Abstract
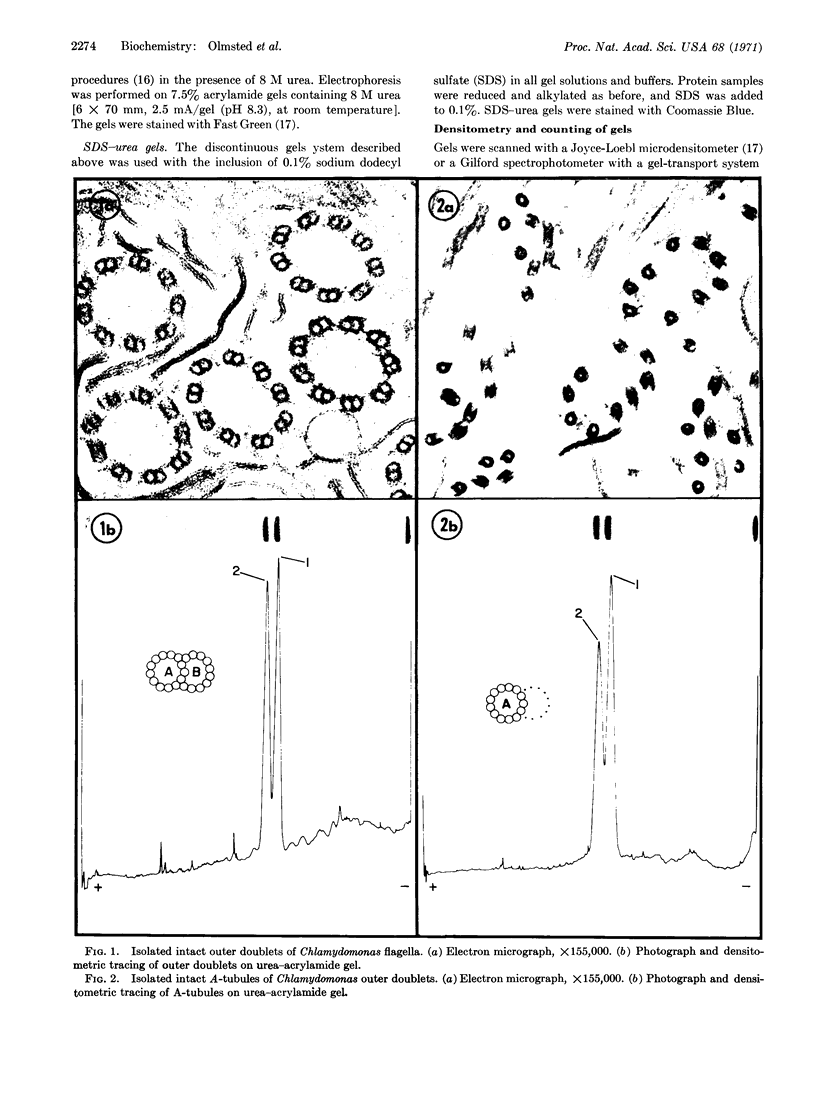
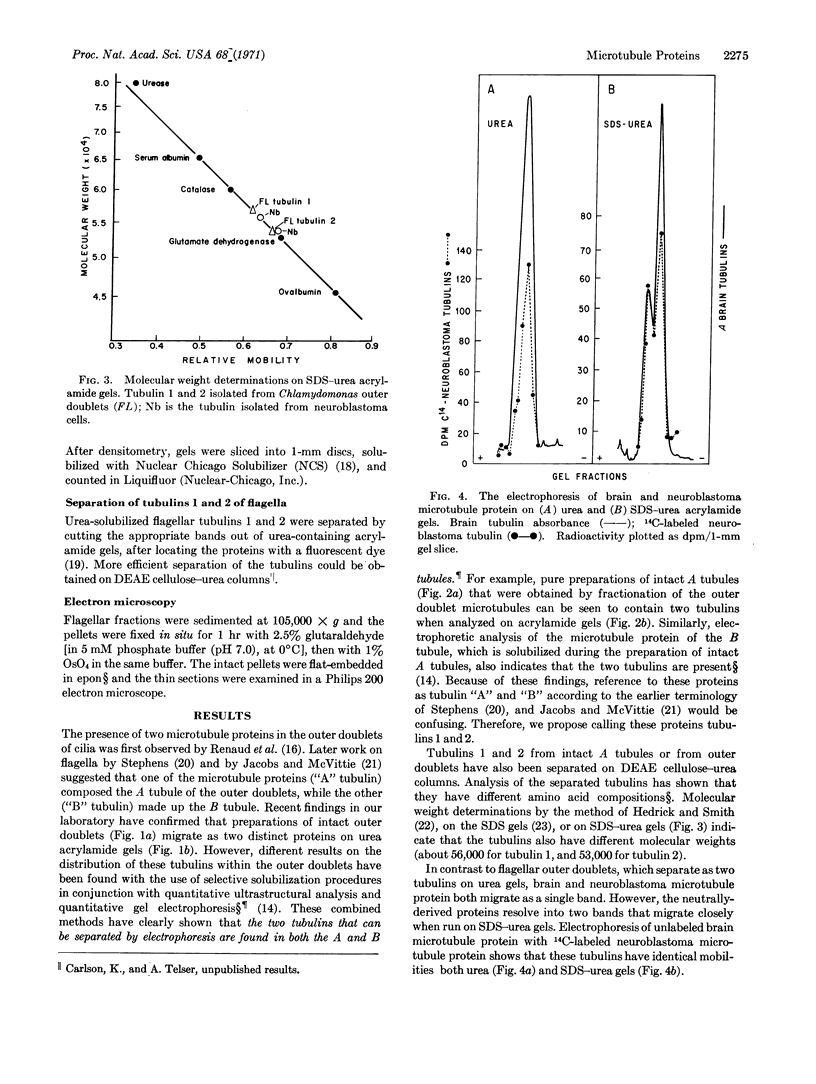
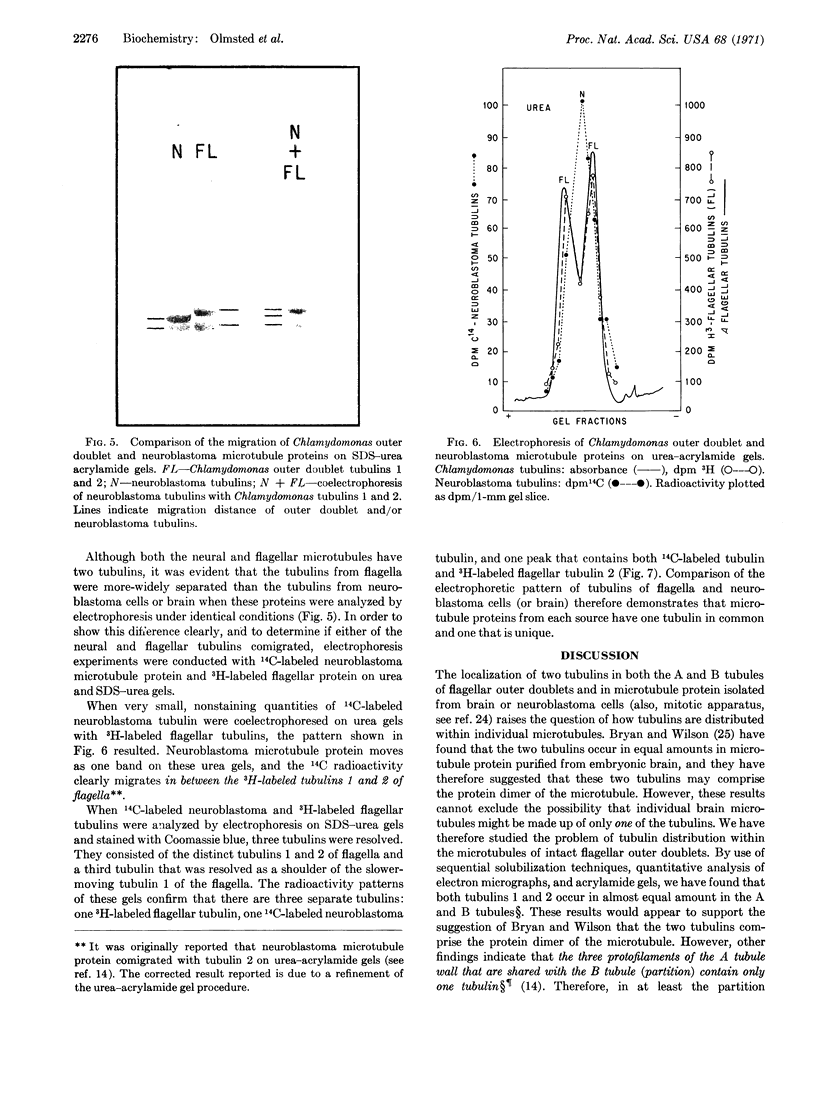
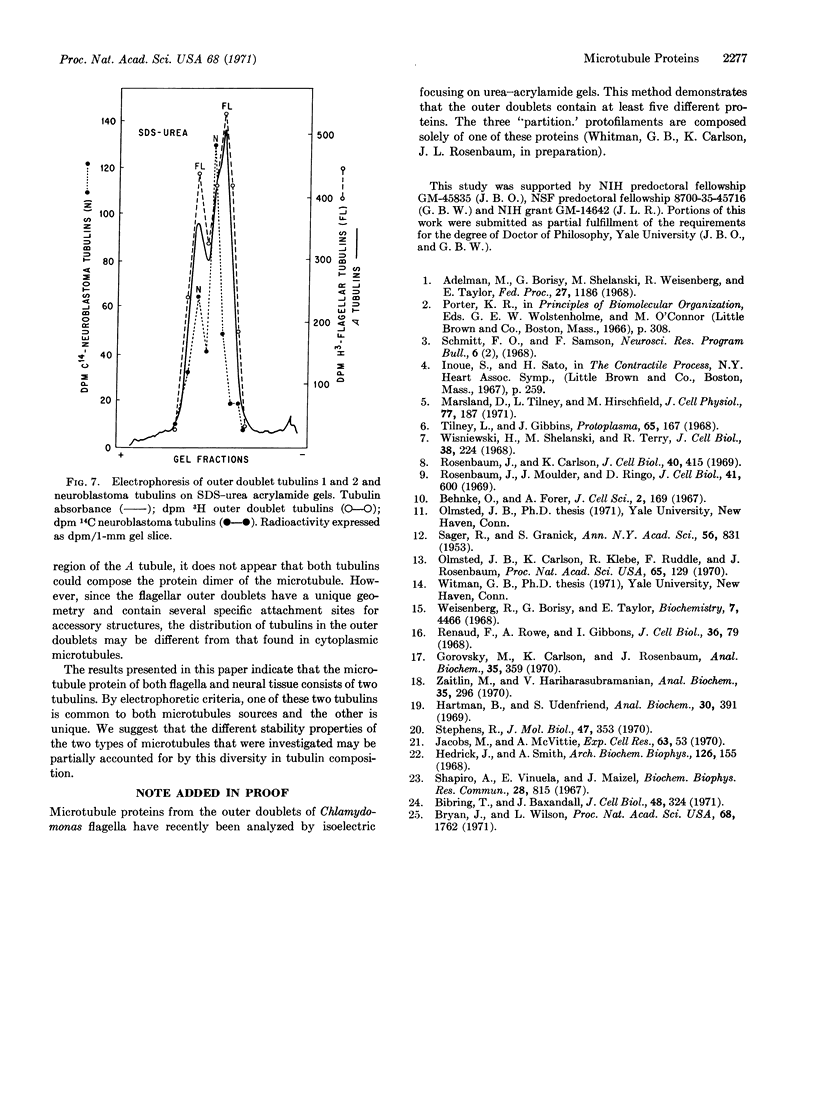
Intact A microtubules isolated from outer doublet microtubules of Chlamydomonas flagella contain two separable proteins (tubulins) that differ in molecular weight and in amino-acid composition. The microtubule protein isolated from brain or neuroblastoma cells also has two electrophoretically distinct tubulins. Although the two tubulins of brain and neuroblastoma cells are electrophoretically similar to each other, only one of these tubulins migrates with the flagellar tubulins. This is the first evidence that (a) isolated, morphologically intact, single microtubules from flagella contain at least two different tubulins, and (b) at least one of these tubulins differs from tubulins that are isolated from other sources.
Keywords: tubulin, flagellar outer doublets, electron microscopy, acrylamide gel electrophoresis
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman M. R., Borisy G. G., Shelanski M. L., Weisenberg R. C., Taylor E. W. Cytoplasmic filaments and tubules. Fed Proc. 1968 Sep-Oct;27(5):1186–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O., Forer A. Evidence for four classes of microtubules in individual cells. J Cell Sci. 1967 Jun;2(2):169–192. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Wilson L. Are cytoplasmic microtubules heteropolymers? