Abstract
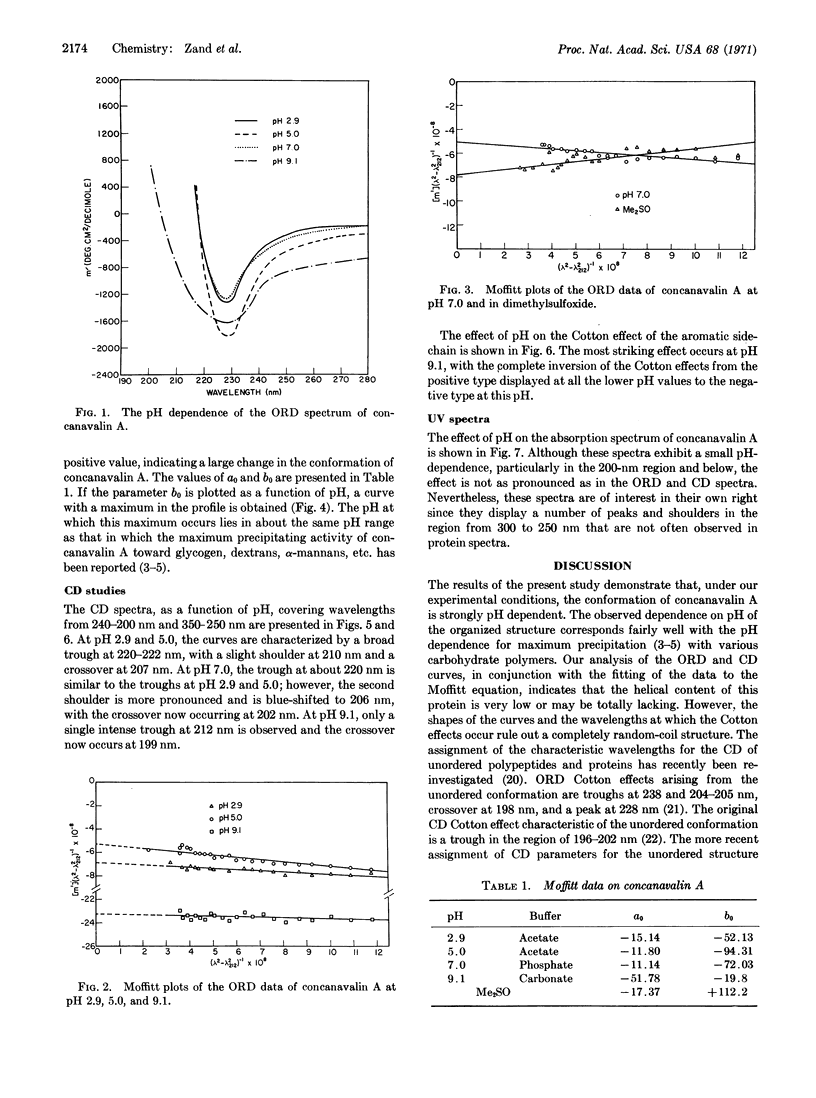
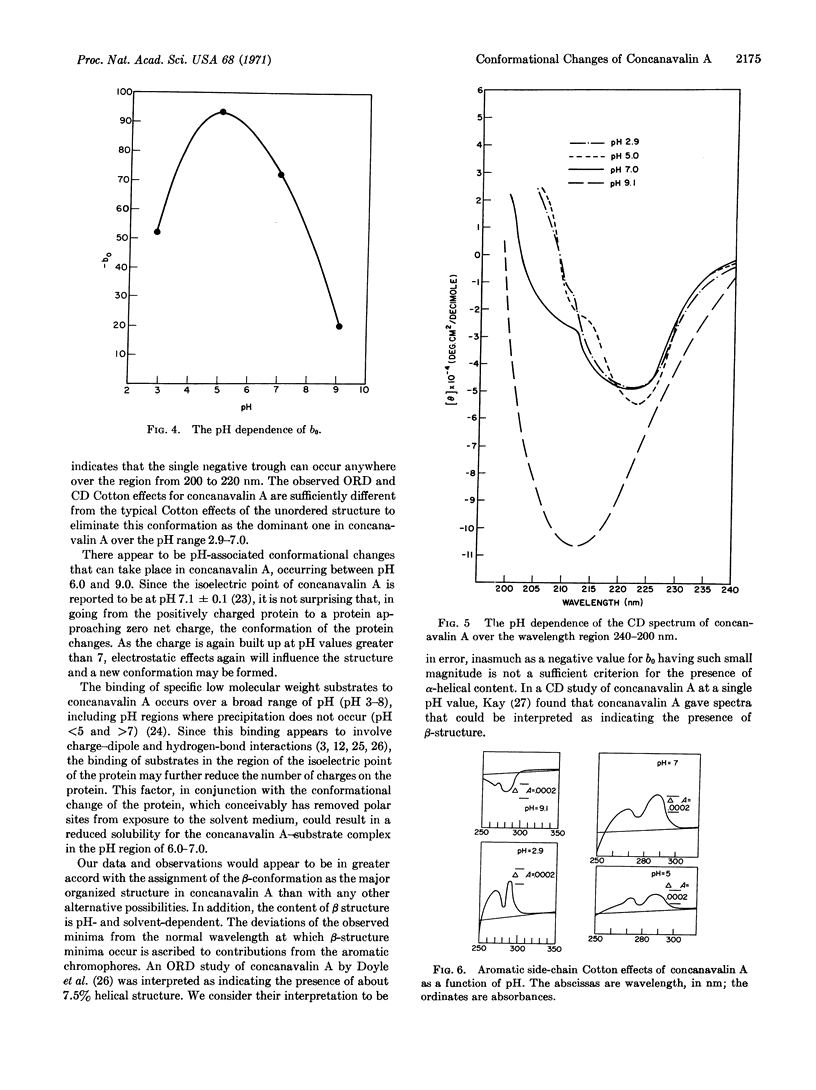
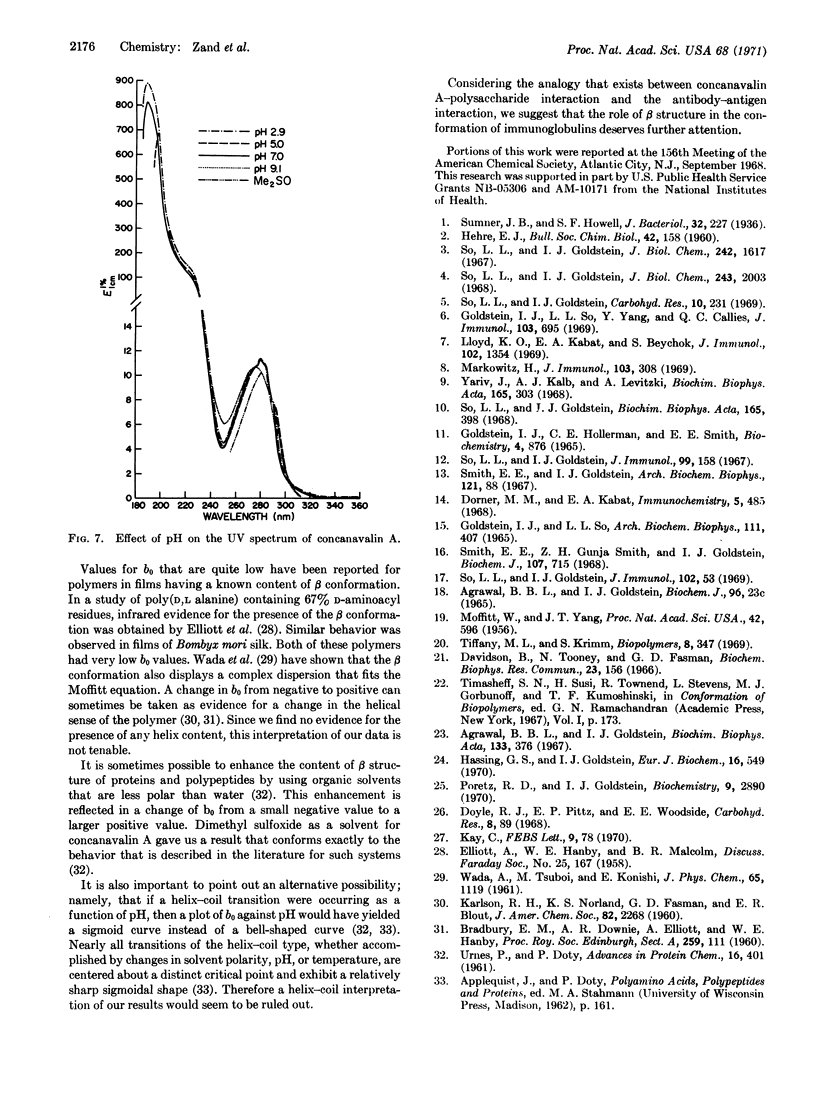
The pH dependence of the conformation of concanavalin A has been studied by means of optical rotatory dispersion and circular dichroism spectroscopy. At pH 2.9, 5.0, and 7.0, the major contribution to organized structure appears to be the β conformation. At pH 9.1, the conformation of concanavalin A approaches the random coil or unordered form. No evidence could be found for the presence of any significant amount of α helix. The pH of maximum precipitin-like activity of concanavalin A is paralleled by the pH dependence of the parameter b0 in the Moffitt equation.
