Abstract
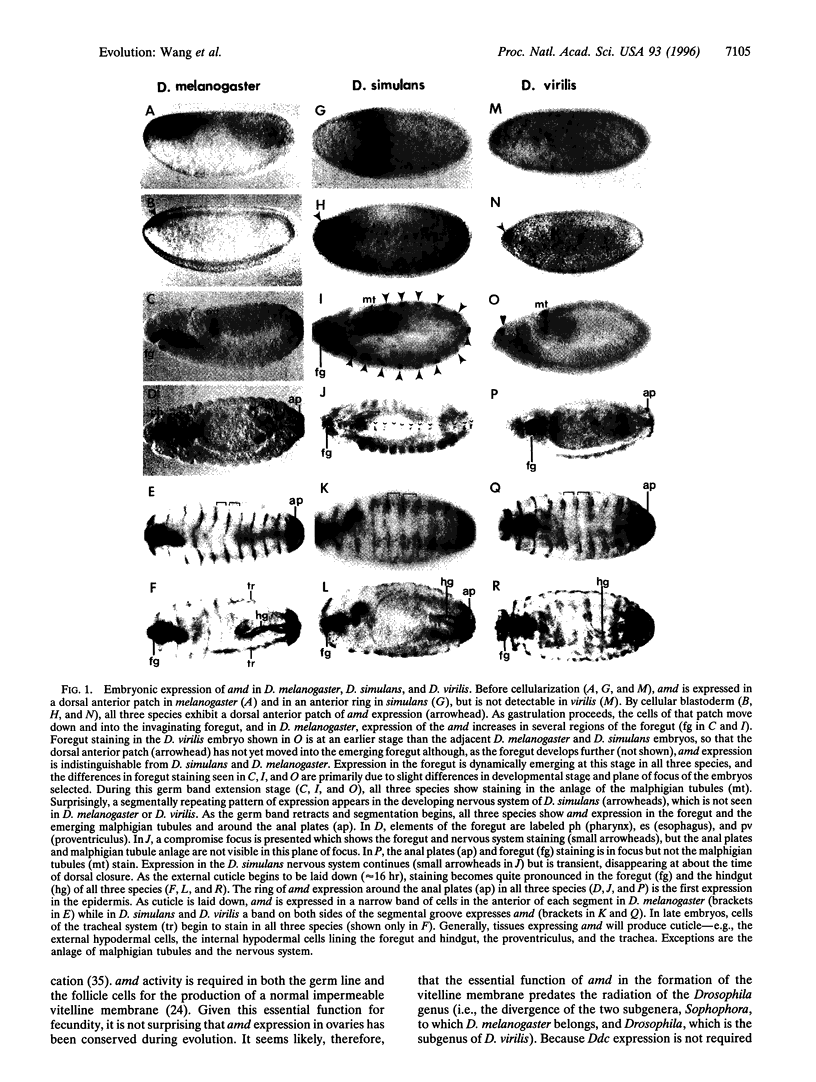
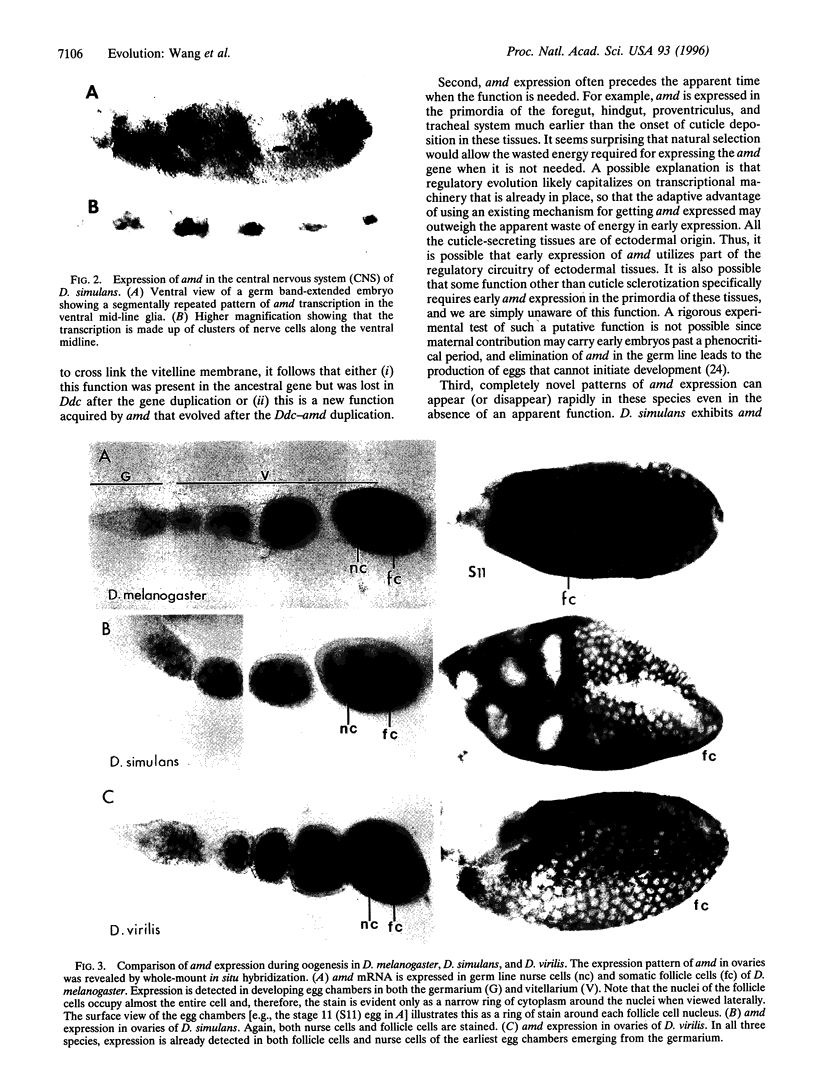
The hypothesis that morphological evolution may largely result from changes in gene regulation rather than gene structure has been difficult to test. Morphological differences among insects are often apparent in the cuticle structures produced. The dopa decarboxylase (Ddc) and alpha-methyldopa hypersensitive (amd) genes arose from an ancient gene duplication. In Drosophila, they have evolved nonoverlapping functions, including the production of distinct types of cuticle, and for Ddc, the production of the neurotransmitters, dopamine and serotonin. The amd gene is particularly active in the production of specialized flexible cuticles in the developing embryo. We have compared the pattern of amd expression in three Drosophila species. Several regions of expression conserved in all three species but, surprisingly, a unique domain of expression is found in Drosophila simulans that does occur in the closely related (2-5 million years) Drosophila melanogaster or in the more remote (40-50 million years) Drosophila virilis. The "sudden" appearance of a completely new and robust domain of expression provides a glimpse of evolutionary variation resulting from changes in regulation of structural gene expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayala F. J. Genetic variation in natural populations: problem of electrophoretically cryptic alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):550–554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall C. J., Hirsh J. Regulation of the Drosophila dopa decarboxylase gene in neuronal and glial cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):510–520. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black B. C., Pentz E. S., Wright T. R. The alpha methyl dopa hypersensitive gene, 1(2)amd, and two adjacent genes in Drosophila melanogaster: physical location and direct effects of amd on catecholamine metabolism. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):306–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00329658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca V., Marineau C., Brisson N. Molecular cloning and analysis of cDNA encoding a plant tryptophan decarboxylase: comparison with animal dopa decarboxylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2582–2586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson W. J. On the architecture of regulatory systems: evolutionary insights and implications. Bioessays. 1988 Jun;8(6):204–208. doi: 10.1002/bies.950080608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eveleth D. D., Gietz R. D., Spencer C. A., Nargang F. E., Hodgetts R. B., Marsh J. L. Sequence and structure of the dopa decarboxylase gene of Drosophila: evidence for novel RNA splicing variants. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2663–2672. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eveleth D. D., Marsh J. L. Evidence for evolutionary duplication of genes in the dopa decarboxylase region of Drosophila. Genetics. 