Abstract
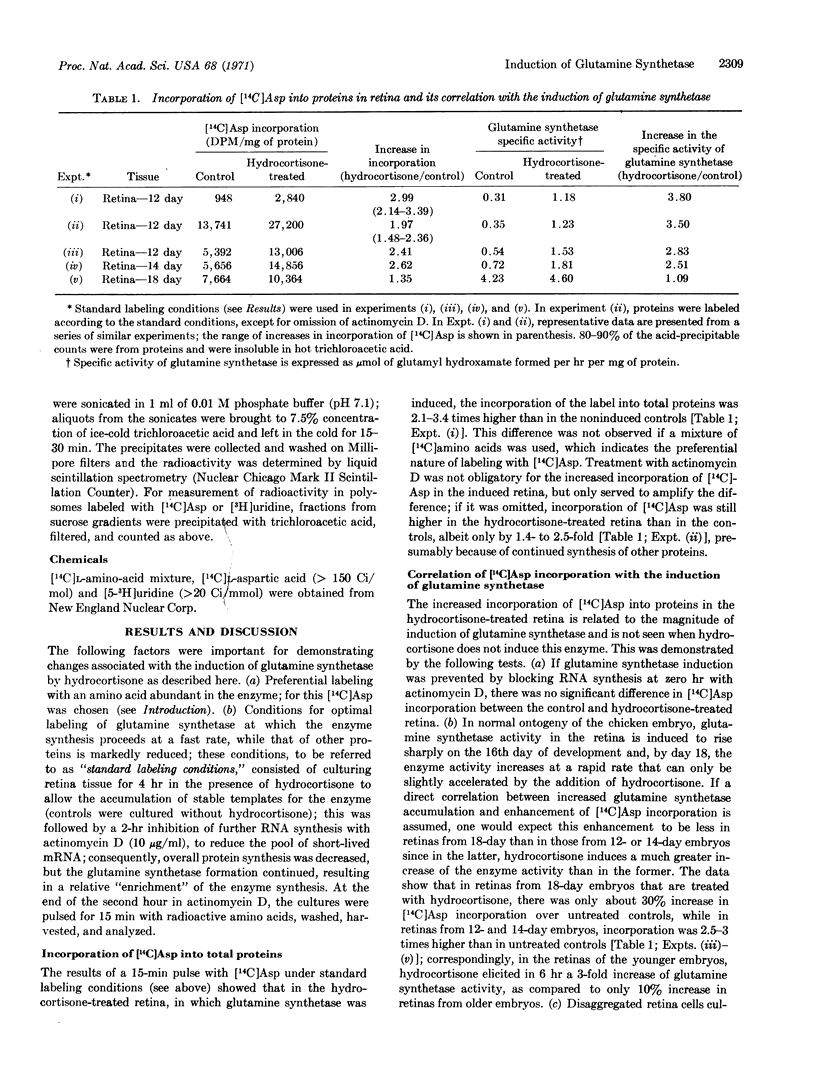
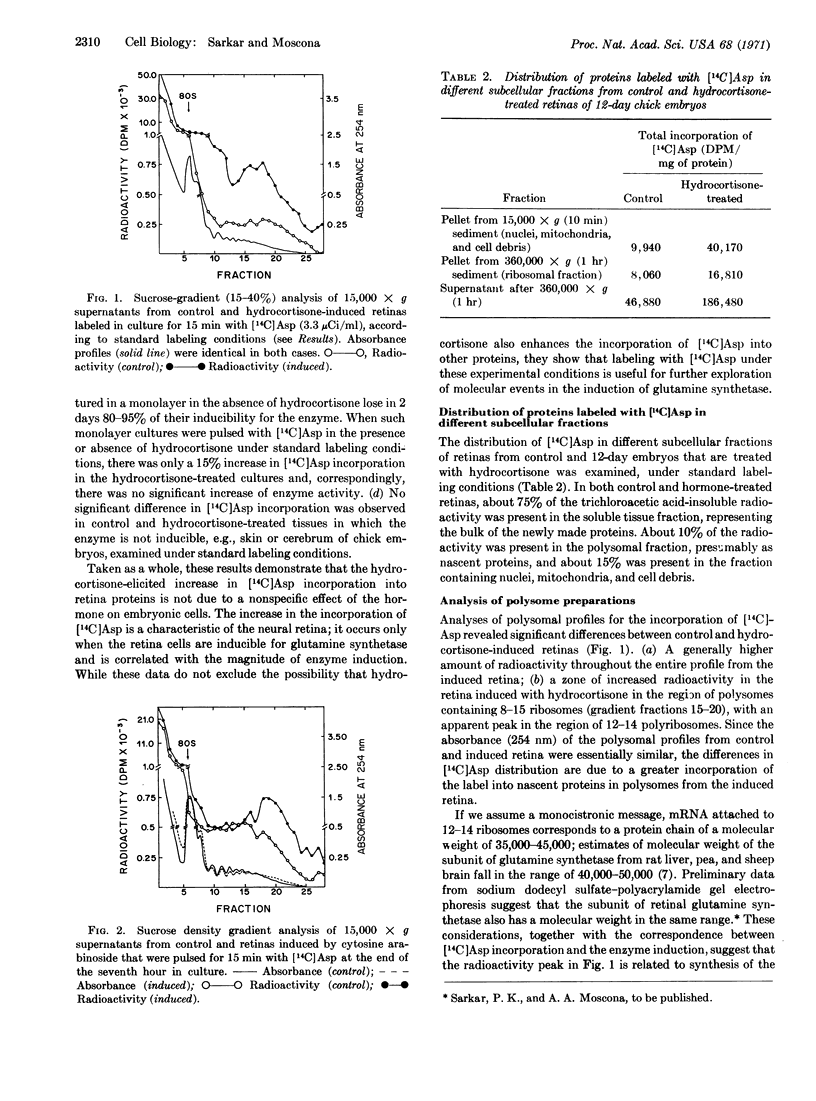
The hydrocortisone-mediated induction of glutamine synthetase in the neural retina of chicken embryo in vitro is correlated with enhanced incorporation into protein of [14C]aspartic acid, an amino acid abundant in this enzyme. In the induced retina labeled with [14C]aspartic acid, a peak of radioactivity was detected in the region of the polysomal profile corresponding to polysomes comprising 12-14 ribosomes. In retinas labeled with [3H]uridine, an increased amount of radioactivity was also detected in the same polysomal region of the hydrocortisone-induced retina. If we assume a monocistronic messenger RNA for retinal glutamine synthetase, this region corresponds to the estimated size of the polysomes necessary for the translation of this enzyme. The evidence presented demonstrates a correlation between these changes in incorporation and the induction of glutamine synthetase.
Keywords: hydrocortisone, differentiation, polysomes, cytosine arabinoside
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alescio T., Moscona A. A. Immunochemical evidence for enzyme synthesis in the hormonal induction of glutamine synthetase in embryonic retina in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jan 27;34(2):176–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90628-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alescio T., Moscona M., Moscona A. A. Induction of glutamine synthetase in embryonic retina. Effects of partial and complete inhibition of RNA synthesis on enzyme accumulation. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Aug;61(2):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90456-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Ginsburg A., Yeh J., Shelton E., Stadtman E. R. Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase. Purification and physical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5195–5205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. E., Moscona A. A. Induction of glutamine synthetase in embryonic retina: its dependence on cell interactions. Science. 1970 Mar 27;167(3926):1736–1738. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3926.1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Moscona M. H., Saenz N. Enzyme induction in embryonic retina: the role of transcription and translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Moscona M., Jones R. E. Induction of glutamine synthetase in embryonic neural retina in vitro by inhibitors of macromolecular synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jun 5;39(5):943–949. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90415-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddington R., Moscona A. A. Correspondence between glutamine synthetase activity and differentiation in the embryonic retina in situ and in cultrue. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):247–252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif-Lehrer L., Amos H. Hydrocortisone requirement for the induction of glutamine synthetase in chick-embryo retinas. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):425–430. doi: 10.1042/bj1060425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Wilk S., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Preparation and studies on the characterization of sheep brain glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2670–2674. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


