Abstract
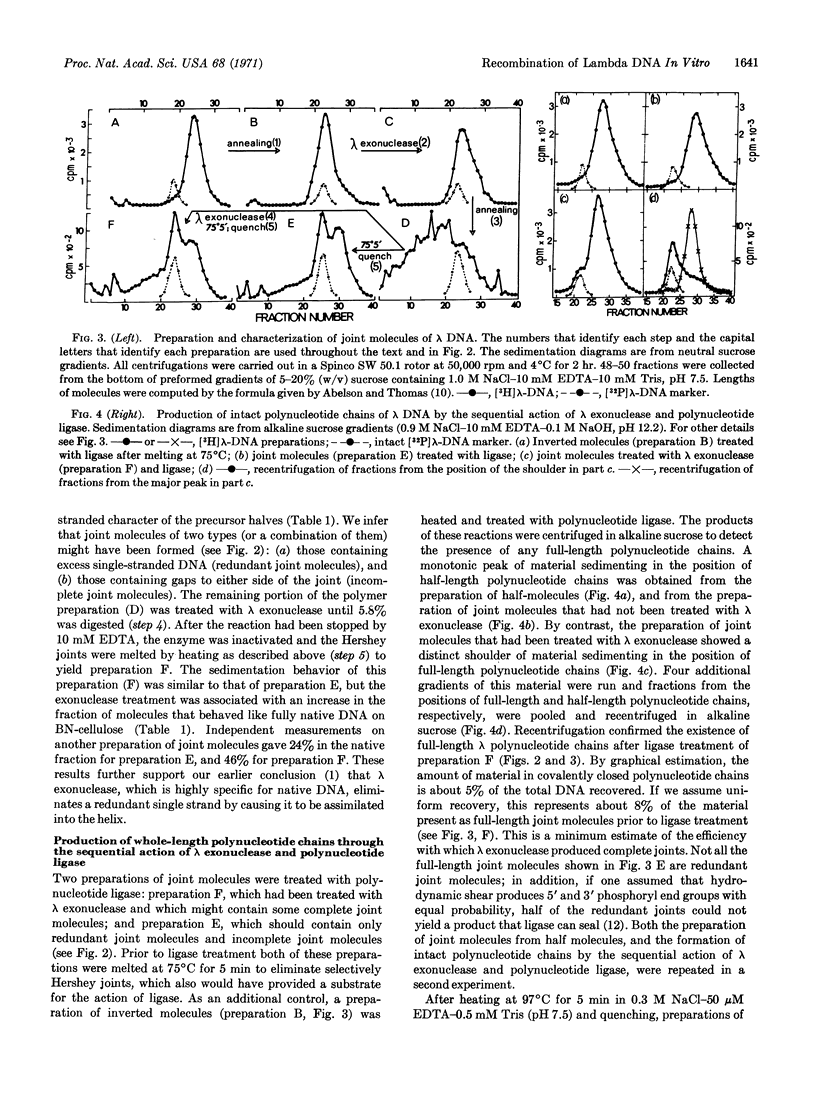
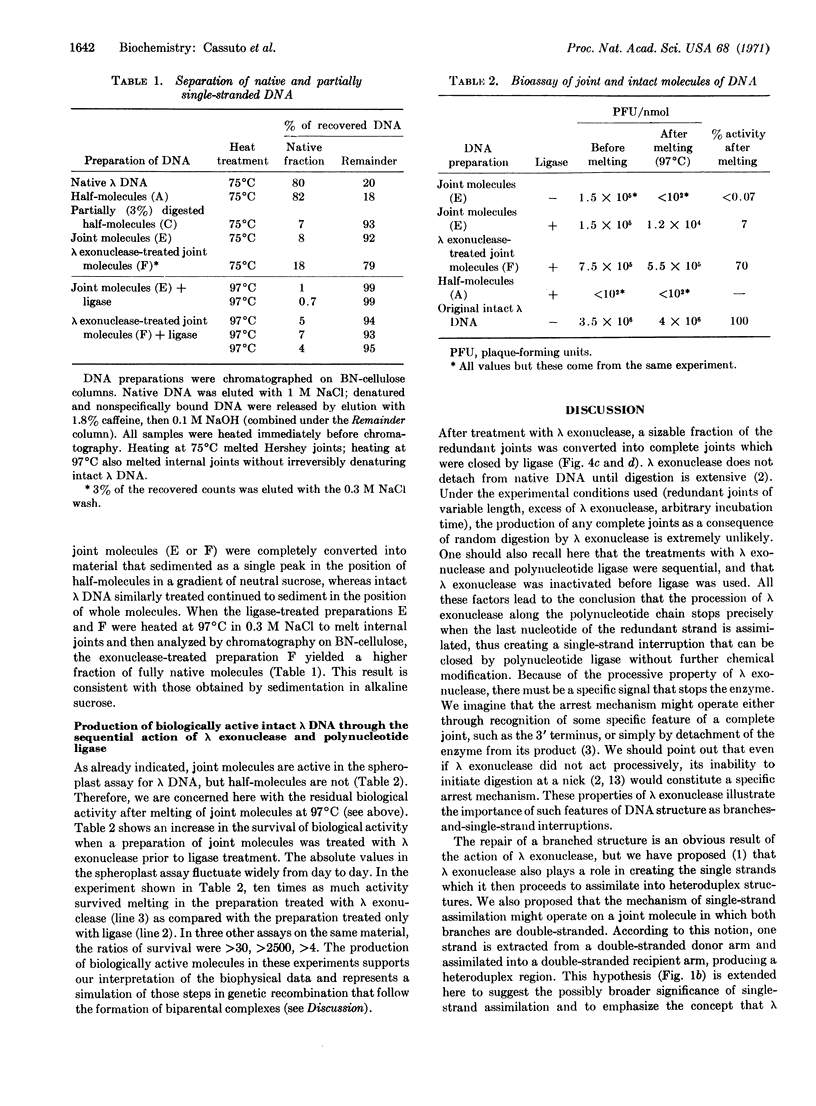
The sequential action of λ exonuclease and polynucleotide ligase upon redundant joint molecules is sufficient to produce intact polynucleotide chains and heat-stable, biologically active molecules of λ DNA, whereas the action of ligase alone is insufficient. These results (a) confirm the previously described mechanism of single-strand assimilation, including a subsidiary mechanism by which the further action of λ exonuclease is arrested when a redundant strand is completely assimilated, and (b) represent a simulation of the steps in genetic recombination that follow the formation of biparental complexes (synapsis). λ exonuclease is postulated to catalyze a concerted reaction that includes exposure of complementary sequences, formation of heteroduplex regions, and elimination of redundant branches.
Keywords: single-strand assimilation, mechanism of arrest
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Frey L. T4 bacteriophage gene 32: a structural protein in the replication and recombination of DNA. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1313–1318. doi: 10.1038/2271313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon T., Zinder N. D. A mechanism for genetic recombination generating one parent and one recombinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):573–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. M., Radding C. M. The role of exonuclease and beta protein of phage lambda in genetic recombination. II. Substrate specificity and the mode of action of lambda exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2502–2512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER D., JERREL E. A. The amino acid composition of T3 bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer V. N., Rupp W. D. Usefulness of benzoylated naphthoylated DEAE-cellulose to distinguish and fractionate double-stranded DNA bearing different extents of single-stranded regions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 1;228(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90551-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. S., Davis R. W., Davidson N. A physical study by electron microscopy of the terminally reptitious, circularly permuted DNA from the coliphage particles of Escherichia coli 15. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. II. Nature of the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackinlay A. G., Kaiser A. D. DNA replication in head mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):679–683. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masamune Y., Fleischman R. A., Richardson C. C. Enzymatic removal and replacement of nucleotides at single strand breaks in deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2680–2691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M., Carter D. M. The role of exonuclease and beta protein of phage lambda in genetic recombination. 3. Binding to deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2513–2518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedat J. W., Kelly R. B., Sinsheimer R. L. Fractionation of nucleic acid on benzoylated-naphthoylated DEAE cellulose. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Thompson A., Richardson C. C. Ezymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. VII. Properties of the enzyme-adenylate intermediate in the polynucleotide ligase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4556–4563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. T., 2nd, Sinsheimer R. L. Vegetative bacteriophage lambda-DNA. I. Infectivity in a spheroplast assay. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):147–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



