Abstract
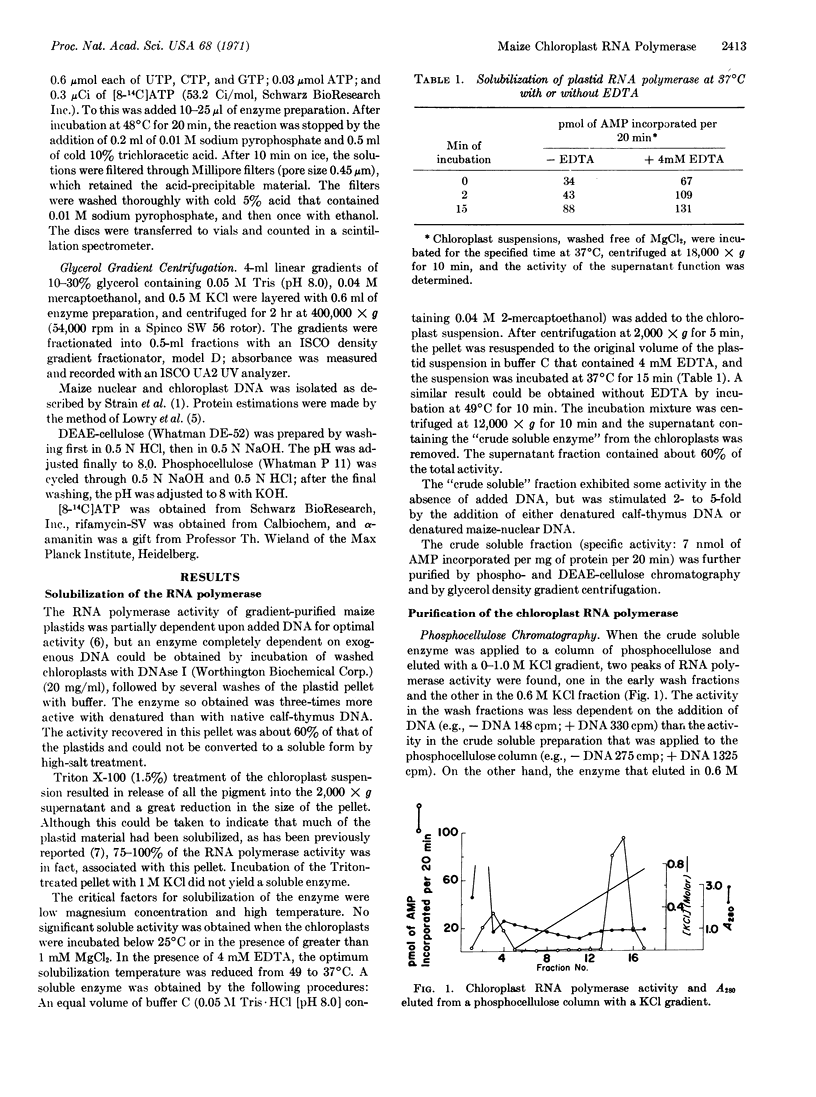
A DNA-dependent RNA polymerase has been solubilized and partially purified from washed chloroplasts prepared from maize seedlings. The purified enzyme was completely dependent on added DNA after purification by phospho- or DEAE-cellulose chromatography. On glycerol density gradients, the enzyme ran ahead of a marker with a sedimentation constant of 18 S, indicating a molecular weight of 500,000 or more. The instability of the highly purified enzyme made intensive study difficult, but the properties of the enzyme purified by phosphocellulose chromatography are reported. Template specificity varied during purification but the activity was always higher with denatured than with native DNA and the preference for maize DNA over calf-thymus DNA increased during purification. The enzyme required magnesium for optimal activity, was inhibited by salt concentrations in excess of 0.1 M, and had a temperature optimum of 48°C. The chloroplast enzyme differed from similar activities so far reported from maize or other sources, particularly in the high salt concentrations needed to elute it from phosphocellulose. The soluble, DNA-dependent enzyme was not inhibited by either α-amanitin or by rifamycin-SV under the assay conditions used.
Keywords: template specificity, DNA dependent, calf-thymus DNA, solubilization
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottomley W. Some effects of triton x-100 on pea etioplasts. Plant Physiol. 1970 Sep;46(3):437–441. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.3.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Spencer D., Wheeler A. M., Whitfeld P. R. The effect of a range of RNA polymerase inhibitors on RNA synthesis in higher plant chloroplasts and nuclei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Mar;143(1):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J. T. DNA-dependent RNA synthesis in chloroplast preparations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:393–397. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(64)80016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J. T. Studies on RNA synthesis in chloroplast preparations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Jun 15;16(3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D., Whitfeld P. R. Ribonucleic acid synthesizing activity of spinach chloroplasts and nuclei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Aug;121(2):336–345. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surzycki S. J. Genetic functions of the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardi: effect of rifampin on chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1327–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari K. K., Wildman S. G. Function of chloroplast DNA. II. Studies on DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity of tobacco chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 20;186(2):358–372. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. Breaks in DNA stimulate transcription by core RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):854–855. doi: 10.1038/223854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


