Abstract
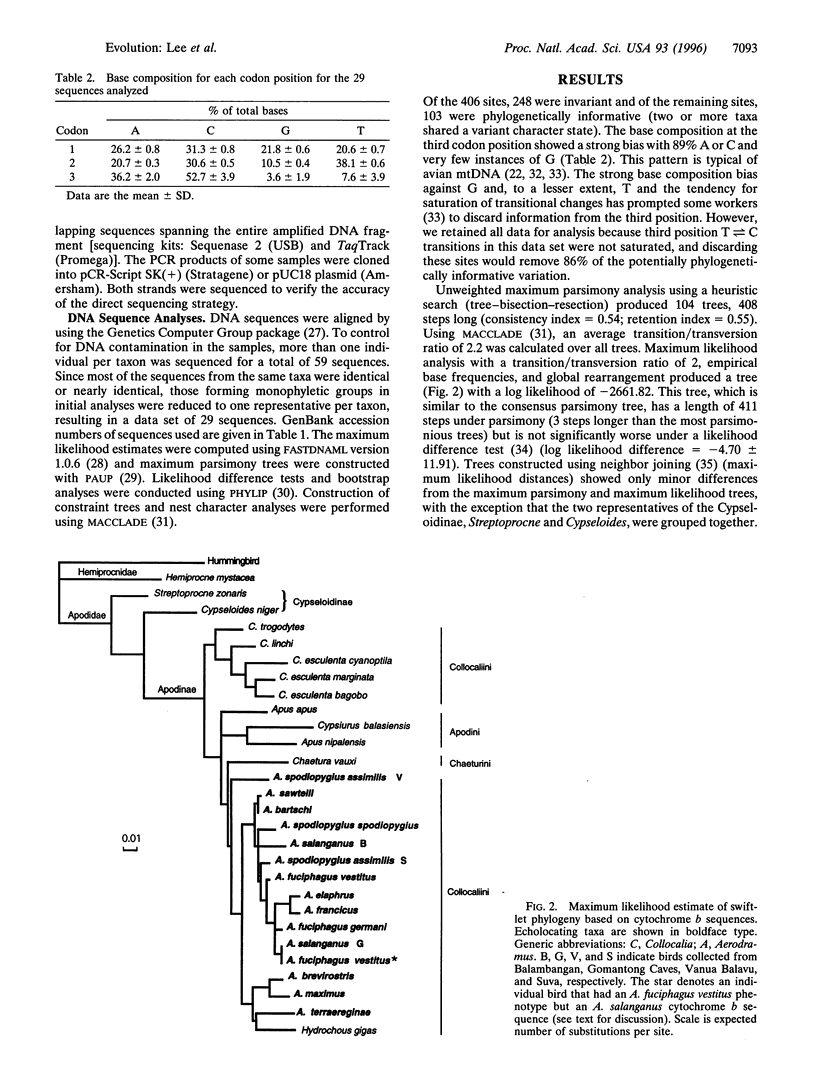
Swiftlets are small insectivorous birds, many of which nest in caves and are known to echolocate. Due to a lack of distinguishing morphological characters, the taxonomy of swiftlets is primarily based on the presence or absence of echolocating ability, together with nest characters. To test the reliability of these behavioral characters, we constructed an independent phylogeny using cytochrome b mitochondrial DNA sequences from swiftlets and their relatives. This phylogeny is broadly consistent with the higher classification of swifts but does not support the monophyly of swiftlets. Echolocating swiftlets (Aerodramus) and the nonecholocating "giant swiftlet" (Hydrochous gigas) group together, but the remaining nonecholocating swiftlets belonging to Collocalia are not sister taxa to these swiftlets. While echolocation may be a synapomorphy of Aerodramus (perhaps secondarily lost in Hydrochous), no character of Aerodramus nests showed a statistically significant fit to the molecular phylogeny, indicating that nest characters are not phylogenetically reliable in this group.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleiweiss R., Kirsch J. A., Lapointe F. J. DNA-DNA hybridization-based phylogeny for "higher" nonpasserines: reevaluating a key portion of the avian family tree. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1994 Sep;3(3):248–255. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1994.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. H., Harvey P. H. Hanging nests on a phylogenetic tree. Curr Biol. 1993 Dec 1;3(12):882–883. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90225-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins P., Morais R. Nucleotide sequence and evolution of coding and noncoding regions of a quail mitochondrial genome. J Mol Evol. 1991 Feb;32(2):153–161. doi: 10.1007/BF02515387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards S. V., Arctander P., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial resolution of a deep branch in the genealogical tree for perching birds. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Feb 22;243(1307):99–107. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishino H., Hasegawa M. Evaluation of the maximum likelihood estimate of the evolutionary tree topologies from DNA sequence data, and the branching order in hominoidea. J Mol Evol. 1989 Aug;29(2):170–179. doi: 10.1007/BF02100115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher T. D., Thomas W. K., Meyer A., Edwards S. V., Päbo S., Villablanca F. X., Wilson A. C. Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Matsuda H., Hagstrom R., Overbeek R. fastDNAmL: a tool for construction of phylogenetic trees of DNA sequences using maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci. 1994 Feb;10(1):41–48. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler D. W., Sheldon F. H. Evolution of nest construction in swallows (Hirundinidae): a molecular phylogenetic perspective. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5705–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