Keywords: Moffitt equation, ORD spectra, CD spectra, precipitin, protein structure
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal B. B., Goldstein I. J. Physical and chemical characterization of concanavalin A, the hemagglutinin from jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):376–379. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B., Tooney N., Fasman G. D. The optical rotatory dispersion of the beta structure of poly-L-lysine and poly-L-serine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Apr 19;23(2):156–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN I. J., HOLLERMAN C. E., SMITH E. E. PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTION. II. INHIBITION STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION OF CONCANAVALIN A WITH POLYSACCHARIDES. Biochemistry. 1965 May;4:876–883. doi: 10.1021/bi00881a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., So L. L. Protein-carbonhydrate interaction. 3. Agar gel-diffusion studies on the interaction of Concanavalin A, a lectin isolated from jack bean, with polysaccharides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Aug;111(2):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., So L. L., Yang Y., Callies Q. C. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. XIX. The interaction of concanavalin A with IgM and the glycoprotein phytohemagglutinins of the waxbean and the soybean. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):695–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassing G. S., Goldstein I. J. Ultraviolet difference spectral studies on concanavalin A. Carbohydrate interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Nov;16(3):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay C. M. The presence of beta-structure in concanavalin A. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jul 29;9(2):78–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O., Kabat E. A., Beychok S. Immunochemical studies on blood groups. 43. The interaction of blood group substances from various sources with a plant lectin, concanavalin A. J Immunol. 1969 Jun;102(6):1354–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz H. Interaction of concanavalin A with polysaccharides of Histoplasma capsulatum. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):308–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt W., Yang J. T. THE OPTICAL ROTATORY DISPERSION OF SIMPLE POLYPEPTIDES. I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):596–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poretz R. D., Goldstein I. J. An examination of the topography of the saccharide binding sites of concanavalin A and of the forces involved in complexation. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 7;9(14):2890–2896. doi: 10.1021/bi00816a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. E., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. V. Further inhibition studies directed toward defining the stereochemical requirements of the reactive sites of concanavalin A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Jul;121(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. E., Smith Z. H., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. A turbidimetric study of the interaction of concanavalin A with amylopectin and glycogen and some of their enzymic and chemical degradation products. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):715–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1070715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So L. L., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. 13. The interaction of concanavalin A with alpha-mannans from a variety of microorganisms. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):2003–2007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So L. L., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. IV. Application of the quantitative precipitin method to polysaccharide-concanavalin A interaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1617–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So L. L., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. IX. Application of the quantitative hapten inhibition technique to polysaccharide-concanavalin A interaction. Some comments on the forces involved n concanavalin A-polysaccharide interaction. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):158–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So L. L., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. XVII. The effect of polysaccharide molecular weight on the concanavalin A-polysaccharide precipitation reaction. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So L. L., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. XX. On the number of combining sites on concanavalin A, the phytohemagglutinin of the jack bean. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 15;165(3):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B., Howell S. F. Identification of Hemagglutinin of Jack Bean with Concanavalin A. J Bacteriol. 1936 Aug;32(2):227–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.2.227-237.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URNES P., DOTY P. Optical rotation and the conformation of polypeptides and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1961;16:401–544. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yariv J., Kalb A. J., Levitzki A. The interaction of concanavalin A with methyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 3;165(2):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



