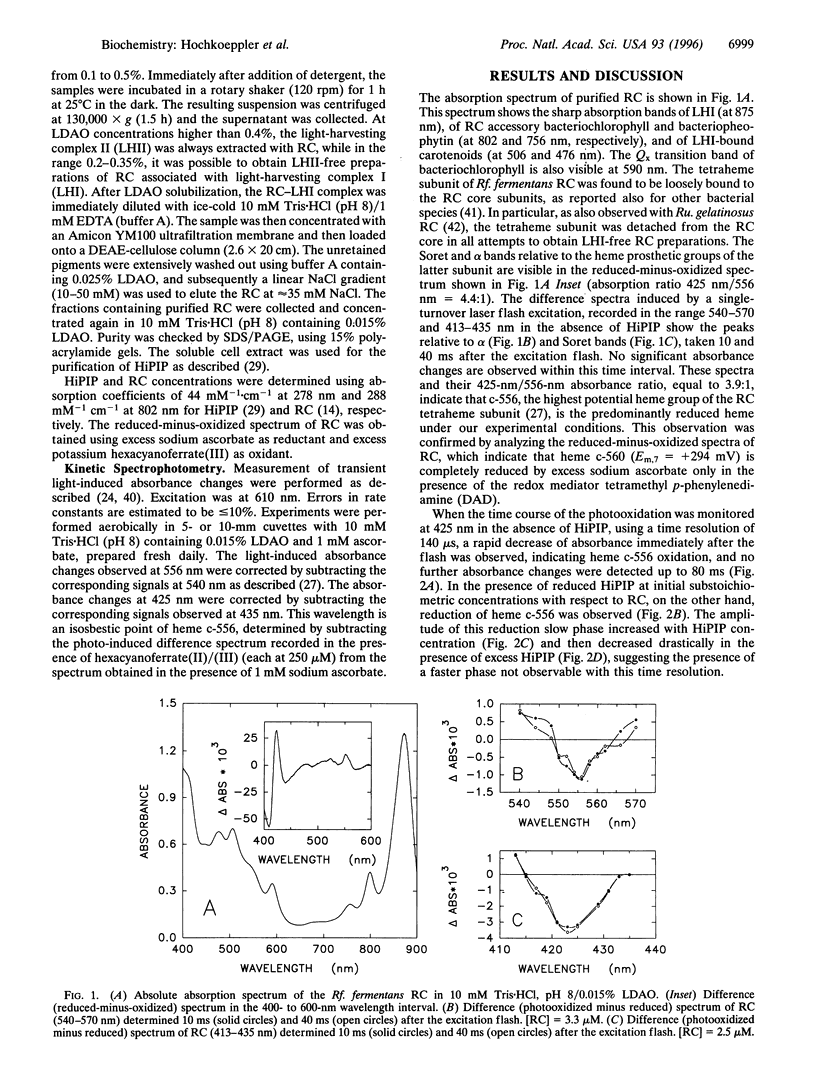
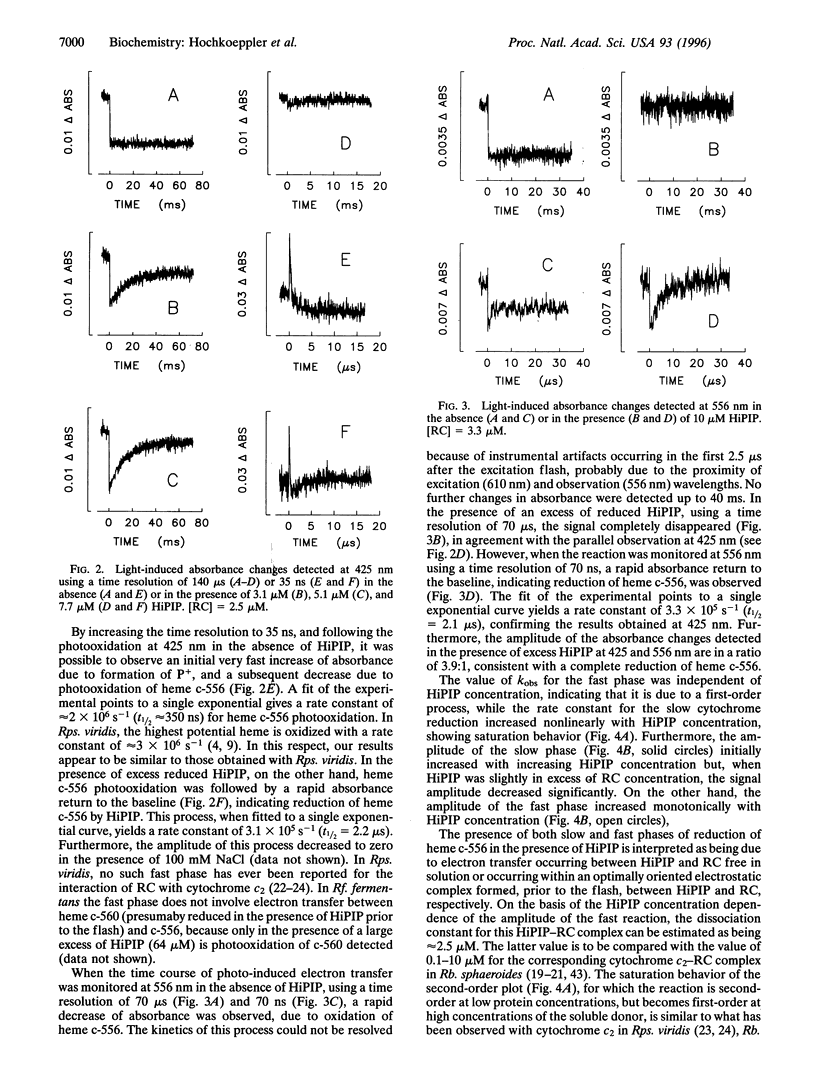
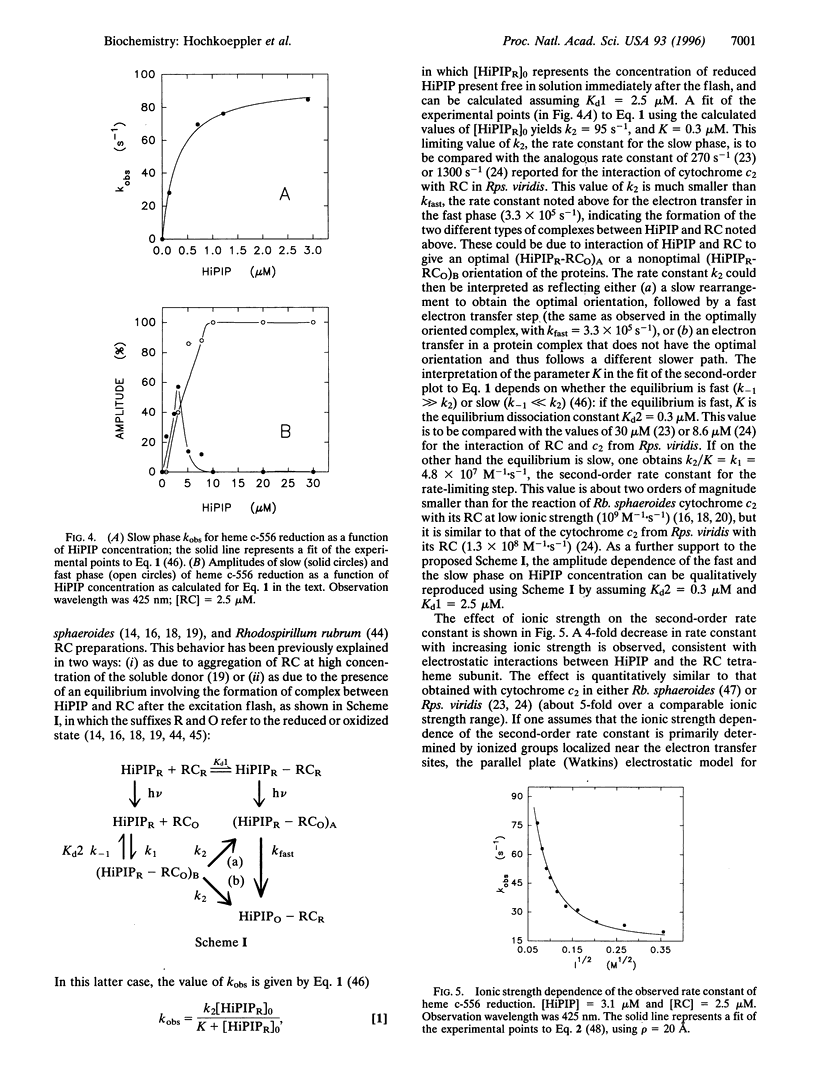
The kinetics of photo-induced electrontransfer from high-potential iron-sulfur protein (HiPIP) to the photosynthetic reaction center (RC) of the purple phototroph Rhodoferarfermentans were studied. The rapid photooxidation of heme c-556 belonging to RC is followed, in the presence of HiPIP, by a slower reduction having a second-order rate constant of 4.8 x 10(7) M(-1) x s(-1). The limiting value of kobs at high HiPIP concentration is 95 s(-1). The amplitude of this slow process decreases with increasing HiPIP concentration. The amplitude of a faster phase, observed at 556 and 425 nm and involving heme c-556 reduction, increases proportionately. The rate constant of this fast phase, determined at 425 and 556 nm, is approximately 3 x 10(5) s(-1). This value is not dependent on HiPIP concentration, indicating that it is related to a first-order process. These observations are interpreted as evidence for the formation of a HiPIP-RC complex prior to the excitation flash, having a dissociation constant of -2.5 microM. The fast phase is absent at high ionic strength, indicating that the complex involves mainly electrostatic interactions. The ionic strength dependence of kobs for the slow phase yields a second-order rate constant at infinite ionic strength of 5.4 x 10(6) M(-1) x s(-1) and an electrostatic interaction energy of -2.1 kcal/mol (1 cal = 4.184 J). We conclude that Rhodoferar fermentans HiPIP is a very effective electron donor to the photosynthetic RC.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Daniel M., Hermoso J., Meyer T. E., Bartsch R. G., Kamen M. D. Cytochrome c2 sequence variation among the recognised species of purple nonsulphur photosynthetic bacteria. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):659–660. doi: 10.1038/278659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aprahamian G., Feinberg B. A. High-potential iron-sulfur proteins and their possible site of electron transfer. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):915–919. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch R. G. The distribution of soluble metallo-redox proteins in purple phototrophic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 23;1058(1):28–30. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80262-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer J. R., Tierney G. V., Crofts A. R. Cytochrome c2--reaction centre coupling in chromatophores of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides and Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Epp O., Miki K., Huber R., Michel H. X-ray structure analysis of a membrane protein complex. Electron density map at 3 A resolution and a model of the chromophores of the photosynthetic reaction center from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Michel H. The Photosynthetic Reaction Center from the Purple Bacterium Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1463–1473. doi: 