1986 Oct;114(2):469–483. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Hodgetts R. B. An analysis of dopa decarboxylase expression during embryogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1985 Jan;107(1):142–155. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J. D., Ayala F. J. Genetic variation for superoxide dismutase level in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Genet. 1986 Apr;24(3-4):153–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00502785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh J. Molecular genetics of dopa decarboxylase and biogenic amines in Drosophila. Dev Genet. 1989;10(3):232–238. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020100312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. C., Wilson A. C. Evolution at two levels in humans and chimpanzees. Science. 1975 Apr 11;188(4184):107–116. doi: 10.1126/science.1090005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad K. D., Marsh J. L. Developmental expression and spatial distribution of dopa decarboxylase in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1987 Jul;122(1):172–185. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad K. D., Wang D., Marsh J. L. Vitelline membrane biogenesis in Drosophila requires the activity of the alpha-methyl dopa hypersensitive gene (I(2)amd) in both the germline and follicle cells. Insect Mol Biol. 1993;1(4):179–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.1993.tb00090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatowski J., Skarecky D., Bailey K., Ayala F. J. Phylogeny of Drosophila and related genera inferred from the nucleotide sequence of the Cu,Zn Sod gene. J Mol Evol. 1994 May;38(5):443–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00178844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie-Ahlberg C. C. Genetic variation affecting the expression of enzyme-coding genes in Drosophila: an evolutionary perspective. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1985;12:33–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie-Ahlberg C. C., Wilton A. N., Curtsinger J. W., Emigh T. H. Naturally occurring enzyme activity variation in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Sources of variation for 23 enzymes. Genetics. 1982 Oct;102(2):191–206. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margaritis L. H., Kafatos F. C., Petri W. H. The eggshell of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Fine structure of the layers and regions of the wild-type eggshell. J Cell Sci. 1980 Jun;43:1–35. doi: 10.1242/jcs.43.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M. P., Leeds C. A. Molecular localization, developmental expression and nucleotide sequence of the alpha-methyldopa hypersensitive gene of Drosophila. Genetics. 1986 Oct;114(2):453–467. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Wright T. R. Developmental relationship between dopa decarboxylase, dopamine acetyltransferase, and ecdysone in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90412-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Wright T. R. Evidence for regulatory variants of the dopa decarboxylase and alpha-methyldopa hypersensitive loci in Drosophila. Genetics. 