Abstract
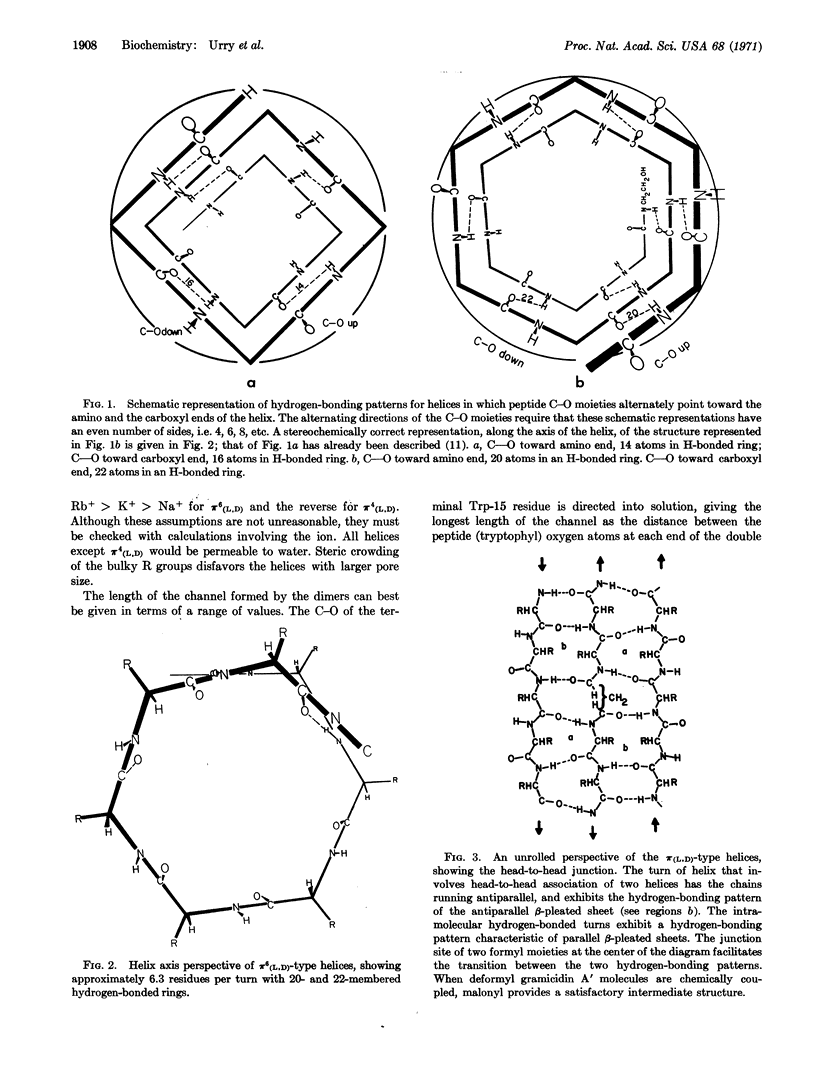
A series of helical structures for gramicidin A, with alternating L and D residues, are characterized as to number of residues per turn, atoms in hydrogenbonded rings, and dihedral angles. Because of alternating peptide C-O directions, these helices are capable of forming head-to-head hydrogen-bonded dimers with the capacity of functioning as transmembrane channels. The dimers are characterized as to channel length, pore size, and expected ion selectivity.