10.1126/science.245.4925.1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dracheva S. M., Drachev L. A., Konstantinov A. A., Semenov AYu, Skulachev V. P., Arutjunjan A. M., Shuvalov V. A., Zaberezhnaya S. M. Electrogenic steps in the redox reactions catalyzed by photosynthetic reaction-centre complex from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):253–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Leigh J. S. Electron spin resonance characterization of Chromatium D hemes, non-heme irons and the components involved in primary photochemistry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 31;314(2):178–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Petty K. M., Bonner H. S., Morse S. D. Cytochrome c2 and reaction center of Rhodospeudomonas spheroides Ga. membranes. Extinction coefficients, content, half-reduction potentials, kinetics and electric field alterations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 17;387(3):536–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Lord A. V., Reeves S. G. The detection and characterization by electron-paramagnetic-resonance spectroscopy of iron-sulphur proteins and other electron-transport components in chromatophores from the purple bacterium Chromatium. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;138(2):177–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1380177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Zha X. H., Durham B., O'Brien P., Vieira B., Davis D., Okamura M., Millett F. Reaction of cytochromes c and c2 with the Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction center involves the heme crevice domain. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4494–4500. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochkoeppler A., Ciurli S., Venturoli G., Zannoni D. The high potential iron-sulfur protein (HiPIP) from Rhodoferax fermentans is competent in photosynthetic electron transfer. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 2;357(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01334-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochkoeppler A., Kofod P., Ferro G., Ciurli S. Isolation, characterization, and functional role of the high-potential iron-sulfur protein (HiPIP) from Rhodoferax fermentans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995 Oct 1;322(2):313–318. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Bartsch R. G., Kamen M. D. Observations on light-induced oxidation reactions in the electron transport system of Chromatium. Biophys J. 1972 Jul;12(7):882–896. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86131-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaff D. B., Willie A., Long J. E., Kriauciunas A., Durham B., Millett F. Reaction of cytochrome c2 with photosynthetic reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1303–1310. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X., Williams J. C., Allen J. P., Mathis P. Relationship between rate and free energy difference for electron transfer from cytochrome c2 to the reaction center in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13517–13523. