Abstract
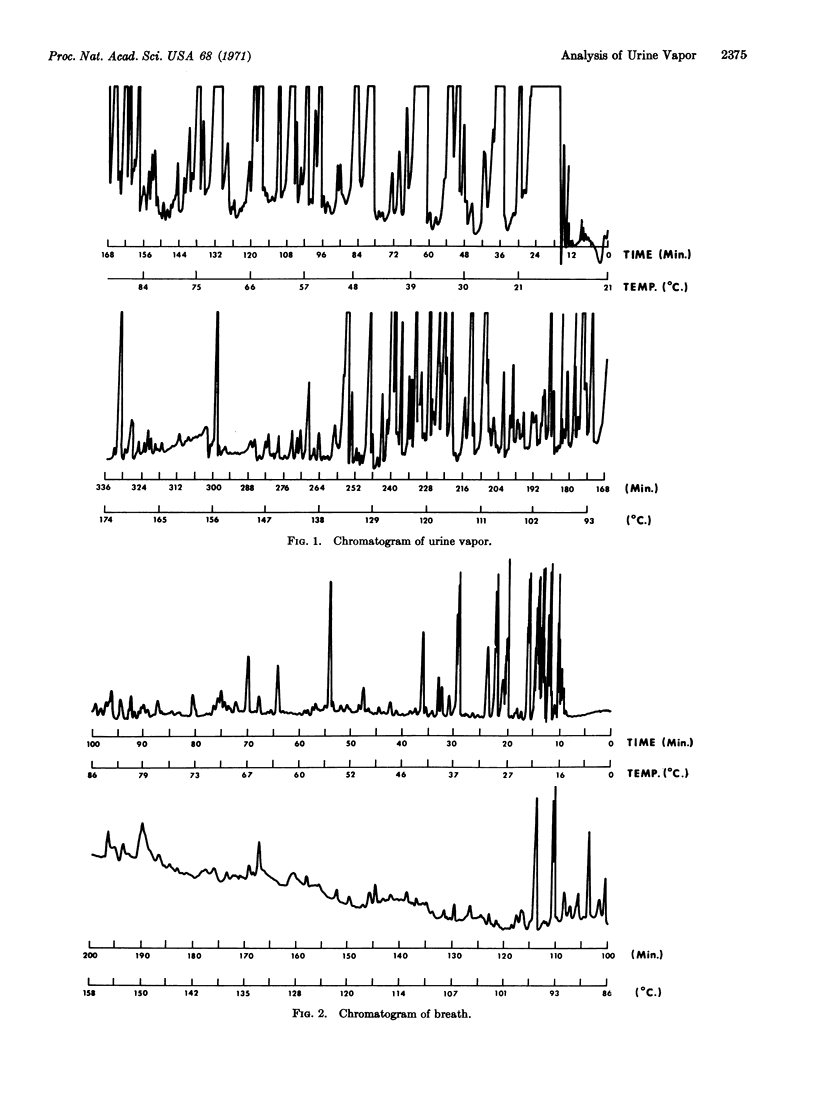
When a human being is placed for several days on a completely defined diet, consisting almost entirely of small molecules that are absorbed from the stomach into the blood, intestinal flora disappear because of lack of nutrition. By this technique, the composition of body fluids can be made constant (standard deviation about 10%) after a few days, permitting significant quantitative analyses to be performed. A method of temperature-programmed gas-liquid partition chromatography has been developed for this purpose. It permits the quantitative determination of about 250 substances in a sample of breath, and of about 280 substances in a sample of urine vapor. The technique should be useful in the application of the principles of orthomolecular medicine.
Keywords: orthomolecular medicine, vitamins, controlled diet
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Pauling L. Evolution and the need for ascorbic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1643–1648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauling L. Orthomolecular psychiatry. Varying the concentrations of substances normally present in the human body may control mental disease. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):265–271. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J., Deason G. Individuality in vitamin C needs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1638–1641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


