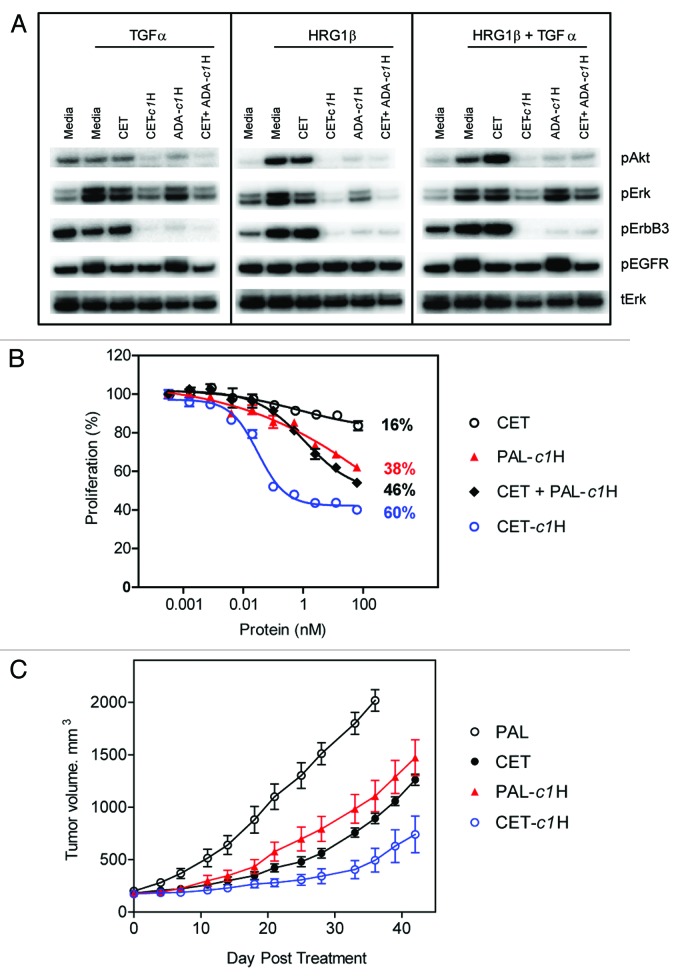
Figure 6. Cetuximab-based zybodies inhibit signaling, cell proliferation and tumor growth in vivo. (A) BxPC-3 cells were pretreated for 3.5 h at 37°C in serum-free media with 63 nM of various combinations of cetuximab (CET), the cetuximab zybody containing and ErbB3 MRD (CET-c1H) or the MRD control zybody (ADA-c1H). Cells then received TGFα or HRG1β for 10 min prior to lysis, western blotting and detection of phosphorylated Erk (pERK), phosphorylated Akt (pAKT), phosphorylated EGFR (pEGFR), pErbB3. (B) Inhibition of proliferation of BxPC-3 cells was assayed after treatment for 96 h with the indicated proteins. Palivizumab (PAL) was used as an irrelevant scaffold (specific for respiratory syncytial virus) on which to build the MRD control, PAL-c1H. (C) The in vivo efficacy of CET-c1H was assessed in a xenograft tumor model sensitive to the independent inhibition of EGFR and ErbB3. Mice with pre-established BxPC-3 tumors were treated with cetuximab (CET) or the bispecific zybody targeting EGFR and ErbB3 (CET-c1H). Palivizumab (PAL) and PAL-c1H were used as the isotype and MRD controls, respectively. The P value for Mann Whitney t-test comparing CET-c1H to cetuximab at day 42 is 0.045.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.