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1762–1766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Carlson K., Rosenbaum J. L. Simple method for quantitive densitometry of polyacrylamide gels using fast green. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jun;35(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. K., Udenfriend S. A method for immediate visualization of proteins in acrylamide gels and its use for preparation of antibodies to enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1969 Sep;30(3):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., McVittie A. Identification of the flagellar proteins of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Nov;63(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsland D., Tilney L. G., Hirshfield M. Stabilizing effects of D2O on the microtubular components and needle-like form of heliozoan axopods: a pressure-temperature analysis. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):187–194. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B., Carlson K., Klebe R., Ruddle F., Rosenbaum J. Isolation of microtubule protein from cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):129–136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. L., Carlson K. Cilia regeneration in Tetrahymena and its inhibition by colchicine. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):415–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. L., Moulder J. E., Ringo D. L. Flagellar elongation and shortening in Chlamydomonas. The use of cycloheximide and colchicine to study the synthesis and assembly of flagellar proteins. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):600–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R., GRANICK S. Nutritional studies with Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Oct 14;56(5):831–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. Thermal fractionation of outer fiber doublet microtubules into A- and B-subfiber components. A- and B-tubulin. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Gibbins J. R. Differential effects of antimitotic agents on the stability and behavior of cytoplasmic and ciliary microtubules. Protoplasma. 1968;65(1):167–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01666377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C., Borisy G. G., Taylor E. W. The colchicine-binding protein of mammalian brain and its relation to microtubules. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4466–4479. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H., Shelanski M. L., Terry R. D. Effects of mitotic spindle inhibitors on neurotubules and neurofilaments in anterior horn cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):224–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaitlin M., Hariharasubramanian V. An improvement in a procedure for counting tritium and carbon-14 in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1970 May;35(1):296–297. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]