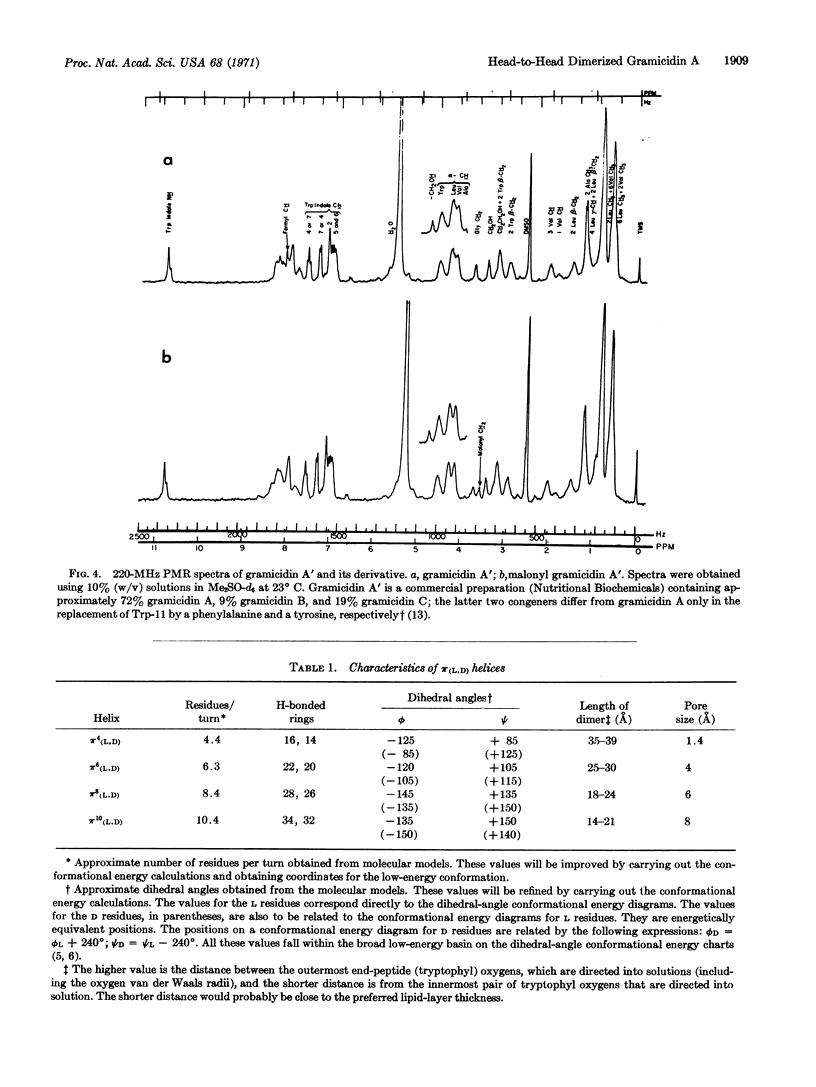
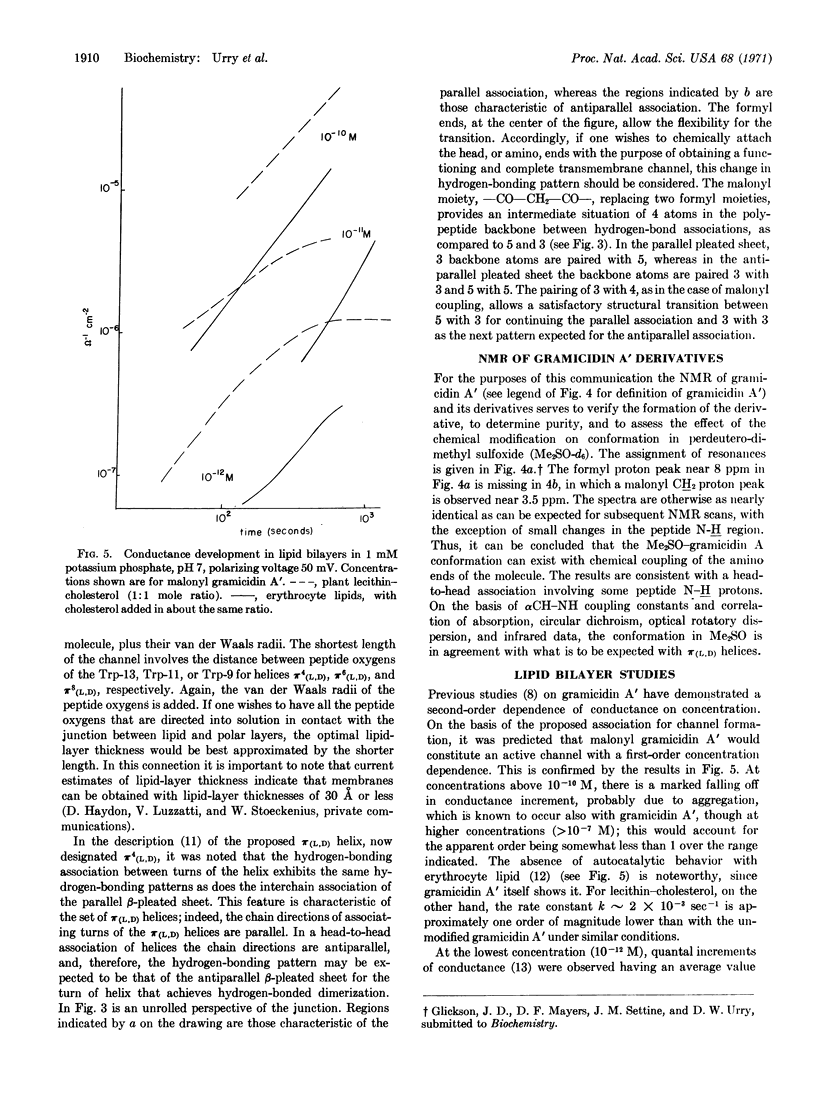
In a test of the proposed head-to-head association for channel formation, the malonyl dimer [N,N′-(dideformyl gramicidin A)-malonamide] was synthesized. The chemical and conformational integrity of the product was verified by nuclear magnetic resonance; in lipid bilayer studies, the dimer was found to be a potent mediator of ion conductance with the predicted concentration dependence.
Thus, the results on malonyl gramicidin A prove head-to-head association in formation of the transmembrane channel, and the results are consistent with the specific geometrical configuration involved in head-to-head dimerization of π(L,D) helices. At this stage, the action of gramicidin A on membranes with lipid-layer thicknesses of 30 Å or less can best be understood in terms of the π(L,D) helix with 6.3 residues per turn.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Donohue J. Hydrogen Bonded Helical Configurations of the Polypeptide Chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Jun;39(6):470–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.6.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall M. C. Structural effects in the action of antibiotics on the ion permeability of lipid bilayers. 3. Gramicidins "A" and "S", and lipid specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 1;219(2):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall M. C. Structural effects in the action of antibiotics on the ion permeability of lipid bilayers. I. Tyrocidine B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 17;203(1):28–33. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Discreteness of conductance change in bimolecular lipid membranes in the presence of certain antibiotics. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):451–453. doi: 10.1038/225451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi T., Scott R. A., Vanderkooi G., Scheraga H. A. Conformation of analysis of macromolecules. IV. Helical structures of poly-L-alanine, poly-L-valine, poly-beta-methyl-L-aspartate, poly-gamma-methyl-L-glutamate, and poly-L-tyrosine. J Chem Phys. 1967 Jun 1;46(11):4410–4426. doi: 10.1063/1.1840561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B. Atomic coordinates and structure factors for two helical configurations of polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 May;37(5):235–240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.5.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B., BRANSON H. R. The structure of proteins; two hydrogen-bonded helical configurations of the polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 Apr;37(4):205–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.4.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMACHANDRAN G. N., RAMAKRISHNAN C., SASISEKHARAN V. Stereochemistry of polypeptide chain configurations. J Mol Biol. 1963 Jul;7:95–99. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARGES R., WITKOP B. GRAMICIDIN A. V. THE STRUCTURE OF VALINE- AND ISOLEUCINE-GRAMICIDIN A. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 May 5;87:2011–2020. doi: 10.1021/ja01087a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