1986 Feb;112(2):249–265. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. F., Ayala F. J. Genetic and biochemical basis of enzyme activity variation in natural populations. I. Alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1978 Jun;89(2):371–388. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. F., Chambers G. K., David J., Ayala F. J. Adaptive response due to changes in gene regulation: a study with Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4562–4566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. A., Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Regulated splicing produces different forms of dopa decarboxylase in the central nervous system and hypoderm of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3335–3342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. H., Wyman A. R., Kafatos F. C. Specific protein synthesis in cellular differentiation. III. The eggshell proteins of Drosophila melanogaster and their program of synthesis. Dev Biol. 1976 Mar;49(1):185–199. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90266-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan R. G., Dickinson W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the genomic region encoding alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila affinidisjuncta. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):43–54. doi: 10.1007/BF02143496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen J., Hirsh J. cis-regulatory sequences responsible for alternative splicing of the Drosophila dopa decarboxylase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7385–7393. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow J. C., Wright T. R. The selection for mutants in Drosophila melanogaster hypersensitive to alpha-methyl dopa, a dopa decarboxylase inhibitor. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 May 21;130(2):127–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00269084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine J. W., Campbell C. A. Genetic regulation and the fossil record. Am Sci. 1975 Nov-Dec;63(6):673–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Marsh J. L. Developmental regulation of the alpha-methyldopa hypersensitive gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1995 Apr;168(2):598–612. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. R. The genetic and molecular organization of the dense cluster of functionally related, vital genes in the DOPA decarboxylase region of the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1987;14:95–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-47783-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. R. The genetics of biogenic amine metabolism, sclerotization, and melanization in Drosophila melanogaster. Adv Genet. 1987;24:127–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]