Abstract
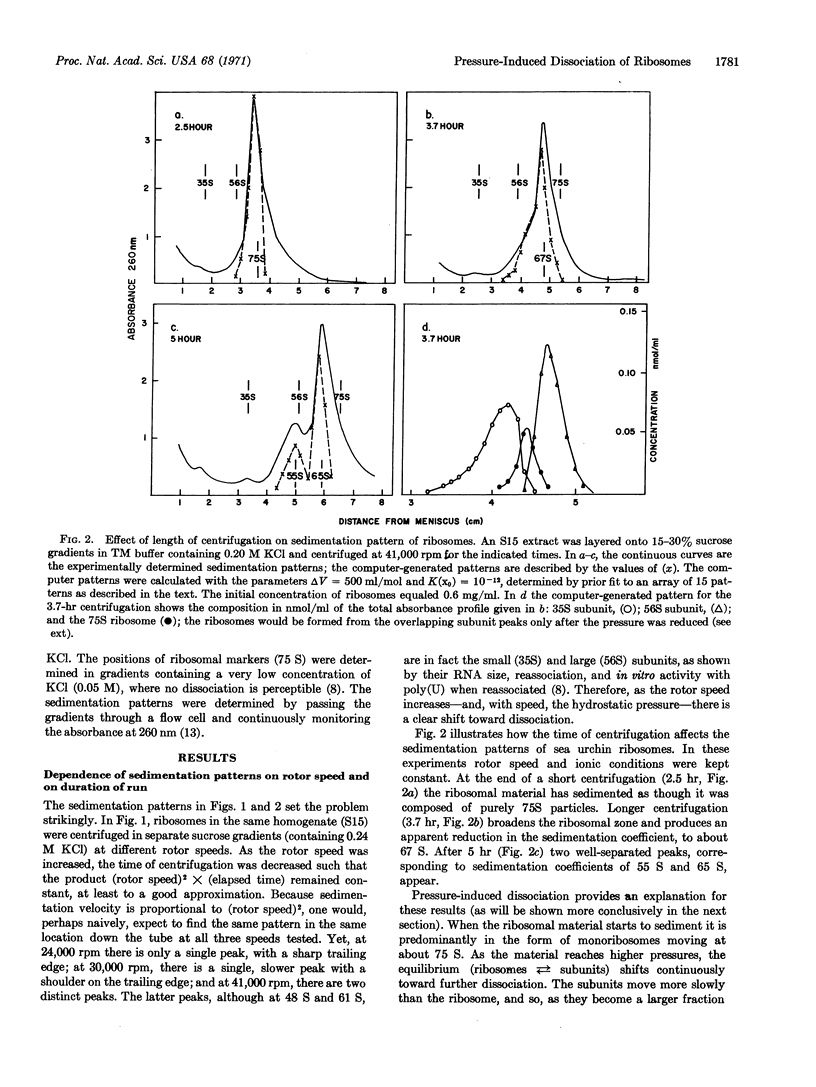
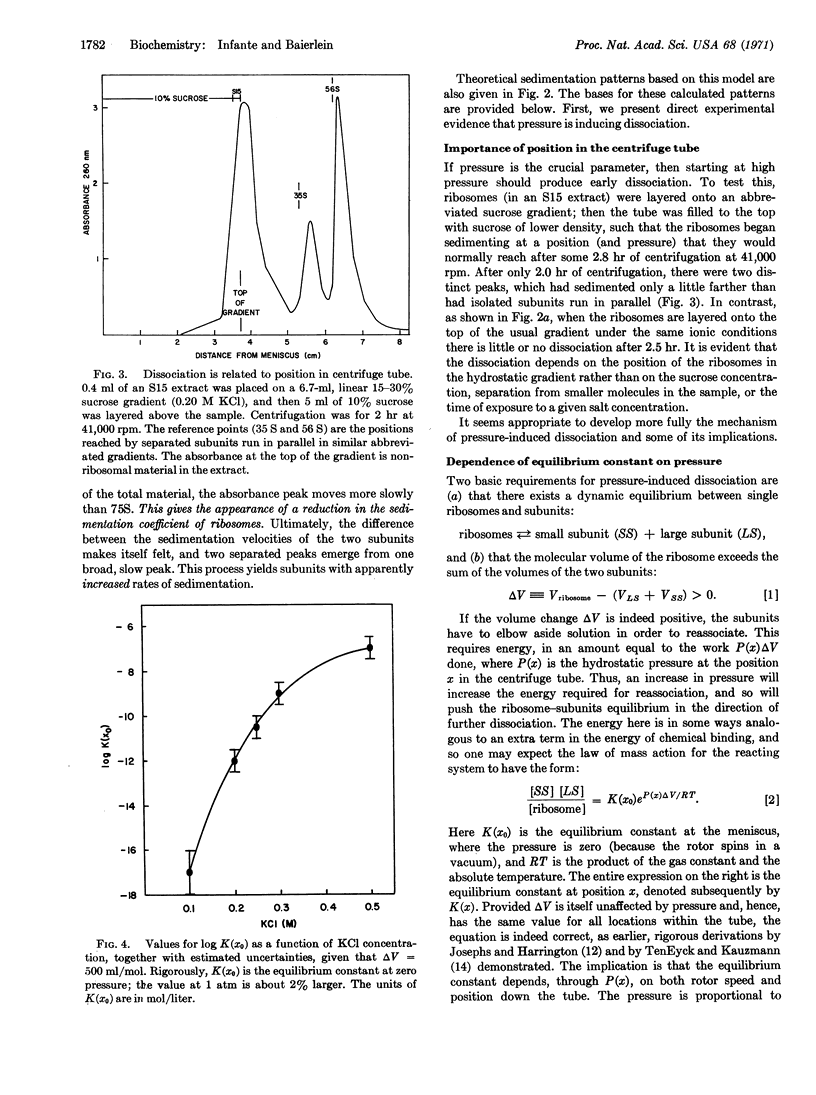
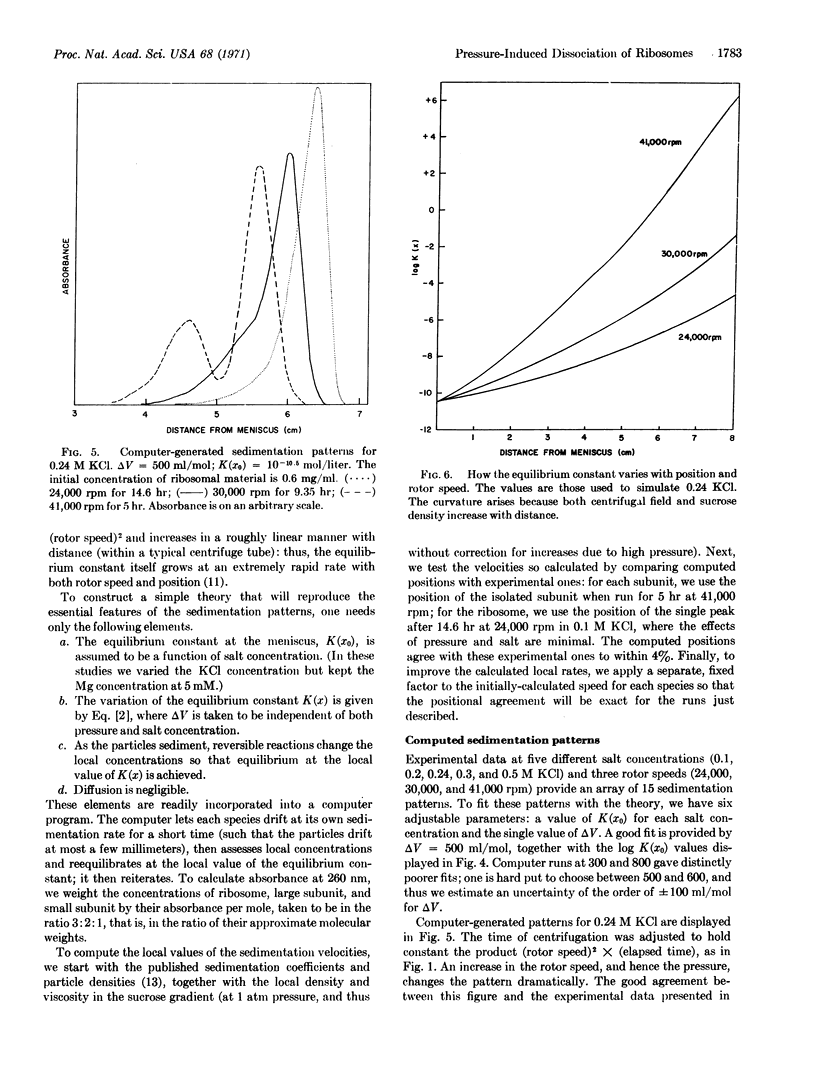
Anomalous sedimentation patterns arise when free ribosomes from sea urchin eggs are centrifuged at high speeds. Pressure-induced dissociation of the ribosomes during sedimentation can explain the peculiar behavior; the assumption of such dissociation also yields estimates of the equilibrium constant (as a function of KCl concentration) and the change in molecular volume (500 ± 100 ml/mol) in the reaction: subunits ⇄ ribosome. Such dissociation during centrifugation may explain many experiments in which apparent reduced sedimentation coefficients for ribosomes, and increased coefficients for the subunits, have been ascribed to conformational changes.
Keywords: ultracentrifuge, sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus, ribosomal conformation
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAKKE M. K. NONIDEAL SEDIMENTATION AND THE CAPACITY OF SUCROSE GRADIENT COLUMNS FOR VIRUS IN DENSITY-GRADIENT CENTRIFUGATION. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Sep;107:388–403. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarini C., Campo M. S., Andronico F. Biosynthesis and distribution of ribosomal particles in the cellular slime mould, Dictyostelium purpureum. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90444-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey A. K., Staehelin T. Structure and function of mammalian ribosomes. II. Exchange of ribosomal subunits at various stages of in vitro polypeptide synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):21–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Graves P. N. Stability of free ribosomes, derived ribosomes and polysomes of the sea urchin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 12;246(1):100–110. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Krauss M. Dissociation of ribosomes induced by centrifugation: evidence for doubting conformational changes in ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 12;246(1):81–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Nemer M. Heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles in the cytoplasm of sea urchin embryos. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 28;32(3):543–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs R., Harrington W. F. An unusual pressure dependence for a reversibly associating protein system; sedimentation studies on myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1587–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs R., Harrington W. F. On the stability of myosin filaments. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2834–2847. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R. Dissociation of ribosomes on polypeptide chain termination and origin of single ribosomes. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):534–537. doi: 10.1038/228534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kegeles G., Rhodes L., Bethune J. L. Sedimentation behavior of chemically reacting systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):45–51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. E., Rolleston F. S., Low R. B., Wool I. G. Dissociation and reassociation of skeletal muscle ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):135–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto T. Intermediate stage in the association and dissociation of Escherichia coli ribosomes and the combining properties of their subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 20;182(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90528-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner A. H., Rowe J., Macindoe H. M. Structural studies on the ribosomes of Paramecium: evidence for a "primitive" animal ribosome. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 28;32(3):587–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron E. Z., Kohler R. E., Davis B. D. Magnesium ion dependence of free and polysomal ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 28;36(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Noll H. Chain initiation in primitive protein synthesis: a 60S intermediate in the formation of active 70S ribosomes. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):128–133. doi: 10.1038/227128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Noll H. Conformational changes in ribosomes during protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Ron E. Z., Davis B. D. A factor required for ribosome dissociation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):761–767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuka I. Effect of ethylendiaminetetraacetate on Escherichia coli B ribosomes--binding of phenylalanyl sRNA to 50S particles converted from 70S ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Dec 15;29(5):667–673. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASHIRO Y., SIEKEVITZ P. ULTRACENTRIFUGAL STUDIES ON THE DISSOCIATION OF HEPATIC RIBOSOMES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:149–165. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teneyck L. F., Kauzmann W. Pressure and hydration effects on chemically reacting systems in the ultracentrifuge. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):888–894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