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. E., Durham B., Okamura M., Millett F. Role of specific lysine residues in binding cytochrome c2 to the Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction center in optimal orientation for rapid electron transfer. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 22;28(17):6970–6974. doi: 10.1021/bi00443a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Bartsch R. G., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G. Kinetics of photooxidation of soluble cytochromes, HiPIP, and azurin by the photosynthetic reaction center of the purple phototrophic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biochemistry. 1993 May 11;32(18):4719–4726. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Przysiecki C. T., Watkins J. A., Bhattacharyya A., Simondsen R. P., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G. Correlation between rate constant for reduction and redox potential as a basis for systematic investigation of reaction mechanisms of electron transfer proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6740–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser C. C., Dutton P. L. Cytochrome c and c2 binding dynamics and electron transfer with photosynthetic reaction center protein and other integral membrane redox proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2450–2461. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega J. M., Mathis P. Electron transfer from the tetraheme cytochrome to the special pair in isolated reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1141–1151. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overfield R. E., Wraight C. A., Devault D. Microsecond photooxidation kinetics of cytochrome c2 from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides: in vivo and solution studies. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 1;105(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80903-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overfield R. E., Wraight C. A. Oxidation of cytochromes c and c2 by bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers in phospholipid vesicles. 1. Studies with neutral membranes. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3322–3327. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Bashford C. L., Takamiya K. I., van den Berg W. H., Dutton P. L. Second order kinetics of the reduction of cytochrome c2 by the ubiquinone cytochrome b-c2 oxidoreductase of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4137–4142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Cogdell R. J., Crofts A. R. The photo-oxidation of horse heart cytochrome c and native cytochrome c2 by reaction centres from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides R26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 23;347(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings J., Wherland S., Gray H. B. Kinetic studies of the oxidation and reduction of Chromatium high potential iron-sulfur protein (HiPIP) by inorganic complexes. Comparison of the electron transfer reactivities of HiPIP and horse heart cytochrome c. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Apr 14;98(8):2177–2180. doi: 10.1021/ja00424a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickle G. K., Cusanovich M. A. The kinetics of photooxidation of c-type cytochromes by Rhodospirillum rubrum reaction centers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Oct 15;197(2):589–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp B., Parot P., Menin L., Gaillard J., Richaud P., Verméglio A. In vivo participation of a high potential iron-sulfur protein as electron donor to the photochemical reaction center of Rubrivivax gelatinosus. Biochemistry. 1995 Sep 19;34(37):11736–11742. doi: 10.1021/bi00037a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogabe S., Ezoe T., Kasai N., Saeda M., Uno A., Miki M., Miki K. Structural similarity of cytochrome c2 from Rhodopseudomonas viridis to mitochondrial cytochromes c revealed by its crystal structure at 2.7 A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 23;345(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Palmer G., Massey V. Determination of dissociation constants and specific rate constants of enzyme-substrate (or protein-ligand) interactions from rapid reaction kinetic data. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4048–4052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiede D. M., Vashishta A. C., Gunner M. R. Electron-transfer kinetics and electrostatic properties of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction center and soluble c-cytochromes. Biochemistry. 1993 May 4;32(17):4515–4531. doi: 10.1021/bi00068a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollin G., Hazzard J. T. Intra- and intermolecular electron transfer processes in redox proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 May 15;287(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90380-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venturoli G., Mallardi A., Mathis P. Electron transfer from cytochrome c2 to the primary donor of Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction centers. A temperature dependence study. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 7;32(48):13245–13253. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. A., Cusanovich M. A., Meyer T. E., Tollin G. A "parallel plate" electrostatic model for bimolecular rate constants applied to electron transfer proteins. Protein Sci. 1994 Nov;3(11):2104–2114. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Kabbani O., Chang C. H., Tiede D., Norris J., Schiffer M. Comparison of reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Rhodopseudomonas viridis: overall architecture and protein-pigment interactions. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5361–5369. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



